Abstract
Purpose
To assess the changes in anterior, posterior, and total corneal astigmatism after cataract surgery with on-axis clear corneal incision cataract surgery.
Methods
This study included 48 eyes (24 eyes with ‘with-the-rule [WTR]’ and 24 eyes with ‘against-the-rule [ATR]’) that under-went phacoemulsification and intraocular lens insertion through on-axis clear corneal incision. The ATR group with vertically steep axis of posterior corneal astigmatism was divided into subgroups 1 and 2 for the opposite axis. Autorefraction, uncorrected and best-corrected visual acuities were measured. Corneal astigmatism (anterior, posterior and total) was measured using Pentacam® preoperatively and 1 week, 1 month, and 2 months postoperatively.
Results
Multivariate linear regression analysis of preoperative data showed positive correlations among anterior, posterior and total astigmatism. Anterior corneal astigmatism showed a significant decrease in both WTR and ATR groups in all measured points (all p < 0.05). Posterior corneal astigmatism showed no statistical difference in the WTR group and ATR subgroup 2 ( p > 0.05) and significant decrease in the ATR subgroup 1 ( p < 0.05) at 2 months postoperatively. Total corneal astigmatism showed significant decrease 2 months after surgery in the WTR group and ATR subgroup 1 (all p < 0.05), but not in the ATR subgroup 2 ( p > 0.05). According to correlation analysis based on trend line equations, 1.7 diopters of anterior astigmatism could expect 0.3 diopters of posterior astigmatism and 0.5 diopters of total astigmatism for the WTR group and 0.4 diopters of anterior astigma-tism could expect 0.2 diopters of posterior astigmatism and 0.4 diopters of total astigmatism for the ATR group.
Conclusions
Considering the majority of cataract patients have vertically steep posterior corneal astigmatism, temporal incision for ATR patients is generally effective. Moreover, for patients with WTR astigmatism of more than 1.7 diopters or ATR astigma-tism greater than 0.8 diopters, additional preoperative correction based on posterior astigmatism is needed for more precise pre-diction of postoperative total corneal astigmatism.
References
2. Tejedor J, Murube J. Choosing the location of corneal incision based on preexisting astigmatism in phacoemulsification. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:767–76.

3. Nielsen PJ. Prospective evaluation of surgically induced astigma-tism and astigmatic keratotomy effects of various self-sealing small incisions. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:43–8.

4. Kohnen S, Neuber R, Kohnen T. Effect of temporal and nasal un-sutured limbal tunnel incisions on induced astigmatism after phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:821–5.

5. Tejedor J, Murube J. Choosing the location of corneal incision based on preexisting astigmatism in phacoemulsification. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:767–76.

6. Royston JM, Dunne MC, Barnes DA. Measurement of posterior corneal surface toricity. Optom Vis Sci. 1990; 67:757–63.

7. Dunne MC, Royston JM, Barnes DA. Posterior corneal surface tor-icity and total corneal astigmatism. Optom Vis Sci. 1991; 68:708–10.

8. Ho JD, Tsai CY, Liou SW. Accuracy of corneal astigmatism esti-mation by neglecting the posterior corneal surface measurement. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:788–95. 795.e1-2.

9. Dubbelman M, Sicam VA, Van der Heijde GL. The shape of the an-terior and posterior surface of the aging human cornea. Vision Res. 2006; 46:993–1001.

10. Prisant O, Hoang-Xuan T, Proano C. . Vector summation of an-terior and posterior corneal topographical astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1636–43.

11. Módis L Jr, Langenbucher A, Seitz B. Evaluation of normal cor-neas using the scanning-slit topography/pachymetry system. Cornea. 2004; 23:689–94.

12. Koch DD, Ali SF, Weikert MP. . Contribution of posterior cor-neal astigmatism to total corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2080–7.

13. Koch DD, Jenkins RB, Weikert MP. . Correcting astigmatism with toric intraocular lenses: effect of posterior corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1803–9.

