Abstract
Purpose
Case summary
Figures and Tables
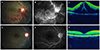 | Figure 1Color fundus photograph, fluorescein angiography (FAG), and optical coherence tomography (OCT) from right eye of a 23-year-old woman with central retinal vein occlusion and transient decrease in Protein S antigen. Color fundus photograph presented dilated retinal veins, flame-shaped hemorrhages in inferior area, multiple cotton-wool spots, and mild disk elevation (A ). FAG demonstrated disc hyperemia, leakage from retinal vein, macular edema and blocked hypofluorescence compatible with the hemorrhages (B). OCT demonstrated a significant macular edema with subretinal fluid (C) and bevacizumab was injected into vitreous at once. Following fundus photography (D) and FAG (E) of the same patient after 15 months later returned to normal. The macular edema had resorbed completely and visual acuity was also restored (F). |
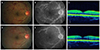 | Figure 2Color fundus photograph, fluorescein angiography (FAG), and optical coherence tomography (OCT) from right eye of a 22-year-old man with central retinal vein occlusion and transient decrease in Protein C antigen. Fundus photograph presented dilated retinal veins, flame-shaped retinal hemorrhages in 4 quadrant, and mild disk elevation (A). FAG demonstrated mild disc hyperemia, leakage from retinal vein, and blocked hypofluorescence compatible with the hemorrhages (B). OCT demonstrated nearly normal macular structure (C). Following fundus photography (D) and FAG (E) of the same patient after 15 months showing that almost retinal hemorrhage was absorbed but vessel tortuosity, small amount of retinal and disc hemorrhage, and leakage from capillary remained. The macula had maintained normal structure in following OCT (F) and the best corrective visual acuity was 1.0. |
Table 1
Initial hematologic test for general condition in 2 CRVO patients

CRVO = central retinal vein occlusion; Hb = hemoglobin; Hct = hematocrit; WBC = white blood cell; PLT = platelet; BUN = blood urea nitrogen; AST = aspartate transaminase; ALT = alanine transaminase; Na = sodium; K = potassium; Cl = chloride; ESR = erythrocyte sedimentation rate; PT = prothrombin time; aPTT = activated partial thromboplastin time; HDL = high-density lipoprotein; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; CRP = C-reactive protein.
*These criteria is for men and slightly different from women's. Normal range of Hb for women is from 12 to 16 g/dL, Hct from 36 to 48%.
Table 2
Coagulation profile in patients

Ag = antigen; Ab = antibody; IgG = immunoglobulin G; IgM = immunoglobulin M; GPI = glucose 6 phosphate isomerase; MPO = myeloperoxidase antibodie; P-ANCA = perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; PR3 = proteinase 3 antibody; C-ANCA = cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; IFA =immunofluorescence assay; RA = rheumatoid factor.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download