Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of fragmentation and anterior migration occurred after dexamethasone intravitreal implant (Ozurdex®, Allergan, Irvine, CA, USA) injection in a branch retinal vein occlusion patient.
Case summary
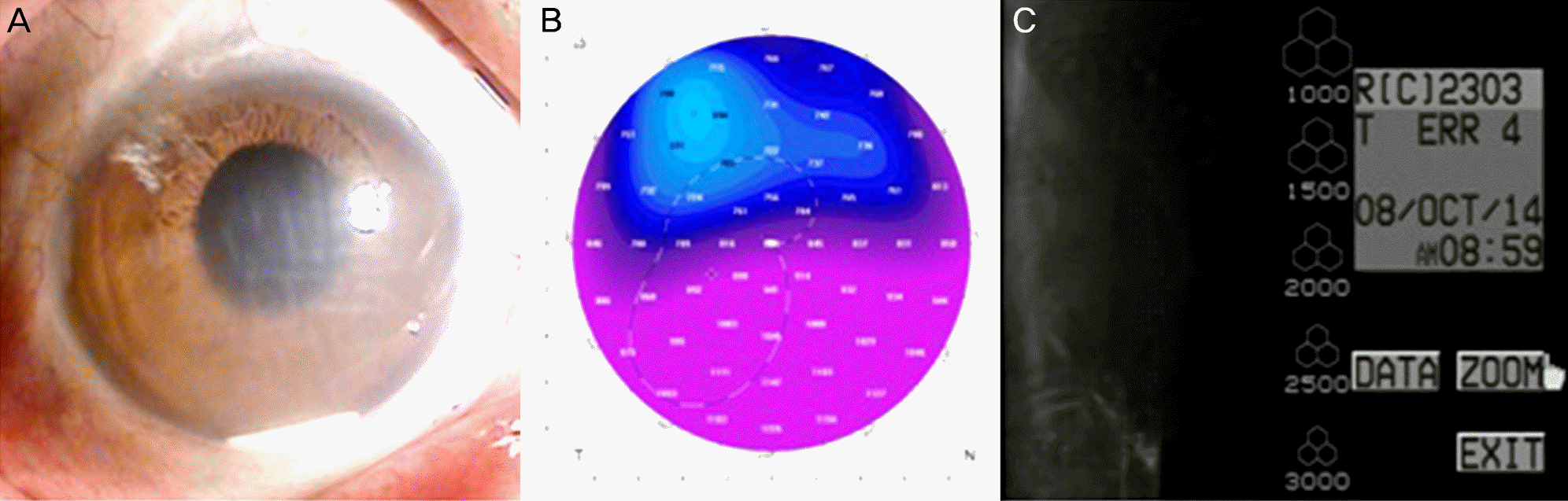
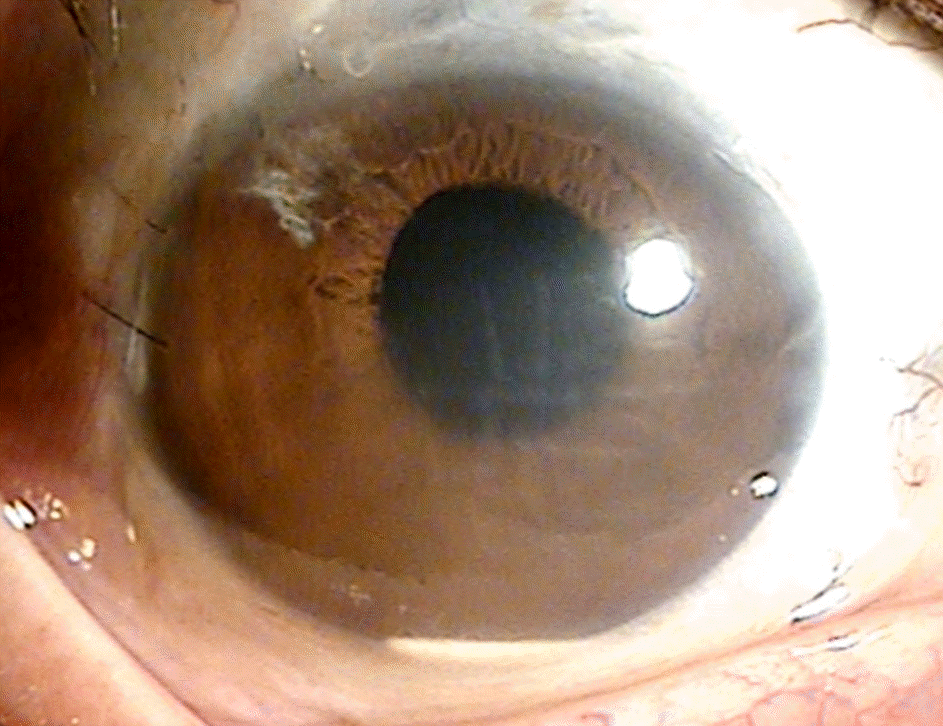
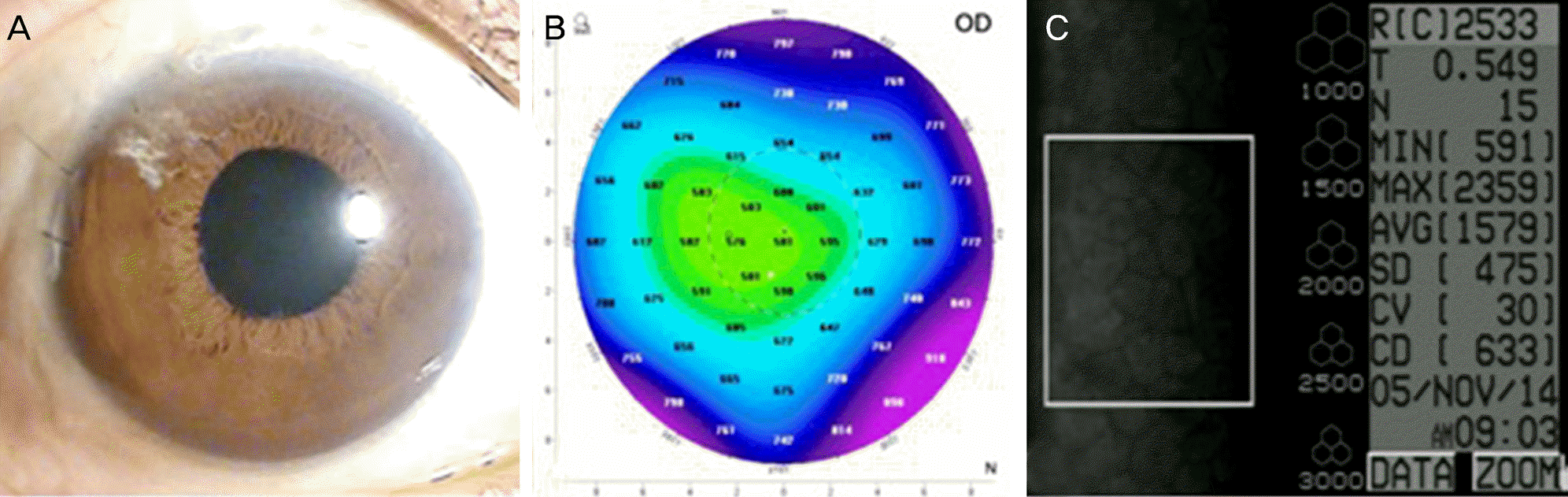
A 66-year-old male was referred for blurred vision. He received cataract surgery in 1986 and was diagnosed with central retinal vein obstruction in 2011 in the right eye. For treatment of macular edema, dexamethasone intravitreal implant was performed in the right eye. One week after implantation, a fragment of the dexamethasone implant migrated to the anterior chamber with corneal edema and surgical removal was performed immediately. One day after removal, the remaining fragmented implant migrated to the anterior chamber and corneal edema still existed. The fragmented implant was removed with anterior chamber irrigation. After removal, corneal edema improved and visual acuity was recovered.
Conclusions
Anterior migrated dexamethasone implant could induce corneal complications, such as corneal edema and corneal decompensation and might lower the corneal endothelial cell even if immediately removed. We report a case of corneal edema, which was induced by anterior migration of a fragmented dexamethasone implant and recovered with immediate surgical removal.
References
1. Hayreh SS, Zimmerman MB, Podhajsky P. Incidence of various types of retinal vein occlusion and their recurrence and demographic characteristics. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994; 117:429–41.

