Abstract
Purpose
To compare the corneal refraction, astigmatism, and corneal marking for toric intraocular lens measured with a VERION® Image Guided System and an autorefractor in order to precisely determine the toric intraocular lens target.
Methods
The medical records of 29 eyes of 29 patients were retrospectively reviewed to compare the corneal refraction, axis, and amount of astigmatism measured with a VERION® Image Guided System and an autorefractor. We compared the differenc in marked axis for toric intraocular lenses as measured by a VERION Digital Marker and a manual marker.
Results
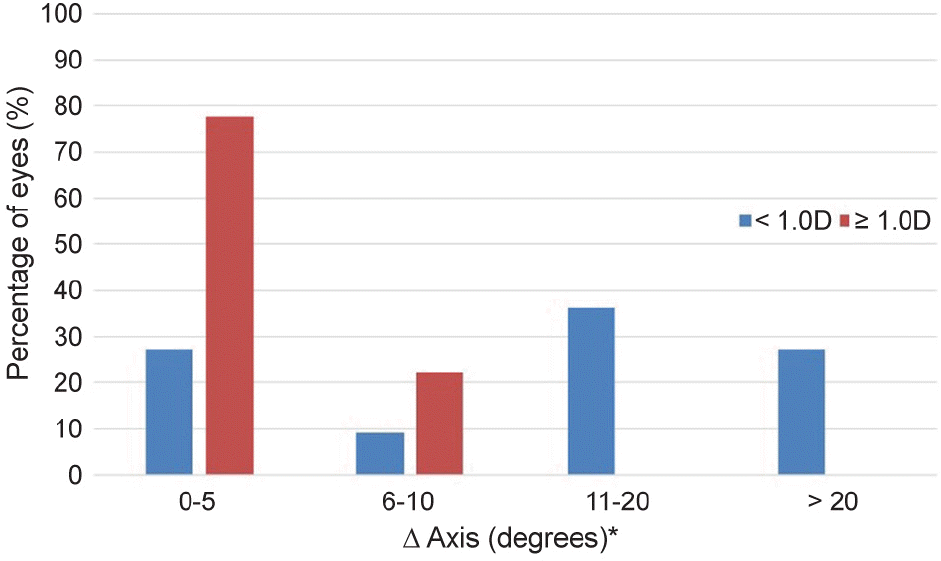
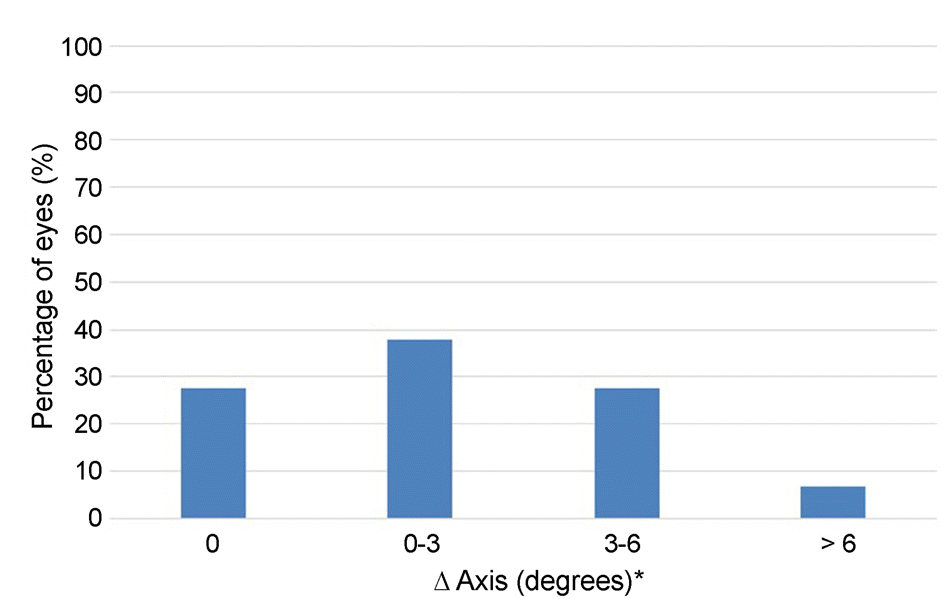
The average corneal refraction and amount of astigmatism were greater with the VERION® Image Guided System than with the autorefractor. The average difference in axis of astigmatism was 9.62°. The difference in axis of astigmatism in patients with more than 1.0 D of astigmatism (18 eyes) was 2.82 ± 2.27°, while that in patients with less than 1.0 D of astigmatism (11 eyes) was 20.27 ± 28.14°. The average difference in marked axis for toric intraocular lens measured by the VERION® Digital Marker and manual marker was 2.50° (0°-9.27°).
Go to : 
References
1. Olsen T. Calculation of intraocular lens power: a review. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1961; 66:111–24.

3. Potvin R, Fonn D, Optom D, et al. In vivo comparison of corneal topography and keratometry systems. Int Contact Lens Clin. 1961; 66:111–24.

