Abstract
Purpose
To analyze both the effects and the eyelid contour of Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection and levator aponeurosis advancement in patients with mild to moderate belpharoptosis.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional study including 20 eyes of 16 patients who underwent Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection and 25 eyes of 17 patients who underwent levator aponeurosis advancement from January 2012 to December 2015, where each patient was followed up for at least 6 months. Surgical success was defined as either a marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1) elevation greater than 2.5 mm postoperatively or a bilateral MRD1 difference less than 0.5 mm. Both the conventional and 12 oblique mid-pupil lid distances were measured every 15 degrees using custom software developed in the MATLAB program (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA).
Results
The average correction of Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection was 1.1 mm, while that of levator aponeurosis advancement was 0.9 mm. There was no significant difference in MRD1, MRD2, function of levator palpebrae muscle, or lid contour in the preoperative status between the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group and the levator aponeurosis advancement group. The surgical success rate was 85% in the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group and 84% in the levator aponeurosis advancement group, but this difference was not significant. The postoperative lid contour (superomedial side, 15°) was more effective in the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Overall, both types of blepharoptosis surgery were effective at correcting mild to moderate blepharoptosis. The correction of mild to moderate blepharoptosis using Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection is an effective technique for elevating the eyelid and normalizing the eyelid contour.
Figures and Tables
 | Figure 1Measurement of marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1), marginal reflex distance 2 (MRD2), and brow to pupil distance (BPD). MRD1, MRD2, BPD are measured by Image J program (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA). |
 | Figure 2Eyelid contour analysis. Equally spaced multiple radial mid-pupil lid lines (15°) by MATLAB program (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA). |
 | Figure 3Polar plot of lid contour of preoperative of ptosis patients. (A) Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group. (B) levator aponeurosis advancement group. (C) Comparision with two groups. MMCR Pre-OP = preoperative lid contour of Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group; LAA Pre-OP = preoperative lid contour of levator aponeurosis advancement group. |
 | Figure 4Polar plot of lid contour between preoperative and postoperative ptosis patients. (A) Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group. (B) Levator aponeurosis advancement group. MMCR Pre-OP = preoperative lid contour of Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group; MMCR Post-OP = postoperative lid contour of Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group; LAA Pre-OP = preoperative lid contour of levator aponeurosis advancement group; LAA Post-OP = postoperative lid contour of levator aponeurosis advancement group. |
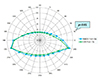 | Figure 5Polar plot of postoperative lid contour between Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group and levator aponeurosis advancement group. The postoperative lid contour (superomedial side, 15°) was more effective in the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group (p < 0.05). MMCR Post-OP = postoperative lid contour of Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection group; LAA Post-OP = postoperative lid contour of levator aponeurosis advancement group. |
References
1. Finesterer J. Ptosis: causes, presentation, and management. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2003; 27:193–204.
2. Escalas P. Ptosis treated by resection of the Muller muscle: analysis of a series of 51 patients. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2006; 29:908–915.
3. Older JJ. Levator aponeurosis surgery for the correction of acquired ptosis. Analysis of 113 procedures. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:1056–1059.
4. Fasanella RM, Servat J. Levator resection for minimal ptosis: another simplified operation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961; 65:493–496.
5. Putterman AM, Urist MJ. Müller muscle-conjunctiva resection. Technique for treatment of blepharoptosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975; 93:619–623.
6. Ben Simon GJ, Lee S, Schwarcz RM, et al. Muller's muscle-conjunctival resection for correction of upper eyelid ptosis: relationship between phenylephrine testing and the amount of tissue resected with final eyelid position. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2007; 9:413–417.
7. Weinstein GS, Buerger GF Jr. Modification of the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection operation for blepharoptosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982; 93:647–651.
8. McCord CD Jr. An external minimal ptosis procedure--external tarsoaponeurectomy. Trans Sect Ophthalmol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1975; 79:683–686.
9. Park DI, Ha SW, Lew H. Clinical outcomes of conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection and factors which affect success. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:1263–1268.
10. Milbratz GH, Garcia DM, Guimarães FC, Cruz AA. Multiple radial midpupil lid distances: a simple method for lid contour analysis. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:625–628.
11. Guyuron B, Davies B. Experience with the modified Putterman procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988; 82:775–780.
12. Dresner SC. Further modifications of the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection procedure for blepharoptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991; 7:114–122.
13. Mercandetti M, Putterman AM, Cohen ME, et al. Internal levator advancement by Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection: technique and review. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001; 3:104–110.
14. Bae JS, Ha MS, Lee JY, et al. Results of conjunctiva-Muller muscle resection in mild eyelid ptosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1365–1370.
15. Zauberman NA, Koval T, Kinori M, et al. Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection for upper eyelid ptosis: correlation between amount of resected tissue and outcome. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:408–411.
16. Kim YS, Yoon JS, Jang SY. Comparison of two- and three-point sutures for advancing the levator aponeurosis in Asian eyelids. Eye (Lond). 2015; 29:1181–1185.
17. Liu D. Ptosis repair by single suture aponeurotic tuck. Surgical technique and long-term results. Ophthalmology. 1993; 100:251–259.
18. Anderson RL, Dixon RS. Aponeurotic ptosis surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979; 97:1123–1128.
19. Berlin AJ, Vestal KP. Levator aponeurosis surgery. A retrospective review. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:1033–1036. discussion 1037.
20. McCulley TJ, Kersten RC, Kulwin DR, Feuer WJ. Outcome and influencing factors of external levator palpebrae superioris aponeurosis advancement for blepharoptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 19:388–393.
21. Shore JW, Bergin DJ, Garrett SN. Results of blepharoptosis surgery with early postoperative adjustment. Ophthalmology. 1990; 97:1502–1511.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download