2. Mitchell P, Smith W, Chang A. Prevalence and associations of retinal vein occlusion in Australia. The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996; 114:1243–7.
3. A randomized clinical trial of early panretinal photocoagulation for ischemic central vein occlusion. The Central Vein Occlusion Study Group N Report. Ophthalmology. 1995; 102:1434–44.
4. Brown DM, Campochiaro PA, Singh RP, et al. Ranibizumab for macular edema following central retinal vein occlusion: six-month primary end point results of a phase III study. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:1124–33.e1.
5. Gan IM, Ugahary LC, van Dissel JT, van Meurs JC. Effect of intravitreal dexamethasone on vitreous vancomycin concentrations in patients with suspected postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005; 243:1186–9.

6. Kuppermann BD, Blumenkranz MS, Haller JA, et al. Randomized controlled study of an intravitreous dexamethasone drug delivery system in patients with persistent macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007; 125:309–17.

7. Haller JA, Bandello F, Belfort R Jr, et al. Randomized, sham-controlled trial of dexamethasone intravitreal implant in patients with macular edema due to retinal vein occlusion. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:1134–46.e3.

8. Dang Y, Mu Y, Li L, et al. Comparison of dexamethasone intravitreal implant and intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for the treatment of pseudophakic cystoid macular edema in diabetic patients. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014; 8:1441–9.