4. Shirayama M, Wang L, Koch DD, Weikert MP. Comparison of ac-curacy of intraocular lens calculations using automated kera-tometry, a Placido-based corneal topographer, and a combined Placido-based and dual Scheimpflug corneal topographer. Cornea. 1961; 66:111–24.
5. Nemeth G, Szalai E, Hassan Z, et al. Repeatability data and agree-ment of keratometry with the VERION system compared to the IOLMaster. J Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

6. Holladay JT, Prager TC, Ruiz RS, et al. Improving the predict-ability of intraocular lens power calculations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961; 66:111–24.

7. Mamalis N. Complications of foldable intraocular lenses requiring explanation or secondary intervention--1998 survey. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.
8. Shin YJ, Kim NH, Kim DH. Comparison of pentacam with orbscan. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1961; 66:111–24.
9. Park SJ, Wee WR, Lee JH, Kim MK. Comparison of wavescan aberrometer refraction to subjective manifest refraction and autorefractor. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1961; 66:111–24.

10. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

11. Norrby S. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

12. Jo DH, Oh JY, Kim MK, et al. Corneal power estimation using Orbscan II videokeratography in eyes with previous corneal re-fractive surgeries. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1961; 66:111–24.

13. Maeng HS, Ryu EH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Effects of anterior chamber depth and axial length on refractive error after intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1961; 66:111–24.

14. Olsen T. Prediction of the effective postoperative (intraocular lens) anterior chamber depth. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

15. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. Improved prediction of in-traocular lens power using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

16. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. High precision biometry of pseudophakic eyes using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

17. Elbaz U, Barkana Y, Gerber Y, et al. Comparison of different tech-niques of anterior chamber depth and keratometric measurements. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961; 66:111–24.

18. Shirayama M, Wang L, Weikert MP, Koch DD. Comparison of cor-neal power obtained from 4 different devices. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 148:528–35.
19. Huynh SC, Mai TQ, Kifley A, et al. An evaluation of keratometry in 6-year-old children. Cornea. 1961; 66:111–24.

20. Karabatsas CH, Papaefthymiou I, Aslanides IM, Chatzoulis DZ. Comparison of keratometric and topographic cylinder and axis measurements on normal corneas with low astigmatism. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1961; 66:111–24.

21. Kobashi H, Kamiya K, Igarashi A, et al. Comparison of corneal power, corneal astigmatism, and axis location in normal eyes ob-tained from an autokeratometer and a corneal topographer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

22. Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: correct-ing astigmatism while controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1961; 66:111–24.

Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Difference between manual marker and digital marker. ‘A’ is ‘Manual marker’ and ‘B’ is ‘VERION® digital marker microscope’. DMM = Digital Marker Microscope. |
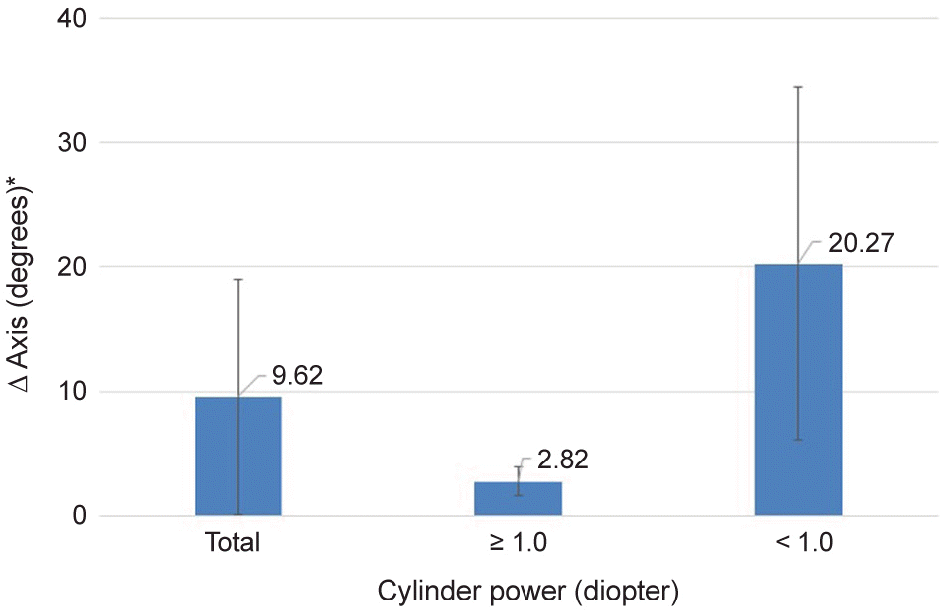 | Figure 2.Difference between steep axis measured by autore-fractor and VERION® measurement module. There is no sig-nificant difference between autorefractor and VERION® measurement module ( p > 0.05, Mann-Whitney test). *△ Axis means axis difference between VERION® and autorefractor. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download