Abstract
Purpose
To compare clinical outcomes between iris fixation and scleral fixation as treatments for dislocated Intra Ocular Lens.
Methods
Ten eyes of 10 patients underwent scleral fixation (scleral fixation group) and 8 eyes of 8 patients underwent iris fixation (iris fixation group) were enrolled in this retrospective study. In each group, visual acuity and intra ocular pressure, slit lamp examination, fundus examination, refraction, keratometry, axial length and anterior chamber depth were measured before the surgery. Regular follow up was made 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, and 2 months after surgery and visual acuity, intra ocular pressure, slit lamp exam, refractory error, anterior chamber depth, intraocular lens (IOL) tilting, and decentration were measured at each visit.
Results
There were no significant differences in uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA), best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and refractive error for patients with iris and scleral fixation before and after surgery. Patients with iris fixation had significantly deeper anterior chamber depth (ACD) and more IOL tilting than patients with scleral fixation.
Go to : 
References
1. Gross JG, Kokame GT, Weinberg DV; Dislocated In-The-Bag Intraocular Lens Study Group. In-the-bag intraocular lens dislocation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:630–5.
2. Smiddy WE, Ibanez GV, Alfonso E, Flynn HW Jr. Surgical abdominal of dislocated intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:64–9.
3. Wagoner MD, Cox TA, Ariyasu RG, et al. Intraocular lens abdominalation in the absence of capsular support: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:840–59.
4. Krė pštė L, Kuzmienė L, Miliauskas A, Janulevič ienė I. Possible predisposing factors for late intraocular lens dislocation after abdominal cataract surgery. Medicina (Kaunas). 2013; 49:229–34.
5. Fernández-Buenaga R, Alio JL, Pérez-Ardoy AL, et al. Late in-the-bag intraocular lens dislocation requiring explantation: risk factors and outcomes. Eye (Lond). 2013; 27:795–801. quiz 802.

6. Davis D, Brubaker J, Espandar L, et al. Late in-the-bag abdominal intraocular lens dislocation: evaluation of 86 consecutive cases. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:664–70.
7. Masket S, Osher RH. Late complications with intraocular lens abdominal after capsulorhexis in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1481–4.
8. Brod RD, Flynn Jr HW, Clarkson JG, Blankenship GW. Management options for retinal detachment in the presence of a posteriorly dislocated intraocular lens. Retina. 1990; 10:50–6.

9. Gimbel HV, Condon GP, Kohnen T, et al. Late in-the-bag abdominal lens dislocation: incidence, prevention, and management. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:2193–204.
10. Lim MC, Doe EA, Vroman DT, et al. Late onset lens particle abdominal as a consequence of spontaneous dislocation of an abdominal lens in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:261–3.
11. Kim KH, Kim WS. Comparison of clinical outcomes of iris fixation and scleral fixation as treatment for intraocular lens dislocation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015; 160:463–9. e1.

12. Scharioth GB, Prasad S, Georgalas I, et al. Intermediate results of sutureless intrascleral posterior chamber intraocular lens fixation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:254–9.

13. Garcia-Rojas L, Paulin-Huerta JM, Chavez-Mondragon E, Ramirez-Miranda A. Intraocular lens iris fixation. Clinical and macular OCT outcomes. BMC Res Notes. 2012; 5:560.

14. Lyle W, Jin JC. Secondary intraocular lens implantation: anterior chamber vs posterior chamber lenses. Ophthalmic Surg. 1993; 24:375–81.

15. Hall JR, Muenzler WS. Intraocular lens replacement in abdominal bullous keratopathy. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1985; 104(Pt 5):541–5.
16. Michaeli A, Soiberman U, Loewenstein A. Outcome of iris abdominal of subluxated intraocular lenses. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:1327–32.
17. Engren AL, Behndig A. Anterior chamber depth, intraocular lens position, and refractive outcomes after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:572–7.