14. Hoffmann PC, Auel S, Hütz WW. Results of higher power toric in-traocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1411–8.

15. Bauer NJ, de Vries NE, Webers CA. . Astigmatism manage-ment in cataract surgery with the AcrySof toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1483–8.

16. Tejedor J, Guirao A. Agreement between refractive and corneal as-tigmatism in pseudophakic eyes. Cornea. 2013; 32:783–90.

17. Nemeth G, Berta A, Lipecz A. . Evaluation of posterior astig-matism measured with scheimpflug imaging. Cornea. 2014; 33:1214–8.

Figure 1.
Location of steep meridian on anterior and posterior corneal astigmatism. * Vertical alignment of the steep corneal meridian was seen in 50.0% for the anterior cornea; † Vertical alignment of the steep corneal meridian was seen in 83.3% for the posterior cornea.
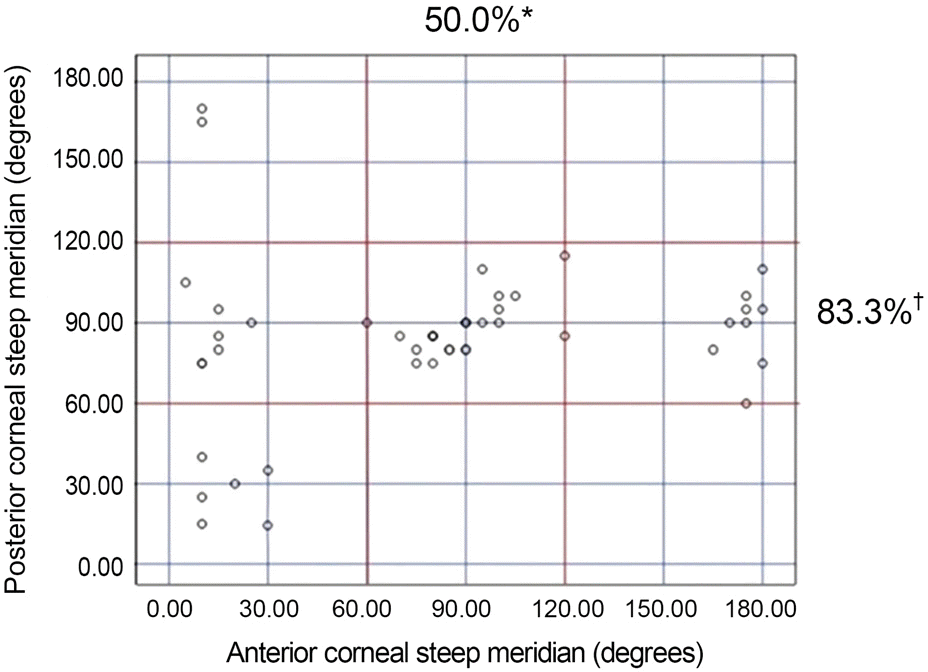
Figure 2.
Double-angle plots of corneal astigmatism and SIA using Pentacam® (Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany) from WTR group. Red dots denote for mean values of the amount and axis of corneal astigmatism for each group in (A) to (C). (A) Preoperative anterior (left), posterior (middle) and total (right) corneal astigmatism. (B) Postoperative 2 months anterior (left), posterior (middle) and total (right) corneal astigmatism. (C) SIA in anterior (left), posterior (middle) and total (right) corneal astigmatism. SIA = surgically in-duced astigmatism; WTR = with-the-rule.

Figure 3.
Double-angle plots of corneal astigmatism and SIA using Pentacam® (Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany) from ATR subgroup 1. Red dots denote for mean values of the amount and axis of corneal astigmatism for each group in (A) to (C). (A) Preoperative ante-rior (left), posterior (middle) and total (right) corneal astigmatism. (B) Postoperative 2 months anterior (left), posterior (middle) and total (right) corneal astigmatism. (C) SIA in anterior (left), posterior (middle) and total (right) corneal astigmatism. SIA = surgi-cally induced astigmatism; ATR = against-the-rule.

