Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the relationships between tear osmolarity and various parameters for ocular and systemic disease in pri-mary Sjögren's syndrome.
Methods
The medical records of 53 patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome were reviewed. Tear osmolarity using a TearLab®(TearLab™ Corp., San Diego, CA, USA) osmometer as well as other dry eye parameters such as tear break-up time, ocular staining score (Sjögren's International Collaboration Clinical Alliance [SICCA] ocular staining score, SICCA score), Schirmer-I score, symptoms with Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), and Visual Analog Scale (VAS) were obtained. Systemic laboratory data and medication history were also collected. The correlations between the parameters were analyzed using the Spearman's rank correlation test.
Results
53 patients with a mean age of 54.1 ± 13.2 years and female predominance (96.23%) were enrolled. The majority of patients (28.3%) were receiving systemic therapy for severe Sjögren's syndrome. The tear osmolarity in Sjögren's syndrome patients was 307 ± 13.6 (mOsm/L). Higher tear osmolarity was associated with lower tear film break-up time (BUT) scores and with higher SICCA scores. Tear osmolarity and the Schirmer test results were not significantly related. Higher tear osmolarity was paradoxically associated with lower VAS scores and lower OSDI scores. Neither current medication nor the salivary gland focus score showed significant associations with tear osmolarity. Although tear osmolarity was not associated with the SSA-Ro or SSA-LA titer, serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) level and serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) level showed positive corre-lations with tear osmolarity.
Conclusions
Tear osmolarity is positively correlated with the severity of dry eye and was associated with lower symptom severity. The significant associations of tear osmolarity with IgG and ESR suggest that high tear osmolarity may be correlated with autoantibody load and the systemic inflammatory state.
Go to : 
References
1. Moss SE, Klein R, Klein BE. Prevalence of and risk factors for dry eye syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000; 118:1264–8.

2. Schargus M, Wolf F, Tony HP. . Correlation between tear film osmolarity, dry eye disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. Cornea. 2014; 33:1257–61.

3. Akpek EK, Klimava A, Thorne JE. . Evaluation of patients with dry eye for presence of underlying Sjögren syndrome. Cornea. 2009; 28:493–7.

4. Sullivan BD, Whitmer D, Nichols KK. . An objective approach to dry eye disease severity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:6125–30.

5. Schargus M, Ivanova S, Kakkassery V. . Correlation of tear film osmolarity and 2 different MMP-9 tests with common dry eye tests in a cohort of non-dry eye patients. Cornea. 2015; 34:739–44.

6. Segerberg-Konttinen M, Konttinen YT, Bergroth V. Focus score in the diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1986; 61:47–51.
7. Schiffman RM, Christianson MD, Jacobsen G. . Reliability and validity of the Ocular Surface Disease Index. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000; 118:615–21.

8. Pflugfelder SC, Tseng SC, Sanabria O. . Evaluation of sub-jective assessments and objective diagnostic tests for diagnosing tear-film disorders known to cause ocular irritation. Cornea. 1998; 17:38–56.

9. Whitcher JP, Shiboski CH, Shiboski SC. . A simplified quanti-tative method for assessing keratoconjunctivitis sicca from the Sjögren's Syndrome International Registry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:405–15.

11. Baldini C, Talarico R, Tzioufas AG, Bombardieri S. Classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome: a critical review. J Autoimmun. 2012; 39:9–14.

12. Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R. . Classification criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria pro-posed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:554–8.
13. Franceschini F, Cavazzana I, Andreoli L, Tincani A. The 2016 clas-sification criteria for primary Sjogren's syndrome: what's new? BMC Med. 2017; 15:69.

14. Shiboski CH, Shiboski SC, Seror R. . 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classi-fication criteria for primary Sjögren's syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76:9–16.
15. Luo L, Li DQ, Doshi A. . Experimental dry eye stimulates pro-duction of inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 and activates MAPK signaling pathways on the ocular surface. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:4293–301.

16. Tomlinson A, Khanal S, Ramaesh K. . Tear film osmolarity: determination of a referent for dry eye diagnosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:4309–15.

17. Khanal S, Tomlinson A, McFadyen A. . Dry eye diagnosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:1407–14.

18. Lemp MA, Bron AJ, Baudouin C. . Tear osmolarity in the diag-nosis and management of dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:792–8.e1.

19. Versura P, Profazio V, Campos EC. Performance of tear osmolarity compared to previous diagnostic tests for dry eye diseases. Curr Eye Res. 2010; 35:553–64.

