Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of brinzolamide 1%/brimonidine 0.2% fixed combination (BBFC) in normal tension glaucoma (NTG) patients.
Methods
This prospective study included patients treated with brinzolamide 1% monotherapy, brimonidine 0.2% monotherapy or brinzolamide 1% and brimonidine 0.2% concomitant therapy, as well as newly diagnosed NTG patients. The enrolled patients who used brinzolamide 1% or brimonidine 0.2% switched to BBFC and newly diagnosed NTG patients were treated with BBFC. The patients receiving brinzolamide 1% or brimonidine 0.2% monotherapy or brinzolamide 1% and brimonidine 0.2% concomitant therapy switched antiglaucoma drugs to BBFC. Newly diagnosed NTG patients used BBFC as the first therapy. The study consisted of 1 screening/baseline visit and 3 follow-up visits conducted after 1, 4, 8, 12 and 24 weeks of treatment. Intraocular pressure (IOP), mean deviation value and adverse drug reactions were evaluated before treatment and after treatment with BBFC.
Results
The mean IOP in the brinzolamide 1% monotherapy group was 13.5 ± 1.6 mm Hg and the mean IOP after switched from brinzolamide 1% monotherapy to BBFC was 12.1 ± 1.5 mm Hg. The mean IOP in the brimonidine 0.2% monotherapy group was 14.2 ± 1.3 mm Hg and the mean IOP after switched from brimonidine 0.2% monotherapy to BBFC was 11.7 ± 1.5 mm Hg. The mean IOP was 11.9 ± 2.1 mm Hg in the brinzolamide 1% and brimonidine 0.2% concomitant therapy group and the mean IOP after switched from brinzolamide 1% and brimonidine 0.2% concomitant therapy to BBFC was 12.0 ± 1.1 mm Hg. The mean IOP and reduction rate were 10.7 ± 2.1 mm Hg and 35.5%, respectively, in the newly diagnosed NTG patients treated with BBFC. There was no serious adverse drug reaction causing ocular damage.
References
1. Kamal D, Hitchings R. Normal tension glaucoma-a practical approach. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:835–40.

2. Iwase A, Suzuki Y, Araie M, et al. The prevalence of primary open-angle glaucoma in Japanese: the Tajimi Study. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1641–8.
3. Kim CS, Seong GJ, Lee NH, et al. Prevalence of primary open-abdominal glaucoma in central South Korea the Namil study. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:1024–30.
4. Webers CA, Beckers HJ, Nuijts RM, Schouten JS. Pharmacological management of primary open-angle glaucoma: second-line options and beyond. Drugs Aging. 2008; 25:729–59.
5. Quigley HA, Enger C, Katz J, et al. Risk factors for the abdominal of glaucomatous visual field loss in ocular hypertension. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994; 112:644–9.
6. Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:701–13. 829–30.
7. Barnebey HS, Orengo-Nania S, Flowers BE, et al. The safety and efficacy of travoprost 0.004%/timolol 0.5% fixed combination ophthalmic solution. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:1–7.

8. Lee AJ, McCluskey P. Fixed combination of topical brimonidine 0.2% and timolol 0.5% for glaucoma and uncontrolled intraocular pressure. Clin Ophthalmol. 2008; 2:545–55.

9. Inoue K, Shiokawa M, Sugahara M, et al. Three-month evaluation of dorzolamide hydrochloride/timolol maleate fixed-combination eye drops versus the separate use of both drugs. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012; 56:559–63.

10. Higginbotham EJ, Hansen J, Davis EJ, et al. Glaucoma medication persistence with a fixed combination versus multiple bottles. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009; 25:2543–7.

11. Taniguchi T, Kitazawa Y. The potential systemic effect of topically applied beta-blockers in glaucoma therapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1997; 8:55–8.
12. The effectiveness of intraocular pressure reduction in the treatment of normal-tension glaucoma. Collaborative Normal-Tension Glaucoma Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:498–505.
13. Wolfs RC, Borger PH, Ramrattan RS, et al. Changing views on open-angle glaucoma: definitions and prevalences-The Rotterdam Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41:3309–21.
14. Katz G, Dubiner H, Samples J, et al. Three-month randomized trial of fixed-combination brinzolamide, 1%, and brimonidine, 0.2%. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013; 131:724–30.