Figure 4.
Estimated cut-off value for preoperative consideration of posterior astigmatism in WTR group. (A) Trend line equation was calculated with preop.‘A’ and ‘P’. (B) Trend line equation was calculated with preop. ‘P’ and postop ‘T’ corneal astigmatism. WTR = with-the-rule; A = anterior; P = posterior; T = total; preop = preoperative; postop = postoperative; Post. = posterior astigmatism.
Figure 5.
Correlations of magnitude of the ‘A’, ‘P’ and ‘T’ corneal astigmatism in WTR group. (A) Correlations of magnitude of preop ‘A’ and ‘T’ corneal astigmatism. (B) Correlations of magnitude of preop ‘A’ and postop ‘T’ corneal astigmatism. (C) Correlations of magnitude of preop ‘T’ and ‘P’ corneal astigmatism. Trend line equations for each correlation were calculated. WTR = with-the-rule; A = anterior; P = posterior; T = total; preop = preoperative; postop = postoperative.
Figure 6.
Estimated cut-off value for preoperative consideration of posterior astigmatism in WTR group. (A) Trend line equation was calculated with preop. ‘A’ and ‘P’. (B) Trend line equation was calculated with preop. ‘P’ and postop ‘T’ corneal astigmatism. WTR = with-the-rule; A = anterior; P = posterior; T = total; preop = preoperative; postop = postoperative; Post. = posterior astigmatism; ATR = against-the-rule.
Figure 7.
Correlations of magnitude of the ‘A’, ‘P’ and ‘T’ corneal astigmatism in WTR group. (A) Correlations of magnitude of preop ‘A’ and ‘T’ corneal astigmatism. (B) Correlations of magnitude of preop ‘A’ and postop ‘T’ corneal astigmatism. (C) Correlations of magnitude of preop ‘T’ and ‘P’ corneal astigmatism. Trend line equations for each correlation were calculated. WTR = with-the-rule; A = anterior; P = posterior; T = total; preop = preoperative; postop = postoperative.
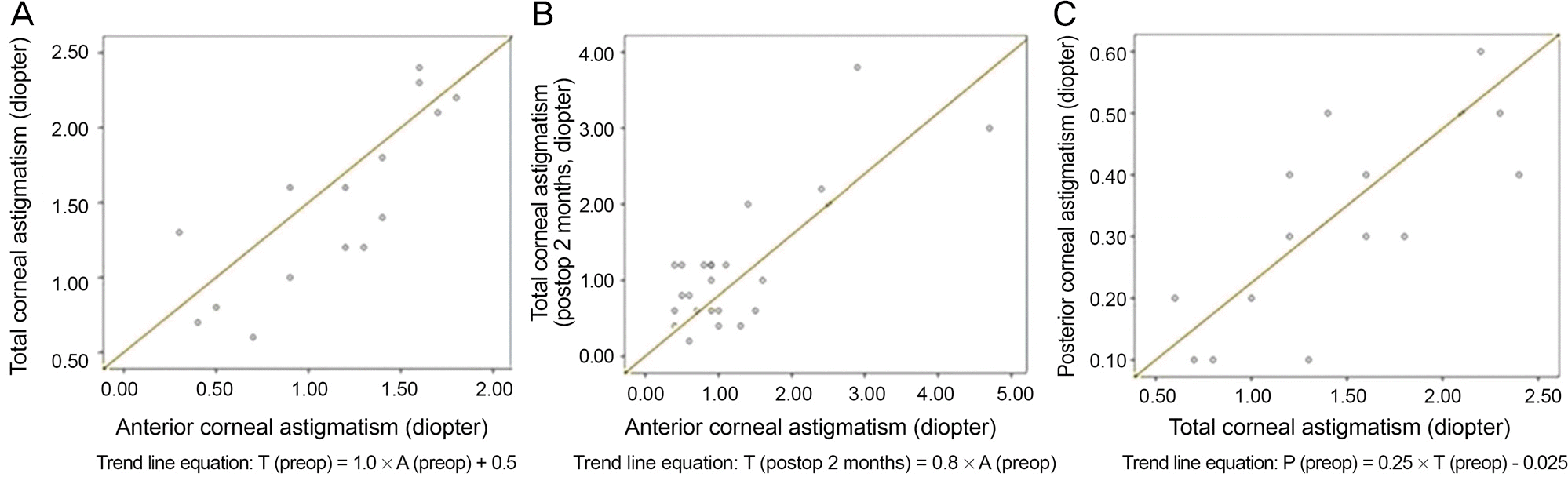
Table 1.
Patient characteristics
| Variables | With-the-rule group | Against-the-rule group | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of eyes | 24 | 24 | |
| Laterality (OD:OS) | 9:15 | 12:12 | |
| Sex (M:F) | 5:19 | 8:16 | |