18. Sasaki K, Sakamoto Y, Shibata T, et al. Measurement of abdominal intraocular lens tilting and decentration using Scheimpflug images. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989; 15:454–7.
19. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Intraocular lens tilt and decentration, anterior chamber depth, and refractive error after abdominal suture fixation surgery. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:878–82.
20. Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Partial coherence abdominal: a novel approach to biometry in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:524–34.
Go to : 
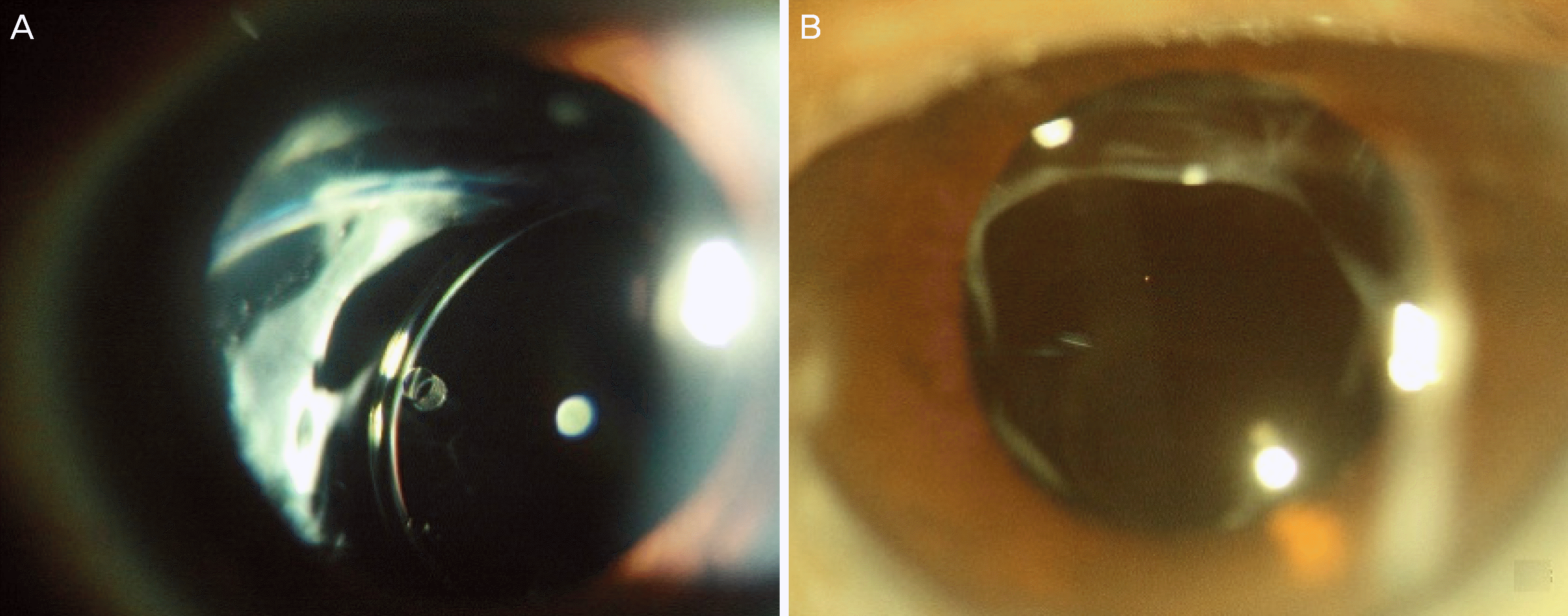 | Figure 1.Representative images of dislocated intraocular lens. (A) Inferonasally tilted lens (B) Inferiorly tilted lens. |
 | Figure 2.Changes of Anterior chamber depth (ACD) over time after Scleral or Iris fixation of intraocular lens (mm). Patients with iris fixation had significantly deeper ACD than patients with scleral fixation. Pre-op. = pre-operative; POD = post operative day; w = week; m = month(s). * Values which are statistically significant. |
 | Figure 3.Changes of intraocular lens (IOL) tilting (°) over time after Scleral or Iris fixation of IOL. Patients with iris fixation had more IOL tilting than patients with scleral fixation. POD = post operative day; w = week; m = month(s). * Values which are statistically significant. |
Table 1.
Preoperative clinical characteristics of Scleral fixation group & Iris fixation group
Table 2.
Changes of UCVA, BCVA, ACD and IOP over time in Scleral fixation group & Iris fixation group
|
Method of surgery |
p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Scleral fixation (n = 10) | Iris fixation (n = 8) | ||
| UCVA (logmar) | |||
| Pre-op. | 1.01 ± 0.09 | 0.98 ± 0.31 | 0.374 |
| POD#1w | 0.48 ± 0.05 | 0.81 ± 0.32 | 0.374 |
| POD#1m | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.69 ± 0.21 | 0.215 |
| POD#2m | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 0.63 ± 0.24 | 0.187 |
| BCVA (logmar) | |||
| Pre-op. | 0.44 ± 0.06 | 0.30 ± 0.11 | 0.110 |
| POD#1w | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.20 | 0.546 |
| POD#1m | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.12 | 0.829 |
| POD#2m | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.27 ± 0.09 | 0.416 |
| ACD (mm) | |||
| Pre-op. | 3.15 ± 0.25 | 3.72 ± 0.31 | 0.215 |
| POD#1w | 3.36 ± 0.11 | 3.95 ± 0.25 | 0.071 |
| POD#1m | 3.30 ± 0.12 | 4.30 ± 0.18 | 0.001* |
| POD#2m | 3.27 ± 0.13 | 4.22 ± 0.20 | 0.002* |
| ACD diff. (mm) | 0.24 ± 0.15 | 0.48 ± 0.23 | 0.032* |
| IOP (mmHg) | |||
| Pre-op. | 16.71 ± 1.00 | 19.38 ± 3.13 | 0.887 |
| POD#1w | 16.12 ± 0.81 | 21.63 ± 2.95 | 0.140 |
| POD#1m | 18.06 ± 0.88 | 19.38 ± 1.92 | 0.511 |
| POD#2m | 17.71 ± 1.06 | 18.14 ± 2.60 | 0.664 |
Table 3.
Changes of IOL tilting, IOL decentration, Spherical equivalent error over time in Scleral fixation group & Iris fixation group
|
Method of surgery |
p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Scleral fixation (n = 10) | Iris fixation (n = 8) | ||
| IOL tilting (°) | |||
| POD#1w | 4.61 ± 0.12 | 7.48 ± 0.97 | <0.001* |
| POD#1m | 4.65 ± 0.14 | 5.08 ± 0.27 | 0.101 |
| POD#2m | 4.60 ± 0.12 | 5.16 ± 0.19 | 0.024* |
| IOL decentration (mm) | |||
| POD#1w | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.144 |
| POD#1m | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 1.000 |
| POD#2m | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.574 |
| Spherical equivalent error (D) | |||
| POD#1w | –0.55 ± 0.27 | –0.50 ± 0.26 | 0.698 |
| POD#1m | –0.63 ± 0.24 | –0.65 ± 0.41 | 0.820 |
| POD#2m | –0.69 ± 0.19 | –0.76 ± 0.59 | 0.820 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download