15. Aung T, Laganovska G, Hernandez Paredes TJ, et al. Twice-daily brinzolamide/brimonidine fixed combination versus brinzolamide or brimonidine in open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:2348–55.

16. Gandolfi SA, Lim J, Sanseau AC, et al. Randomized trial of abdominal/brimonidine versus brinzolamide plus brimonidine for open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Adv Ther. 2014; 31:1213–27.
Figure 1.
Changes of intraocular pressure (IOP) throughout the study (from brinzolamide 1% to BBFC switched group). Asterisk (*) indicated that statistically significant, p < 0.05, versus brinzolamide. BBFC = brinzolamide 1%/brimonidine 0.2% fixed combination.
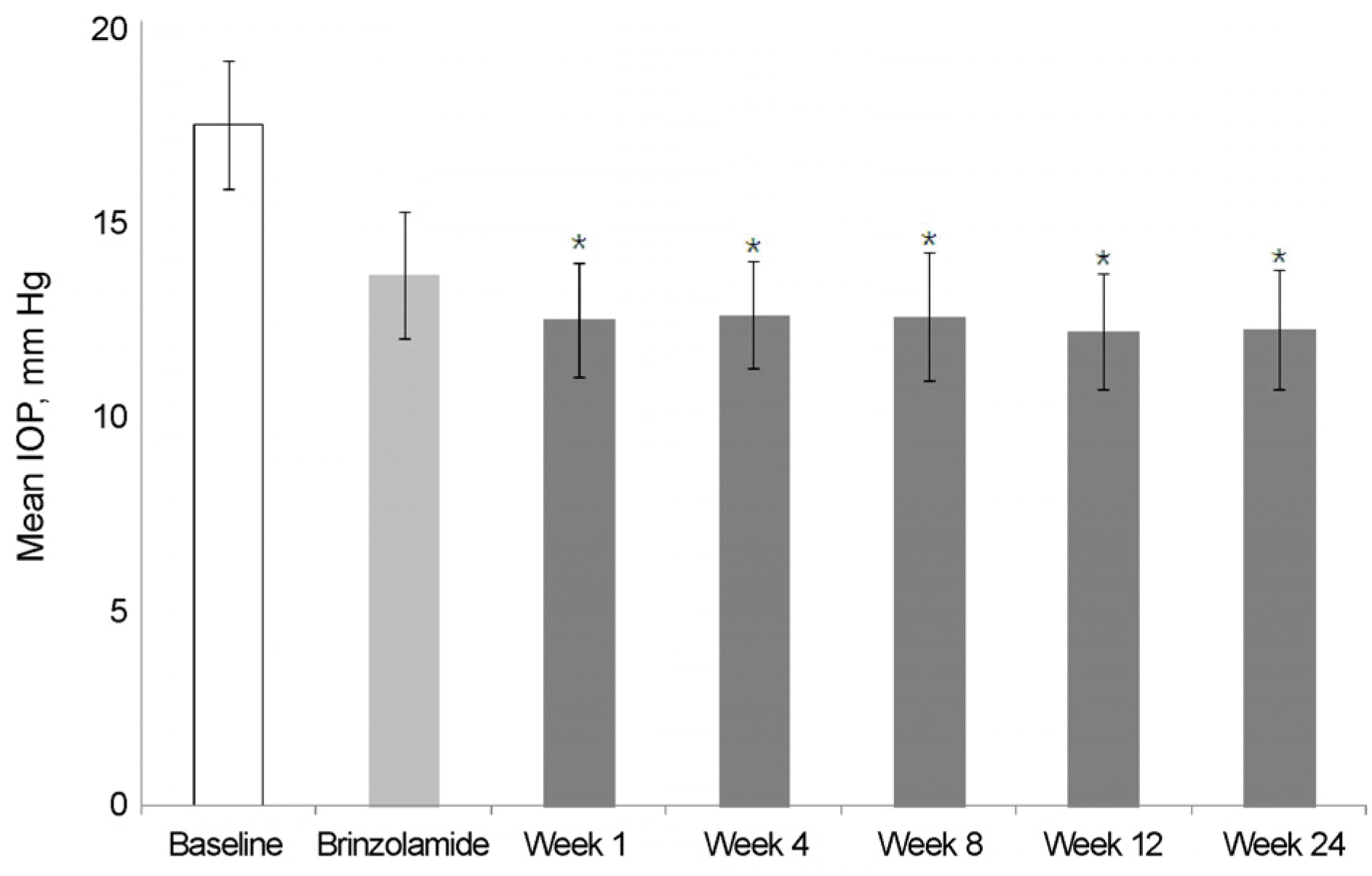
Figure 2.
Changes of intraocular pressure (IOP) throughout the study (from brimonidine 0.2% to BBFC switched group). Asterisk (*) indicated that statistically significant, p < 0.05, versus brimonidine. BBFC = brinzolamide 1%/brimonidine 0.2% fixed combination.