| Age (years) | 61.71 ± 9.56 | 63.91 ± 17.62 | 0.173 |
| IOP (mm Hg) | 14.32 ± 2.53 | 14.68 ± 2.47 | 0.244 |
| Pachymetry (μ m) | 550.66 ± 33.40 | 551.29 ± 30.53 | 0.861 |
| Endothelial cell count (cells/mm2) | 2,798 ± 346 | 2,638 ± 494 | 0.370 |
| Axial length (mm) | 24.02 ± 1.40 | 23.76 ± 2.09 | 0.167 |
Table 2.
Data summary of UCVA, BCVA, SE and topographic astigmatism
| With-the-rule group | Against-the-rule group | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-op | |||
| UCVA (log MAR) | 0.291 ± 0.175 | 0.292 ± 0.195 | 0.860 |
| BCVA (log MAR) | 0.462 ± 0.220 | 0.441 ± 0.217 | 0.925 |
| SE (diopter) | -0.719 ± 3.318 | -0.646 ± 3.561 | 0.992 |
| Auto-refractive astigmatism (diopter) | -1.417 ± 1.433 | -1.542 ± 0.783 | 0.130 |
| Post-op 2 months | |||
| UCVA (log MAR) | 0.468 ± 0.229 | 0.496 ± 0.262 | 0.747 |
| BCVA (log MAR) | 0.815 ± 0.122 | 0.780 ± 0.212 | 0.814 |
| SE (diopter) | -1.156 ± 0.699 | -0.875 ± 0.864 | 0.208 |
| Auto-refractive astigmatism (diopter) | -0.802 ± 0.840 | -0.990 ± 0.640 | 0.089 |
Table 3.
Changes of anterior, posterior, and total corneal astigmatism before and after surgery
Table 4.
Comparisions of anterior, posterior, and total corneal astigmatism before and 2 months after surgery
| Pre-op (D) | Post-op 2 months (D) △ | △ Astigmatism p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With-the-rule group | |||
| Ant. | 1.246 ± 0.999 | 0.717 ± 0.274 | p = 0.018 |
| Post. | 0.258 ± 0.102 | 0.313 ± 0.125 | p = 0.055 |
| Total | 1.104 ± 0.991 | 0.588 ± 0.510 | p = 0.023 |
| Against-the-rule group (Post. corneal steep meridian with 90 ± 30°) | |||
| Ant. | 1.127 ± 0.492 | 0.707 ± 0.394 | p = 0.016 |
| Post. | 0.327 ± 0.181 | 0.220 ± 0.218 | p = 0.049 |
| Total | 1.480 ± 0.587 | 0.900 ± 0.541 | p = 0.008 |
| Against-the-rule group (Post. corneal steep meridian with 180 ± 30°) | |||
| Ant. | 1.478 ± 1.398 | 0.733 ± 0.466 | p = 0.018 |
| Post. | 0.211 ± 0.141 | 0.378 ± 0.128 | p = 0.094 |
| Total | 1.222 ± 0.746 | 1.044 ± 0.410 | p = 0.605 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download