Abstract
Purpose
In this study evaluated clinical outcomes and higher-order aberrations in patients with implanted Tecnis ZCT toric intraocular lens (IOL) (Abbott Medical Optics Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA) and the Zeiss AT TORBI toric IOL (Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany) in eyes with low to moderate corneal astigmatism.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study of 32 consecutive eyes of 26 patients with a visually significant cataract and moderate corneal astigmatism (higher than 1.25 diopter [D] and lower than 4.5 D) undergoing cataract surgery with implantation of the aspheric Tecnis ZCT toric IOL (Abbott Medical Optics Inc.) and the Zeiss AT TORBI toric IOL (Carl Zeiss Meditec AG). Phacoemulsification was performed by the same experienced surgeon using 2.2 mm temporal incision. Visual, refractive and aberrometric changes were evaluated during a 3-month follow-up. Power vector analysis of Cartesian astigmatism (J0) and oblique astigmatism (J45) was performed.
Results
At the 3-month follow-up, corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) and residual astigmatism showed no statistically significant differences between groups (p = 0.203 and p = 0.364, respectively). Pre- and postoperative J0 were 0.71 ± 0.84 and 0.05 ± 0.39 in the Tecnis Toric group and, 0.88 ± 1.27 and -0.02 ± 0.16 in the AT TORBI group, respectively, which showed statistically significant differences (p = 0.029 and p = 0.032, respectively). Pre- and post-operative differences of J0 and J45 were not statistically significant (p = 0.234 and p = 0.603, respectively). No eye had IOL rotation ≥10°. Ocular aberrometry values were statistically significantly differenct between the groups, except for spherical aberration, which was higher in the AT TORBI group (p = 0.0047).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Ferrer-Blasco T, Montés-Micó R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:70–5.

2). Hoffmann PC, Hütz WW. Analysis of biometry and prevalence data for corneal astigmatism in 23,239 eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1479–85.
3). Khan MI, Muhtaseb M. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism in patients having routine cataract surgery at a teaching hospital in the United Kingdom. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1751–5.

4). Atchison DA, Guo H, Charman WN, Fisher SW. Blur limits for defocus, astigmatism and trefoil. Vision Res. 2009; 49:2393–403.

5). Wolffsohn JS, Bhogal G, Shah S. Effect of uncorrected astigmatism on vision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:454–60.

6). Budak K, Friedman NJ, Koch DD. Limbal relaxing incisions with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:503–8.

8). Koch DD. Peripheral corneal relaxing incisions combined with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:712–22.
9). Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: correcting astigmatism while controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994; 20:523–6.

10). Ma JJ, Tseng SS. Simple method for accurate alignment in toric phakic and aphakic intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1631–6.

12). Yu JG, Zhao YE, Shi JL, et al. Biaxial microincision cataract surgery versus conventional coaxial cataract surgery: metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:894–901.

13). Poll JT, Wang L, Koch DD, Weikert MP. Correction of astigmatism during cataract surgery: toric intraocular lens compared to peripheral corneal relaxing incisions. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:165–71.

14). Ahmed II, Rocha G, Slomovic AR, et al. Visual function and patient experience after bilateral implantation of toric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:609–16.

15). Bauer NJ, Webers CA, et al. Astigmatism management in cataract surgery with the AcrySof toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1483–8.

16). De Silva DJ, Ramkissoon YD, Bloom PA. Evaluation of a toric intraocular lens with a Z-haptic. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1492–8.

17). Entabi M, Harman F, Lee N, Bloom PA. Injectable 1-piece hydrophilic acrylic toric intraocular lens for cataract surgery: efficacy and stability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:235–40.

18). Mendicute J, Irigoyen C, Aramberri J, et al. Foldable toric intraocular lens for astigmatism correction in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:601–7.

19). Till JS, Yoder PR Jr, Wilcox TK, Spielman JL. Toric intraocular lens implantation: 100 consecutive cases. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:295–301.

20). Thibos LN, Horner D. Power vector analysis of the optical outcome of refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:80–5.

21). Kim MH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Long-term efficacy and rotational stability of AcrySof toric intraocular lens implantation in cataract surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010; 24:207–12.

22). Na JH, Lee HS, Joo CK. The clinical result of AcrySof Toric intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:831–8.

23). Tonn B, Klaproth OK, Kohnen T. Anterior surface-based keratometry compared with Scheimpflug tomography-based total corneal astigmatism. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014; 56:291–8.

24). Koch DD, Ali SF, Weikert MP, et al. Contribution of posterior corneal astigmatism to total corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2080–7.

25). Savini G, Versaci F, Vestri G, et al. Influence of posterior corneal astigmatism on total corneal astigmatism in eyes with moderate to high astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014; 40:1645–53.

