Abstract
Purpose
To analyze macular layer thickness using spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) in normal subjects.
Methods
One hundred normal eyes were enrolled in this study. Macular thickness was measured via enhanced depth imaging using Heidelberg Spectralis® OCT, using calipers within the program.
Results
Central subfield thickness was 11.35 ± 2.11 μm in the retinal nerve fiber layer, 13.33 ± 4.16 μm in the ganglion cell layer, 19.38 ± 3.20 μm in the inner plexiform layer, 18.23 ± 4.66 μm in the inner nuclear layer, 23.27± 6.83 μm in the outer plexiform layer, 91.97 ± 9.59 μm in the outer nuclear layer, 16.68 ± 1.83 μm in the retinal pigment epithelium layer, 179.82 ± 29.99 μm in the inner retinal layer, and 88.32 ± 2.81 μm in the photoreceptors layer. No significant differences were observed in the spherical equivalent according to age. Despite no significant differences being present, the macular central subfield thickness was thinner in women than in men.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Lee YJ. Analysis of factors associated with variability in measures obtained by spectral domain optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:639–46.

2). Ko TH, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS, et al. Comparison of ultrahigh-and standard-resolution optical coherence tomography for imaging macular pathology. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1922. e1-15.
3). Chae MB, Kim JS. Foveal shape according to age and gender using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1504–10.

4). Nussenblatt RB, Kaufman SC, Palestine AG, et al. Macular thickening and visual acuity. Measurement in patients with cystoid macular edema. Ophthalmology. 1987; 94:1134–9.
5). Ko BW, Shin YW, Lee JM, et al. Comparison of macular thickness measurements between fourier-domain and time-domain optical coherence tomography in normal eyes and eyes with macular diseases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1661–8.

6). Song WK, Lee SC, Lee ES, et al. Macular thickness variations with sex, age, and axial length in healthy subjects: a spectral domain-optical coherence tomography study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:3913–8.

7). Zou H, Zhang X, Xu X, Yu S. Quantitative in vivo retinal thickness measurement in chinese healthy subjects with retinal thickness analyzer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:341–7.

8). Kanai K, Abe T, Murayama K, Yoneya S. Retinal thickness and changes with age. Nihon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2002; 106:162–5.

9). Neuville JM, Bronson-Castain K, Bearse MA Jr, et al. OCT reveals regional differences in macular thickness with age. Optom Vis Sci. 2009; 86:E810–6.

10). Guedes V, Schuman JS, Hertzmark E, et al. Optical coherence tomography measurement of macular and nerve fiber layer thickness in normal and glaucomatous human eyes. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:177–89.

11). Kang JH, Kim SA, Song WG, Yoon HS. Macular thickness changes with age in normal subjects measured by optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:592–8.
12). Kim SH, Choi KS, Lee SJ. Macular thickness changes with age and gender in emmetropia using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:299–307.

13). Wong AC, Chan CW, Hui SP. Relationship of gender, body mass index, and axial length with central retinal thickness using optical coherence tomography. Eye (Lond). 2005; 19:292–7.

14). Duan XR, Liang YB, Friedman DS, et al. Normal macular thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography in healthy eyes of adult Chinese persons: the Handan Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:1585–94.

15). Massin P, Erginay A, Haouchine B, et al. Retinal thickness in healthy and diabetic subjects measured using optical coherence tomography mapping software. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2002; 12:102–8.

16). Evans JR, Schwartz SD, McHugh JD, et al. Systemic risk factors for idiopathic macular holes: a case-control study. Eye (Lond). 1998; 12((Pt 2)):256–9.