20. Utine CA, Bıçakçı gil M, Yavuz S, Çiftçi F. Tear osmolarity meas-urements in dry eye related to primary Sjögren's syndrome. Curr Eye Res. 2011; 36:683–90.

21. Vehof J, Sillevis Smitt-Kamminga N, Nibourg SA, Hammond CJ. Predictors of discordance between symptoms and signs in dry eye disease. Ophthalmology. 2017; 124:280–6.

23. Han SB, Hyon JY, Wee WR. . Reduced corneal sensitivity in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2010; 88:e277–8.

24. Routsias JG, Tzioufas AG. Sjögren's syndrome–study of auto-antigens and autoantibodies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007; 32:238–51.

25. Tzioufas AG, Wassmuth R, Dafni UG. . Clinical, immuno-logical, and immunogenetic aspects of autoantibody production against Ro/SSA, La/SSB and their linear epitopes in primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS): a European multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:398–404.
26. Tzioufas AG, Tatouli IP, Moutsopoulos HM. Autoantibodies in Sjögren's syndrome: clinical presentation and regulatory mechanisms. Presse Med. 2012; 41((9 Pt 2)):e451–60.

27. Ramos-Casals M, Solans R, Rosas J. . Primary Sjögren syndrome in Spain: clinical and immunologic expression in 1010 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008; 87:210–9.
28. Fauchais AL, Martel C, Gondran G. . Immunological profile in primary Sjögren syndrome: clinical significance, prognosis and long-term evolution to other auto-immune disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2010; 9:595–9.
29. Nardi N, Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M. . Circulating au-to-antibodies against nuclear and non-nuclear antigens in primary Sjögren's syndrome: prevalence and clinical significance in 335 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 25:341–6.
30. Martel C, Gondran G, Launay D. . Active immunological pro-file is associated with systemic Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:840–7.

31. Pertovaara M, Pukkala E, Laippala P. . A longitudinal cohort study of Finnish patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome: clin-ical, immunological, and epidemiological aspects. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60:467–72.
32. Tsuboi H, Iizuka M, Asashima H, Sumida T. Anti-M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies and Sjögren's syndrome. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2013; 36:77–85.

33. Tsuboi H, Matsumoto I, Wakamatsu E. . New epitopes and function of anti-M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010; 162:53–61.

34. García-Carrasco M, Mendoza-Pinto C, Jiménez-Hernández C. . Serologic features of primary Sjögren's syndrome: clinical and prognostic correlation. Int J Clin Rheumtol. 2012; 7:651–9.