26). Seo KY, Im CY, Yang H, et al. New equivalent keratometry reading calculation with a rotating Scheimpflug camera for intraocular lens power calculation after myopic corneal surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014; 40:1834–42.

27). Waltz KL, Featherstone K, Tsai L, Trentacost D. Clinical outcomes of TECNIS toric intraocular lens implantation after cataract removal in patients with corneal astigmatism. Ophthalmology. 2015; 122:39–47.
28). Ferreira TB, Almeida A. Comparison of the visual outcomes and OPD-scan results of AMO Tecnis toric and Alcon Acrysof IQ toric intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2012; 28:551–5.

29). Bascaran L, Mendicute J, Macias-Murelaga B, et al. Efficacy and stability of AT TORBI 709 M toric IOL. J Refract Surg. 2013; 29:194–9.

30). Scialdone A, Raimondi G, Monaco G. In vivo assessment of higher-order aberrations after AcrySof toric intraocular lens implantation: a comparative study. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2012; 22:531–40.

31). Hoffmann PC, Auel S, Hütz WW. Results of higher power toric intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1411–8.

32). Koshy JJ, Nishi Y, Hirnschall N, et al. Rotational stability of a single-piece toric acrylic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1665–70.

33). Shah GD, Praveen MR, Vasavada AR, et al. Rotational stability of a toric intraocular lens: influence of axial length and alignment in the capsular bag. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:54–9.