17). Risk factors for idiopathic macular holes. The Eye Disease Case-Control Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994; 118:754–61.
Go to : 
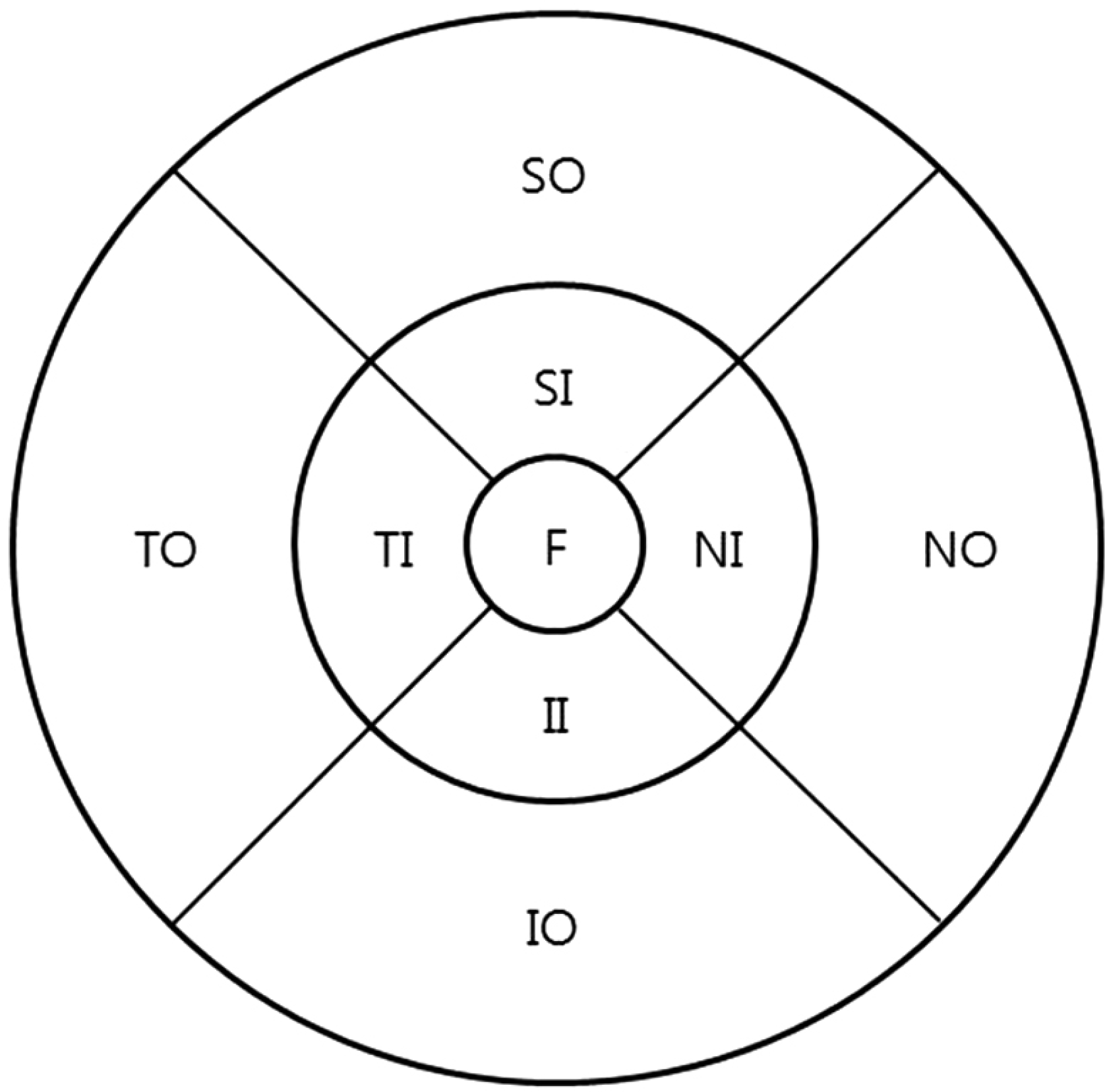 | Figure 1.ETDRS subfields within standard 1-, 3-, and 6-mm di-ameter concentric circles at the right used for reporting retinal thickness (central circle: F, inner ring: SI+NI+II+TI, outer ring: SO+NO+IO+TO). ETDRS = Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study; F = fovea; SI = superior inner; NI = nasal inner; II = inferior inner; TI = temporal inner; SO = superior outer; NO = nasal outer; IO = inferior outer; TO = temporal outer. |
Table 1.
Demographics of patients
| Characteristic | Subjects |
|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 50 |
| Sex (male/female) | 25/25 |
| Eyes (right/left) | 50/50 |
| Age (years) | 44.82 ± 12.32 |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) | −0.87 ± 1.75 |
Table 2.
Macular subfield thicknesses at retinal nerve fiber layer
Table 3.
Macular subfield thicknesses at ganglion cell layer
Table 4.
Macular subfield thicknesses at inner plexiform layer
Table 5.
Macular subfield thicknesses at inner nuclear layer
Table 6.
Macular subfield thicknesses at outer plexiform layer
Table 7.
Macular subfield thicknesses at outer nuclear layer
Table 8.
Macular subfield thicknesses at retinal pigment epithelium layer
Table 9.
Macular subfield thicknesses at inner retinal layer
Table 10.
Macular subfield thicknesses at photoreceptors layer




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download