Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate and compare the efficacy and safety of cyclosporine 0.05% (Cyporin N eye drops 0.05%) to an active com-parator (Restasis®) in moderate to severe dry eye patients.
Methods
This is a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel, active control, non-inferiority, phase Ⅲ study. Patients had a 2-week run-in period (during the run-in period, patients used artificial tears, if applicable), and afterward 158 patients were randomly assigned treatment for 12 weeks with cyclosporine 0.05% (with artificial tears, if applicable), in which the efficacy and safety were evaluated every four weeks.
Results
Corneal staining tests showed that in the per protocol set group, the study group was not inferior to the control group; the results for the full analysis set analytic group were the same. The number of adverse events reported from the 158 patients was not significantly different between groups (p = 0.1107). Additionally, other evaluations, including tolerability evaluations, clinical pathology examinations, and vital signs, show that there is no difference in terms of safety between the groups.
Go to : 
References
1. O'Brien PD, Collum LM. Dry eye: diagnosis and current treatment strategies. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004; 4:314–9.
2. Hikichi T, Yoshida A, Fukui Y, et al. Prevalence of dry eye in Japanese eye centers. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1995; 233:555–8.

3. Jamaliah R, Fathilah J. Prevalence of dry eye in University Malaya Medical Centre. Med J Malaysia. 2002; 57:390–7.
4. Lekhanont K, Rojanaporn D, Chuck RS, Vongthongsri A. Prevalence of dry eye in Bangkok, Thailand. Cornea. 2006; 25:1162–7.

5. The definition and classification of dry eye disease: report of the Definition and Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf. 2007; 5:75–92.
7. Sall K, Stevenson OD, Mundorf TK, Reis BL. Two multicenter, randomized studies of the efficacy and safety of cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion in moderate to severe dry eye disease. CsA Phase 3 Study Group. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:631–9.
8. Byun YS, Rho CR, Cho K, et al. Cyclosporine 0.05% ophthalmic emulsion for dry eye in Korea: a prospective, multicenter, open-la-bel, surveillance study. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:369–74.

9. Kim EC, Choi JS, Joo CK. A comparison of vitamin a and abdominal a 0.05% eye drops for treatment of dry eye syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:206–13.e3.
10. Moon JW, Lee HJ, Shin KC, et al. Short term effects of topical abdominal and viscoelastic on the ocular surfaces in patients with dry eye. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007; 21:189–94.
11. Perry HD, Solomon R, Donnenfeld ED, et al. Evaluation of topical cyclosporine for the treatment of dry eye disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008; 126:1046–50.

12. Stevenson D, Tauber J, Reis BL. Efficacy and safety of cyclosporin A ophthalmic emulsion in the treatment of moderate-to-severe dry eye disease: a dose-ranging, randomized trial. The Cyclosporin A Phase 2 Study Group. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:967–74.
13. Lee JS, Yoon TJ, Kim KH. Cinical effect of Restasis(R) eye drops in mild dry eye syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1489–94.
14. el Tayar N, Mark AE, Vallat P, et al. Solvent-dependent con-formation and hydrogen-bonding capacity of cyclosporin A: abdominal from partition coefficients and molecular dynamics simulations. J Med Chem. 1993; 36:3757–64.
15. Liu H, Wang Y, Li S. Advanced delivery of ciclosporin A: present state and perspective. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2007; 4:349–58.

16. Tadros T. Application of rheology for assessment and prediction of the long-term physical stability of emulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2004; 108–109:227–58.

17. Aksungur P, Demirbilek M, Denkbaş EB, et al. Development and characterization of Cyclosporine A loaded nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery: Cellular toxicity, uptake, and kinetic studies. J Control Release. 2011; 151:286–94.