9. Cabrera M, Yeh S, Albini TA. Sustained-release corticosteroid options. J Ophthalmol. 2014; 2014. 164692.

10. Cronin KM, Govind K, Kurup SK. Late migration of dexamethasone implant into anterior chamber. Arch Ophthalmol. 2012; 130:711.

11. Pardo-López D, Francés-Muñoz E, Gallego-Pinazo R, Díaz-Llopis M. Anterior chamber migration of dexametasone intravitreal implant (Ozurdex[R]). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:1703–4.
12. Khurana RN, Appa SN, McCannel CA, et al. Dexamethasone implant anterior chamber migration: risk factors, complications, and management strategies. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:67–71.
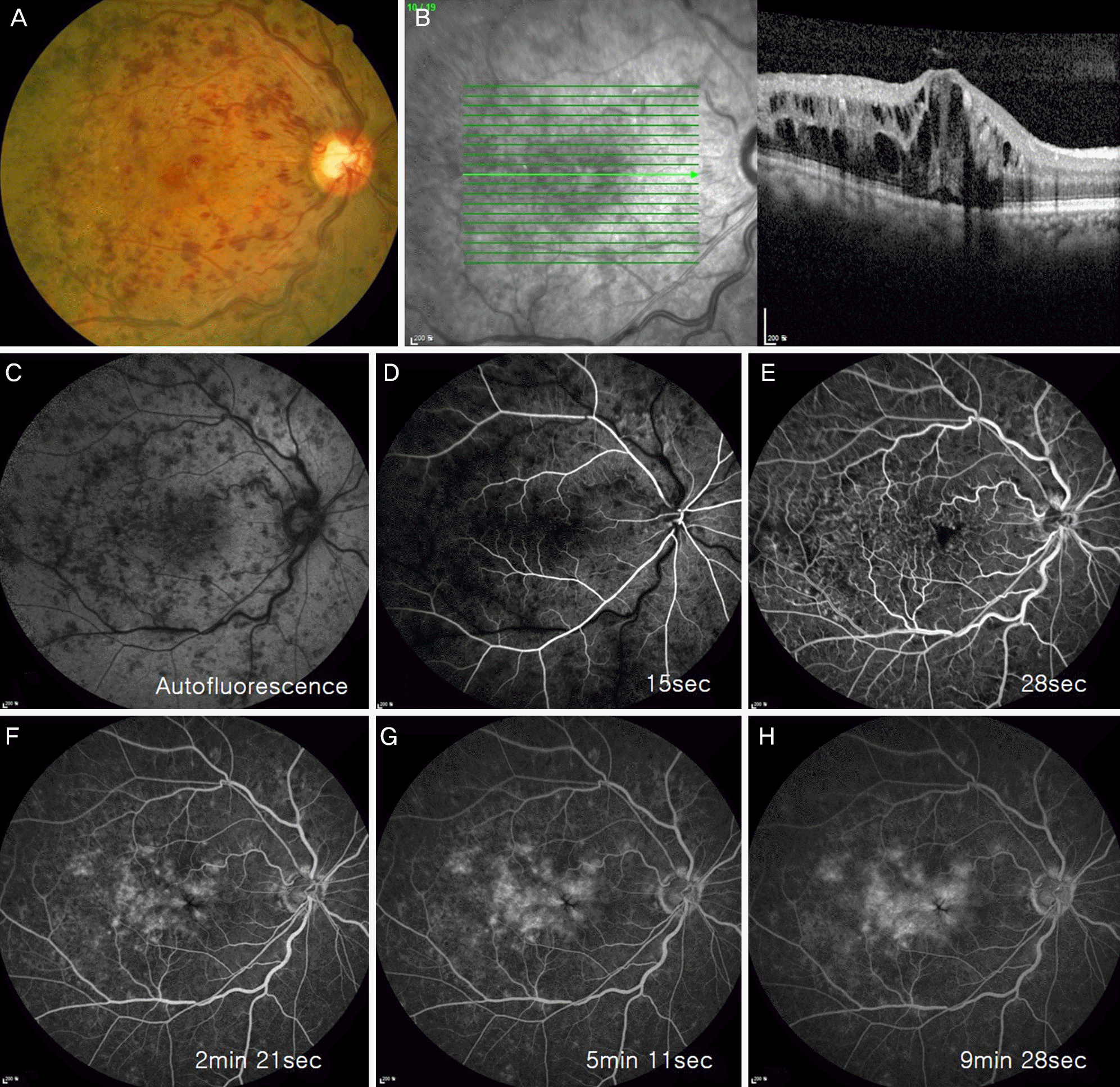
Figure 1.
Fundus photography, optical coherence tomography and fluorescent angiography images in an eye with central retinal vein occlusion. (A) A fundus photography showing tortuosity and dilatation of all branches of the central retinal vein, flame-shaped hemorrhages, optic disc and macular edema before implantation. (B) Optical coherence tomography showing macular edema before implantation. (C-H) Fluorescent angiography images showing retinal hemorrhage and leaking before implantation.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download