Figure 3.
Changes of intraocular pressure (IOP) throughout the study (from brinzolamide 1% + brimonidine 0.2% to BBFC switched group). BBFC = brinzolamide 1%/brimonidine 0.2% fixed combination.

Figure 4.
Changes of intraocular pressure (IOP) throughout the study (BBFC first therapy). Asterisk (*) indicated that statistically significant, p < 0.05, versus baseline. BBFC = brinzolamide 1%/brimonidine 0.2% fixed combination.

Table 1.
Clinical and demographic data of the patients
| Data | |
|---|---|
| Male:Female | 40 (46.0%):47 (54.0%) |
| Mean age (years) | 60.5 ± 5.4 |
| Mean baseline IOP (mm Hg) | 17.7 ± 1.7 |
| Mean MD (dB) | –2.28 ± 0.12 |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) | –1.1 ± 2.0 |
| CCT (mm) | 547.2 ± 13.8 |
Table 2.
Mean IOP and change in mean and percentage of IOP from baseline (from brinzolamide1% to BBFC switched group, n = 24)
| Baseline‡ | Brinzolamide | Week 1 | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | Week 24 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOP (mm Hg) | 17.3 ± 1.6 | 13.5 ± 1.6 | 12.4 ± 1.5 | 12.5 ± 1.4 | 12.5 ± 1.6 | 12.1 ± 1.5 | 12.1 ± 1.5 |
| p-value* | N/A | N/A | 0.019 | 0.044 | 0.029 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| Reduction rate (%) | † N/A | 22.0 | 28.3 | 27.7 | 27.7 | 30.1 | 30.1 |
Table 3.
Mean IOP and change in mean and percentage of IOP from baseline (from brimonidine 0.2% to BBFC switched group, n = 30)
| Baseline‡ | Brimonidine | Week 1 | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | Week 24 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOP (mm Hg) | 18.3 ± 1.7 | 14.2 ± 1.3 | 12.3 ± 1.5 | 12.6 ± 1.5 | 11.9 ± 1.9 | 11.8 ± 1.7 | 11.7 ± 1.5 |
| p-value* | N/A | N/A | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Reduction rate (%)† | N/A | 22.4 | 32.8 | 31.1 | 35.0 | 35.5 | 36.1 |
Table 4.
Mean IOP and change in mean and percentage of IOP from baseline (n = 16)
| Baseline‡ | Brinzolamide + Brimonidine | Week 1 | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | Week 24 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOP (mm Hg) | 19.7 ± 1.9 | 11.9 ± 2.1 | 12.2 ± 1.3 | 12.3 ± 1.1 | 11.8 ± 1.6 | 12.1 ± 1.7 | 12.0 ± 1.1 |
| p-value* | N/A | N/A | 0.700 | 0.616 | 0.880 | 0.852 | 0.891 |
| Reduction rate (%)† | † N/A | 39.6 | 38.1 | 37.6 | 40.1 | 38.6 | 39.1 |
Table 5.
Mean IOP and change in mean and percentage of IOP from baseline (BBFC first therapy group, n = 17)
| Baseline‡ | Week 1 | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | Week 24 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOP (mm Hg) | 16.6 ± 1.7 | 11.3 ± 1.6 | 10.8 ± 1.6 | 10.9 ± 2.1 | 11.1 ± 2.0 | 10.7 ± 2.1 |
| p-value* | N/A | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Reduction rate (%)† | N/A | 32.0 | 34.9 | 34.3 | 33.1 | 35.5 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download