18. Management and therapy of dry eye disease: report of the Management and Therapy Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf. 2007; 5:163–78.
19. Chen M, Gong L, Sun X, et al. A comparison of cyclosporine 0.05% ophthalmic emulsion versus vehicle in Chinese patients with moderate to severe dry eye disease: an eight-week, abdominal, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 26:361–6.
Go to : 
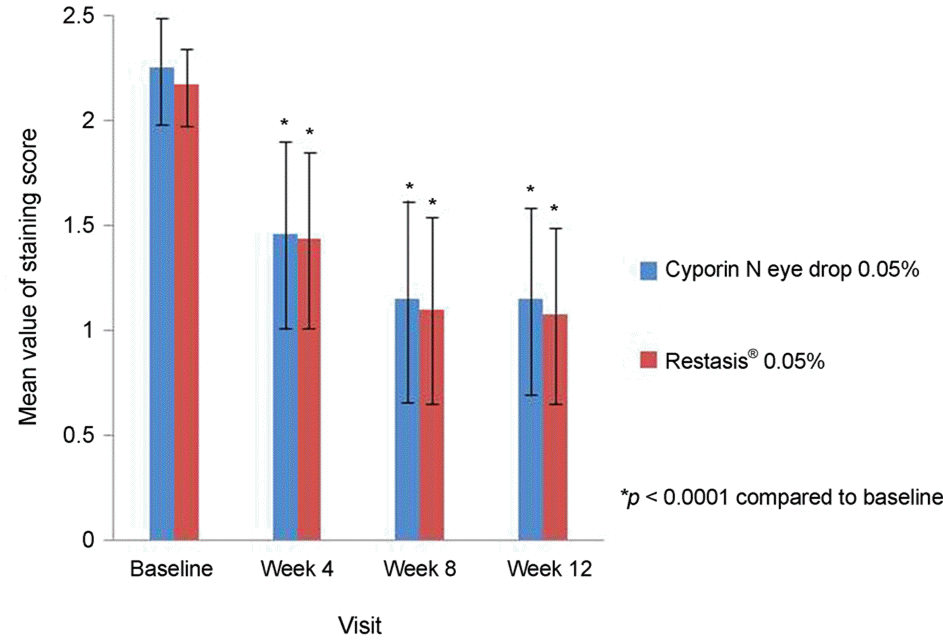 | Figure 1Mean value of corneal staining score for patients with dry eye disease who were treated with two groups of cyclosporine 0.05% eye drop for three months. Corneal staining scores (using Oxford scale from 0 to 5) were assessed. * p < 0.0001 compared with baseline. |
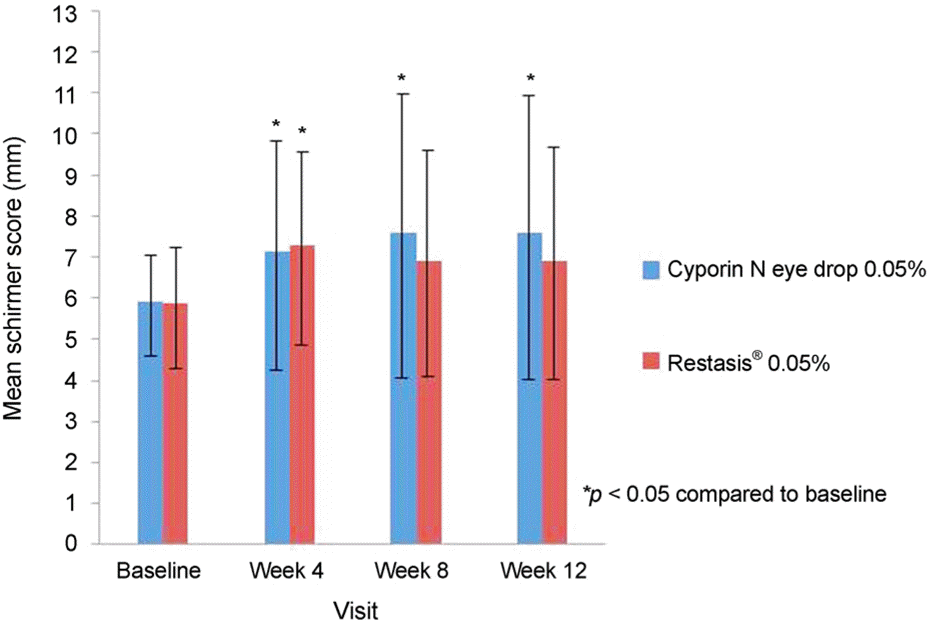 | Figure 2Schirmer scores for patients with dry eye disease who were treated with two groups of cyclosporine 0.05% eye drop for three months. Schirmer scores (change from baseline, mm) were assessed with and without anesthesia. * p < 0.05 compared with baseline (without anesthesia). |
Table 1.
Patient demographics and clinical information
| Parameters | Cyporin N eye drop 0.05% | Restasis® 0.05% | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 80 | 78 | |
| Age (years) | 53.20 ± 14.53 (20–79) | 53.19 ± 12.50 (21–75) | 0.99* |
| Age ≥50 (years, n [%]) | 57 (71.25) | 51 (68.36) | |
| Male sex (n, %) | 20 (25.0) | 20 (25.64) | |
| Height (cm) | 160.59 ± 8.38 | 161.03 ± 7.00 | 0.73* |
| (136.5–183.0) | (149.0–180.0) | ||
| Weight (kg) | 59.90 ± 9.88 | 59.82 ± 7.63 | 0.96* |
| (39.0–90.0) | (44.0–79.0) | ||
| Past medical history (n, %) | 25 (31.25) | 21 (26.92) | 0.55† |
| Past surgical history (n, %) | 9 (11.25) | 8 (10.26) | 0.84† |
Table 2.
Treatment-related adverse events




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download