Go to : 
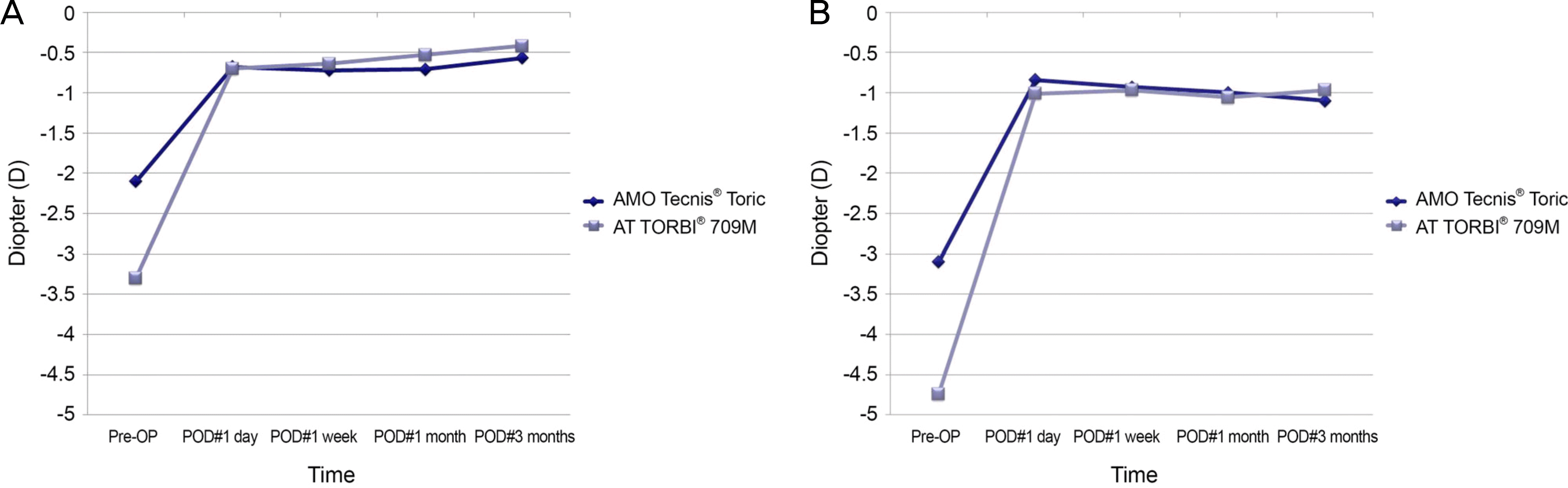 | Figure 2.Refractive results at 3 months postoperatively. (A) Cylinder. (B) Spherical equivalent. Pre-OP = preoperative; POD = postoperative day. |
Table 1.
Patient demographics and clinical information
| Parameters | AMO Tecnis® Toric IOL | AT TORBI® 709M IOL | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes (n) | 18 | 14 | |
| Patients (n) | 14 | 12 | |
| Age (years) | 58.33 ± 12.66 (21~80) | 45.70 ± 18.50 (21~78) | |
| Male sex (n, %) | 5 (35.7) | 1 (8) | |
| Right eyes (n, %) | 8 (57.1) | 9 (64) | |
| UDVA (log MAR) | 0.75 ± 0.57 (1.7~0.2) | 0.89 ± 0.50 (2.0~0.1) | 0.47 |
| CDVA (log MAR) | 0.38 ± 0.43 (1.7~0) | 0.31 ± 0.23 (2.0~0) | 0.27 |
| Sphere (D) | −2.31 ± 3.26 (−9.0~+2.25) | −3.6 ± 3.04 (−8.75~+2.0) | 0.39 |
| Cylinder (D) | −2.10 ± 1.14 (−5.25~−0.5) | −3.30 ± 2.23 (−7.75~−0.25) | 0.33 |
| Corneal astigmatism (D) | 2.10 ± 1.11 (0.75~4.5) | 1.96 ± 0.96 (1.0~4.5) | 0.65 |
| Corneal spherical aberration (μ m) | 0.35 ± 0.37 (−0.409~+0.352) | 0.36 ± 0.31 (+0.035~+0.633) | 0.27 |
| IOL power (D) | 18.25 ± 3.34 (10.5~23.0) | S 12.75 ± 0.99 (1~18) | |
| C 2.67 ± 0.99 (1~4) | |||
| IOL model (n) | ZCT 150 (4), ZCT225 (7), ZCT400 (7) | AT TORBI 709M (14) |
Table 2.
Preoperative and postoperative visual acuity, refraction and in the AMO Tecnis toric intraocular lens
| Parameters | Mean ± SD (range) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre op | Post op | ||
| UDVA (log MAR) | 0.75 ± 0.57 (1.7~0.2) | 0.12 ± 0.16 (0.5~0) | <0.001 |
| CDVA (log MAR) | 0.38 ± 0.43 (1.7~0) | 0.03 ± 0.05 (0.1~0) | <0.001 |
| Sphere (D) | −2.31 ± 3.26 (−9.0~+2.25) | −0.19 ± 0.39 (−0.75~+0.5) | 0.018 |
| Cylinder (D) | −2.10 ± 1.14 (−5.25~−0.5) | −0.45 ± 0.20 (−0.75~−0.25) | 0.0006 |
| Spherical equivalent (D) | −3.24 ± 3.68 (−10.625~+1.375) | −0.15 ± 0.34 (−0.5~+0.5) | 0.0037 |
| Rotation (°) | - | 3.2 ± 2.2 (8~0) | |
Table 3.
Preoperative and postoperative visual acuity, refraction and rotation in the Zeiss AT TORBI toric intraocular lens
| Parameters | Mean ± SD (range) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre op | Post op | ||
| UDVA (log MAR) | 0.87 ± 0.47 (2~0.1) | 0.11 ± 0.13 (0.2~0) | <0.001 |
| CDVA (log MAR) | 0.31 ± 0.48 (2~0) | 0.02 ± 0.05 (0.1~0) | 0.0015 |
| Sphere (D) | −3.6 ± 3.04 (−8.75~+2.0) | 0.05 ± 0.54 (−0.25~+1.0) | 0.02 |
| Cylinder (D) | −3.30 ± 2.23 (−7.75~−0.25) | −0.34 ± 0.38 (−1.0~0) | 0.001 |
| Spherical equivalent (D) | −4.74 ± 2.47 (−10.375~+1.50) | −0.09 ± 0.59 (−0.625~0.75) | 0.015 |
| Rotation (°) | - | 2.4 ± 2.0 (8~0) | |
Table 4.
Preoperative and postoperative J0 and J45 cylindrical vectors
| Refractive astigmatism | Mean ± SD (range) | p-value* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre op | Post op | |||
| AMO Tecnis Toric IOL | J0 (D) | 0.71 ± 0.84 | 0.05 ± 0.39 | 0.029 |
| J45 (D) | 0.50 ± 0.46 | −0.01 ± 0 .17 | 0.472 | |
| AT TORBI 709M IOL | J0 (D) | 0.88 ± 1.27 | −0.02 ± 0.16 | 0.032 |
| J45 (D) | −0.08 ± 0.91 | 0.01 ± 0.25 | 0.750 | |
Table 5.
Ocular aberrometry analysis at 3 months postoperatively
| Parameters | Mean ± SD (range) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMO Tecnis Toric IOL | AT TORBI 709M IOL | ||
| Total RMS (μ m) | 0.39 ± 0.10 (0.22~0.5) | 0.22 ± 0.11 (0.15~0.39) | 0.09 |
| Spherical aberration (μ m) | 0.02 ± 0.04 (−0.04~0.05) | 0.11 ± 0.08 (0.041~0.57) | 0.008 |
| Coma (μ m) | 0.19 ± 0.14 (0.07~0.38) | 0.11 ± 0.07 (0.05~0.21) | 0.33 |
| Trefoil (μ m) | 0.19 ± 0.06 (0.13~0.26) | 0.11 ± 0.11 (0.03~0.27) | 0.27 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download