Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of the combined treatment of anterior stromal puncture with the concurrent use of 5% NaCl eye drops for 6 months for recurrent corneal erosion syndrome.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was conducted for 21 patients (21 eyes) who underwent the combined treatment of anterior stromal puncture with 5% NaCl eye drops qid for 6 months to treat recurrent corneal erosion syndromes. The patients' age, gender, history of corneal trauma, history of ocular surgery, recurrence rate, need for additional treatments after recurrence and complication were analyzed.
Results
The mean age was 42.05 ± 13.83 years (19-68 years) with no significant difference in gender, and the mean follow up period was 8.48 ± 2.76 months (6-15 months). Among the 21 eyes 14 eyes (66.7%) had a previous history of corneal trauma, 2 eyes (9.52%) had previous refractive surgery, 1 eye (4.8%) had corneal dystrophy, 2 eyes (9.5%) had diabetic mellitus and 5 eyes (28.81%) had an unknown origin. Furthermore, 3 eyes (14.3%) developed recurrences and 2 eyes were resolved with conservative treatment while 1 eye needed additional anterior stroma puncture. There was no recurrence after retreatment with anterior stroma puncture. No significant complications such as infection or inflammation developed with the exception of corneal opacity in which one patient developed glare due to corneal opacity.
Figures and Tables
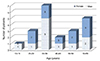 | Figure 1Age and gender distribution at the time of diagnosis of recurrent corneal erosion. There was no differences between genders. |
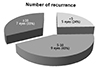
 | Figure 3Previous therapies in 21 eyes of 21 patients with recurrent corneal erosion. All 21 eyes had conservative treatment with eye drops and 3 eyes had anterior stromal puncture at other hospitals. |
References
1. Ramamurthi S, Rahman MQ, Dutton GN, Ramaesh K. Pathogenesis, clinical features and management of recurrent corneal erosions. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:635–644.
2. Suh Y, Kim MS. The longterm evaluation of recurrent corneal erosion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1570–1576.
3. Diez-Feijóo E, Grau AE, Abusleme EI, Durán JA. Clinical presentation and causes of recurrent corneal erosion syndrome: review of 100 patients. Cornea. 2014; 33:571–575.
4. Eke T, Morrison DA, Austin DJ. Recurrent symptoms following traumatic corneal abrasion: prevalence, severity, and the effect of a simple regimen of prophylaxis. Eye (Lond). 1999; 13(Pt 3a):345–347.
5. Dursun D, Kim MC, Solomon A, Pflugfelder SC. Treatment of recalcitrant recurrent corneal erosions with inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase-9, doxycycline and corticosteroids. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:8–13.
6. Wang L, Tsang H, Coroneo M. Treatment of recurrent corneal erosion syndrome using the combination of oral doxycycline and topical corticosteroid. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008; 36:8–12.
7. Ziakas NG, Boboridis KG, Terzidou C, et al. Long-term follow up of autologous serum treatment for recurrent corneal erosions. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010; 38:683–687.
8. Yoon KC, Choi W, You IC, Choi J. Application of umbilical cord serum eyedrops for recurrent corneal erosions. Cornea. 2011; 30:744–748.
9. Moutray TN, Frazer DG, Jackson AJ. Recurrent erosion syndrome--the patient’s perspective. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2011; 34:139–143.
10. Fraunfelder FW, Cabezas M. Treatment of recurrent corneal erosion by extended-wear bandage contact lens. Cornea. 2011; 30:164–166.
11. Ahad MA, Anandan M, Tah V, et al. Randomized controlled study of ocular lubrication versus bandage contact lens in the primary treatment of recurrent corneal erosion syndrome. Cornea. 2013; 32:1311–1314.
12. Singh RP, Raj D, Pherwani A, et al. Alcohol delamination of the corneal epithelium for recalcitrant recurrent corneal erosion syndrome: a prospective study of efficacy and safety. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007; 91:908–911.
13. Ryan G, Lee GA, Maccheron L. Epithelial debridement with diamond burr superficial keratectomy for the treatment of recurrent corneal erosion. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 41:621–622.
14. Avni Zauberman N, Artornsombudh P, Elbaz U, et al. Anterior stromal puncture for the treatment of recurrent corneal erosion syndrome: patient clinical features and outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014; 157:273–279.e1.
15. Tsai TY, Tsai TH, Hu FR, Hou YC. Recurrent corneal erosions treated with anterior stromal puncture by neodymium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:1296–1300.
16. Kim SY, Ko BY. Evaluation of anterior stromal puncture using Nd: YAG laser for refractory recurrent corneal erosion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:331–338.
17. Choi M, Jung JW, Seo KY, et al. Comparison of Nd: YAG laser versus conservative management in the treatment of recurrent corneal erosion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:687–693.
18. Ko BY, Lee GW. Clinical results of phototherapeutic keratectomy for refractory recurrent corneal erosion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:392–400.
19. Rubinfeld RS, Laibson PR, Cohen EJ, et al. Anterior stromal puncture for recurrent erosion: further experience and new instrumentation. Ophthalmic Surg. 1990; 21:318–326.
20. Das S, Seitz B. Recurrent corneal erosion syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008; 53:3–15.
21. Reeves SW, Kang PC, Zlogar DF, et al. Recurrent corneal erosion syndrome: a study of 364 episodes. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2010; 03. 09. 1–2. DOI: 10.3928/15428877-20100215-44. [Epub ahead of print].
22. Lee SH, Kim TI, Chung SH, et al. A case of combined bacterial keratitis with recurrent corneal erosion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:449–454.
23. Bea KH, Ahn M, Cho NC, You IC. Clinical presentation and treatment outcomes of recurrent corneal erosion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:555–561.
24. Liesegang TJ. Physiologic changes of the cornea with contact lens wear. CLAO J. 2002; 28:12–27.
25. Foulks GN. Treatment of recurrent corneal erosion and corneal edema with topical osmotic colloidal solution. Ophthalmology. 1981; 88:801–803.
26. Judge D, Payant J, Frase S, Wood TO. Anterior stromal micropuncture electron microscopic changes in the rabbit cornea. Corena. 1990; 9:152–160.
27. Katsev DA, Kincaid MC, Fouraker BD, et al. Recurrent corneal erosion: pathology of corneal puncture. Cornea. 1991; 10:418–423.
28. Hsu JK, Rubinfeld RS, Barry P, Jester JV. Anterior stromal puncture. Immunohistochemical studies in human corneas. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:1057–1063.
29. Geggel HS. Successful treatment of recurrent corneal erosion with Nd:YAG anterior stromal puncture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990; 110:404–407.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download