Abstract
Case summary
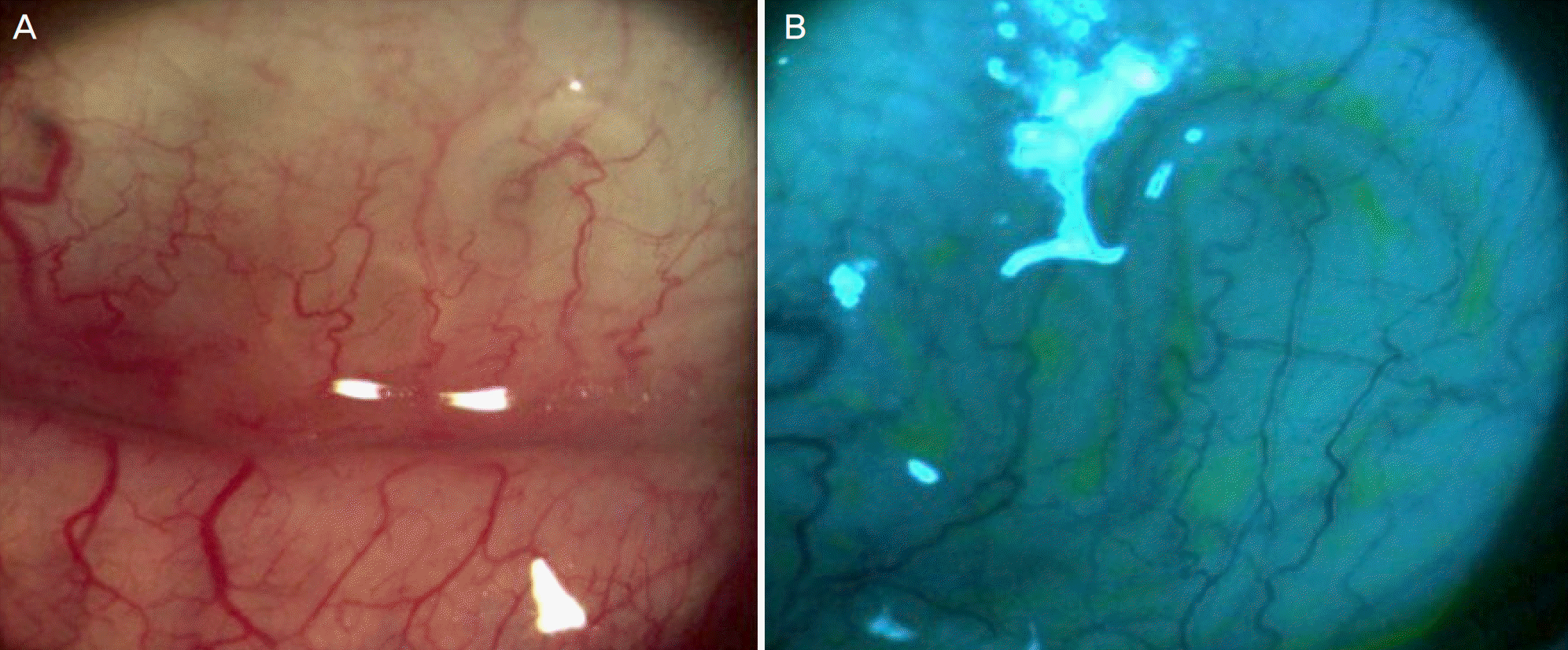
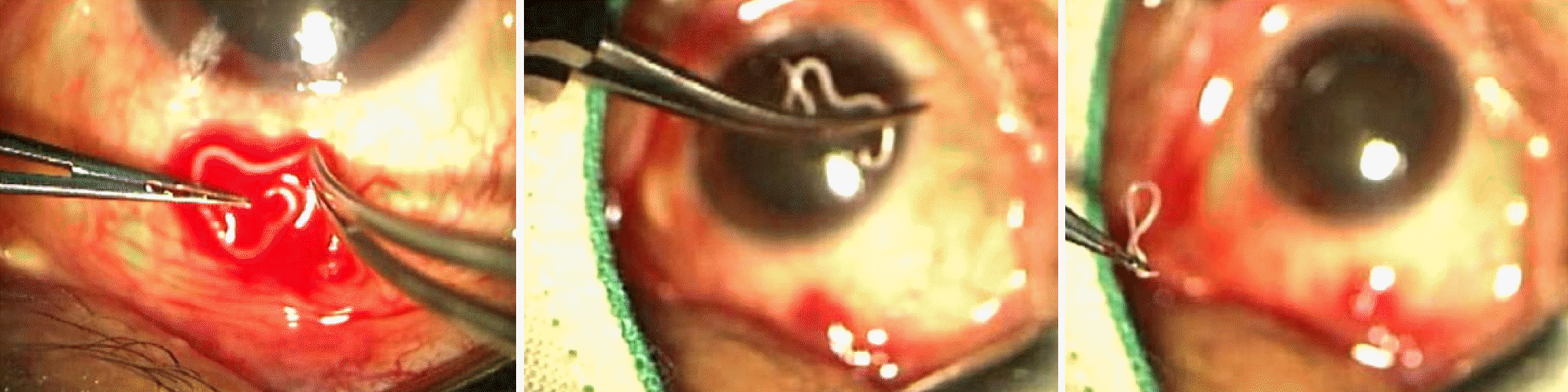
A 52-year-old man came in with left eye discomfort that started about a month prior to hospital visit. Slit lamp examination identified a live white translucent parasite about 10 mm in length and about 0.3 mm in width moving under the lower left eye subconjunctiva. No other abnormal findings were found in the front or fundus. An incision of about 5 mm in the conjunctiva where the parasite was located was carried out, and after opening the area, the parasite was slowly pulled out using a clamp. Then, the bottom of the conjunctiva was washed with normal saline. Further, five additional parasites were found in the conjunctival sac and were removed. The parasite was identified as Thelazia callipaeda, and through outpatient follow-up for 1 month after removal, additional parasites were not found.
Go to : 
References
1. Oh CK, Youn WS, Cho SY, Seo BS. A case report of human thelaziasis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1975; 16:431–4.
2. Kofoid CA, Williams OL. The nematode Thelazia californiensis as a parasite of the eye of man in California. Arch Ophthalmol. 1935; 13:176–80.