35. El Annan J, Jiang G, Wang D. . Elevated immunoglobulin to tissue KLK11 in patients with Sjögren syndrome. Cornea. 2013; 32:e90–3.
Go to : 
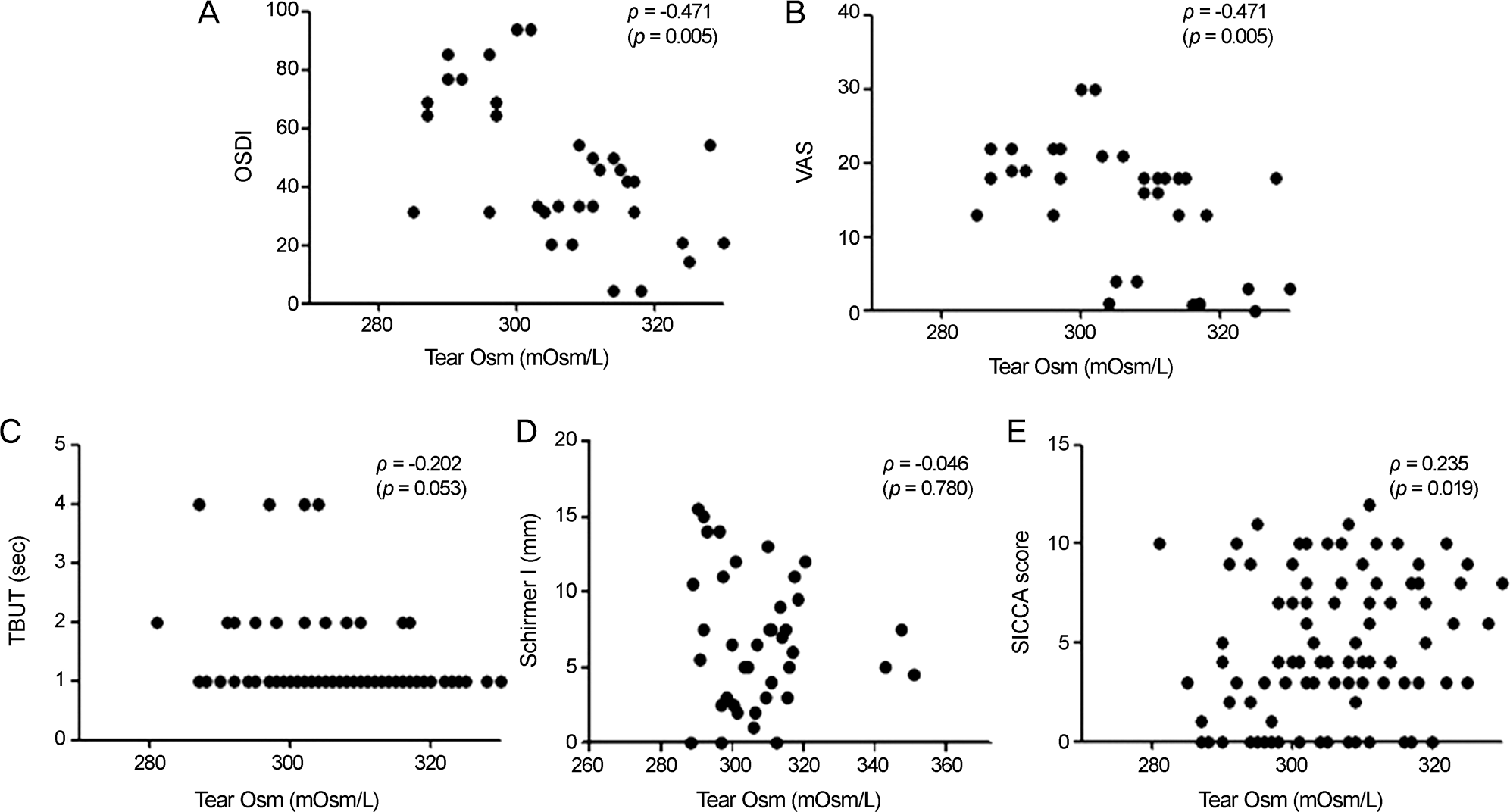 | Figure 1.Scatter plot showing significant correlations between tear film osmolarity and ocular and systemic parameters in primary Sjögren's syndrome. (A) Correlation between ocular surface disease index (OSDI) score and average tear film osmolarity (ρ = -0.471, p = 0.005). (B) Correlation between visual analog scale (VAS) score and average tear film osmolarity (ρ = -0.471, p = 0.005). (C) Correlation between average tear film break-up time (TBUT) and average tear film osmolarity (ρ = -0.202, p = 0.053). (D) Correlation between average Schirmer I test score and average tear film osmolarity (ρ = -0.046, p = 0.780). (E) Correlation between average average ocular staining score (SICCA score) and average tear film osmolarity (ρ = 0.235, p = 0.019). The Spearman rank-order correlation test was used to evaluate the relationship between variables. |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of study participants
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Participant | 53 |
| Female (n, %) | 51 (96.23) |
| Male (n, %) | 2 (3.77) |
| Age (years) | 54.06 ± 13.20 |
| 20-30 (n, %) | 2 (3.77) |
| 30-40 (n, %) | 9 (16.98) |
| 40-50 (n, %) | 7 (13.21) |
| 50-60 (n, %) | 20 (37.74) |
| >60 (n, %) | 15 (28.30) |
| OSDI score | 45.36 ± 24.88 |
| VAS score | 14.45 ± 8.15 |
| Tear film break-up time (s) | 1.29 ± 0.68 |
| Schirmer I test (mm) | 6.74 ± 4.38 |
| SICCA score* | 4.88 ± 3.72 |
| Tear osmolarity (mOsm/L) | 306.96 ± 13.59 |
Table 2.
Correlation with Systemic laboratory test results (Serum)
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Correlation with tear osmolarity | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| C3 | 100.95 ± 11.91 | 0.089 | 0.448 |
| C4 | 21.15 ± 5.53 | -0.510 | 0.667 |
| WBC | 4.71 ± 1.35 | -0.420 | 0.699 |
| B2M | 2.25 ± 0.74 | 0.160 | 0.242 |
| IgG | 1,569.19 ± 393.95 | 0.347 | 0.003* |
| ESR | 18.73 ± 13.34 | 0.277 | 0.010* |
| Anit-Ro/SSA Ab | 57.75 ± 65.53 | 0.199 | 0.170 |
| Anit-La/SSA Ab | 13.19 ± 32.99 | 0.169 | 0.247 |
Table 3.
Correlation with topical and systemic therapy
Table 4.
Correlation with salivary gland test results




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download