3. Nakata R. Study on Thelazia callipaeda. Jpn J Parasitol. 1964; 13:600–9.
4. Hong ST, Lee SH, Shim YB, et al. A Human case of Thelaziasis in Korea. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi. 1981; 19:76–80.

7. Jin Y, Shen C, Huh S, et al. Serodiagnosis of toxocariasis by ELISA using crude antigen of Toxocara canis larvae. Korean J Parasitol. 2013; 51:433–9.

8. Jacquier P, Gottstein B, Stingelin Y, Eckert J. Immunodiagnosis of toxocarosis in humans: evaluation of a new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. J Clin Microbiol. 1991; 29:1831–5.

9. Romasanta A, Romero JL, Arias M, et al. Diagnosis of parasitic zo-onoses by immunoenzymatic assays–analysis of cross-reactivity among the excretory/secretory antigens of Fasciola hepatica, Toxocara canis, and Ascaris suum. Immunol Invest. 2003; 32:131–42.
10. Ishida MM, Rubinsky-Elefant G, Ferreira AW, et al. Helminth abdominals (Taenia solium, Taenia crassiceps, Toxocara canis, Schistosoma mansoni and Echinococcus granulosus) and cross-reactivities in human infections and immunized animals. Acta Trop. 2003; 89:73–84.
12. Zakir R, Zhong-Xia Z, Chioddini P, Canning CR. Intraocular infestation with the worm, Thelazia callipaeda. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:1194–5.

13. Lee J, Chung SH, Lee SC, Koh HJ. A technique for removal of a live nematode from the vitreous. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:1444–6.

14. Jeong JW, Park JW, Kong HH, et al. A case of Intraocular Thelasia callipaeda infestation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1517–22.
15. Chen W, Zheng J, Hou P, et al. A case of intraocular thelaziasis with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Clin Exp Optom. 2010; 93:360–2.

16. Kim DC, Shin H. Two cases of human Thelaziasis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:801–5.
17. Lee CH, Kim SY, Kim DC, Choi TY. 5 cases of human Thelaziasis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:2827–31.
18. Lee BS, Jung HR, Eom KS, et al. A case of human Thelaziasis in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1986; 27:85–90.
19. Lee SW, Kang SW, Lee JO, Kee SE. Two cases of Thelazia callipaeda infestation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1132–6.
20. Choi DK, Cho SY. A case of human Thelaziasis concomitantly found with a reservoir host. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1978; 19:125–9.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download