Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical features and prevalence of patients with laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy in Korea.
Methods
Using a retrospective study, the patients with laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy who underwent penetrating keratoplasty were selected. We investigated the duration from iridotomy to corneal decompensation, preoperative anterior chamber depth, axial length, keratometry, and survival time of the grafted cornea. The data were compared with the data of pa-tients with pseudophakic bullous keratopathy as controls.
Results
Laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy was found in 17 eyes, which represented 2.3% of penetrating keratoplasty cases (727) and 8.5% of bullous keratopathy cases (201), with a mean age of 66.9 years. The laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy group showed a higher female ratio (15 out of 17), shorter mean axial length (22.09 ± 0.79 mm) and anterior cham-ber depth (1.91 ± 0.36 mm) than the control group (15 out of 50, 24.30 ± 2.54 mm and 3.27 ± 0.66 mm, respectively) with a stat-istical significance ( p = 0.002, p < 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively). Mean survival time of the grafted cornea was 39.9 ± 8.6 months in the group of laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy, which was shorter than the control group (47.8 ± 3.1 months) without statistical significance ( p = 0.47).
Go to : 
References
2. Robin AL, Pollack IP. Argon laser peripheral iridotomies in the treatment of primary angle closure glaucoma. Long-term fol-low-up. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:919–23.
3. Schwartz AL, Martin NF, Weber PA. Corneal decompensation af-ter argon laser iridectomy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:1572–4.

4. Lim LS, Ho CL, Ang LP. . Inferior corneal decompensation following laser peripheral iridotomy in the superior iris. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:166–8.

5. Ang LP, Higashihara H, Sotozono C. . Argon laser iridot-omy-induced bullous keratopathy a growing problem in Japan. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007; 91:1613–5.
7. Smith J, Whitted P. Corneal endothelial changes after argon laser iridotomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98:153–6.

8. Jeng S, Lee JS, Huang SC. Corneal decompensation after argon la-ser iridectomy-a delayed complication. Ophthalmic Surg. 1991; 22:565–9.

9. Zabel RW, MacDonald IM, Mintsioulis G. Corneal endothelial de-compensation after argon laser iridotomy. Can J Ophthalmol. 1991; 26:367–73.
10. Kim YY, Lee JH, Ahn MD. . Angle closure in the Namil study in central South Korea. Arch Ophthalmol. 2012; 130:1177–83.

11. Lee TY, Yu S, Kim JH. . Seasonal variations of acute angle-clo-sure glaucoma in patients visiting the hospital. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1637–41.

12. Shimazaki J, Amano S, Uno T. . National survey on bullous keratopathy in Japan. Cornea. 2007; 26:274–8.

13. Robin AL, Pollack IP. A comparison of neodymium: YAG and ar-gon laser iridotomies. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:1011–6.
14. Moster MR, Schwartz LW, Spaeth GL. . Laser iridectomy. A controlled study comparing argon and neodymium: YAG. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:20–4.
15. Foster PJ. The epidemiology of primary angle closure and asso-ciated glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Semin Ophthalmol. 2002; 17:50–8.

16. Moon SW, Lim SH, Lee HY. Accuracy of biometry for intraocular lens implantation using the new partial coherence interferometer, AL-scan. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2014; 28:444–50.

17. Bourne WM, O'Fallon WM. Endothelial cell loss during penetrat-ing keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978; 85:760–6.

18. Chung SH, Kim HK, Kim MS. Corneal endothelial cell loss after penetrating keratoplasty in relation to preoperative recipient endo-thelial cell density. Ophthalmologica. 2010; 224:194–8.

Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Clinical photograph of two patients with laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy. Both eyes (A and B) are phakic and have iridotomy site on the superior-nasal side. Diffuse edematous cornea is noted which is consistent with bullous keratopathy. |
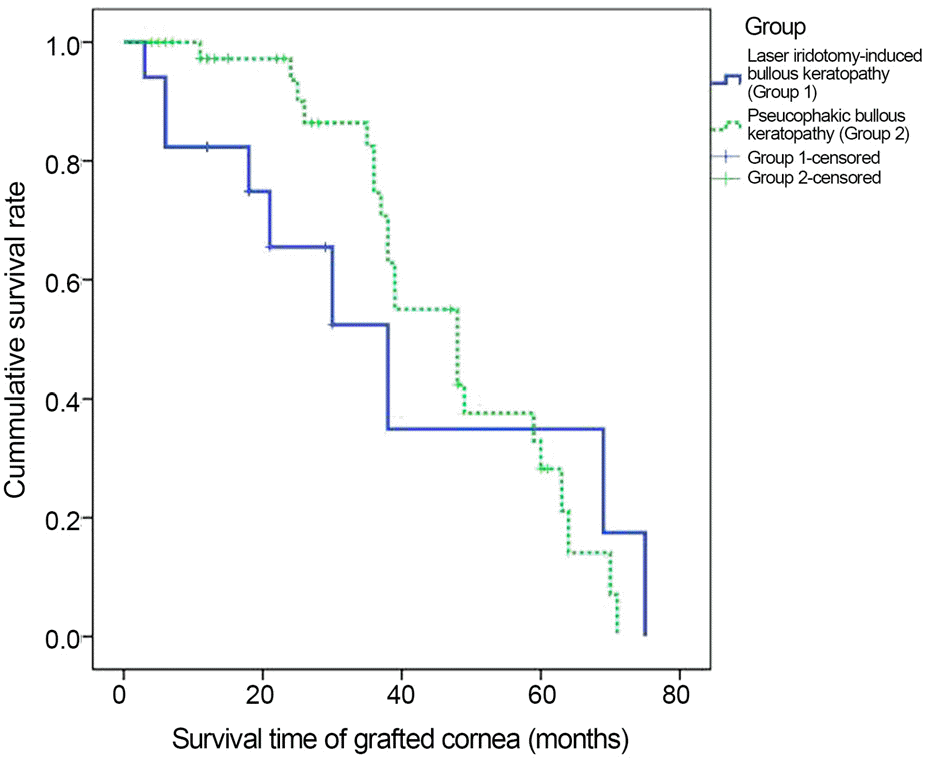 | Figure 2.Survival time analyzed by Kaplan-Meier curve. Mean survival time of the group of pseudophakic bullous ker-atopathy (47.8 months) is superior to that of the group of laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy (39.9 months) without statistical significance by log-rank test ( p = 0.47). |
Table 1.
Demographic data and clinical features of 17 eyes of laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy
Table 2.
Comparison of laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy and pseudophakic bullous keratopathy by Mann-Whitney U-test
| Laser iridotomy-induced bullous keratopathy (n = 17) | Pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (n = 50) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, range) | 66.6 (48-84) | 64.9 (42-85) | 0.92 |
| Sex (male:female) | 2:15 | 35:15 | 0.002 |
| Axial length (mm) | 22.09 ± 0.79 | 24.30 ± 2.54 | <0.001 |
| Anterior chamber depth (mm) | 1.91 ± 0.36 | 3.27 ± 0.66 | <0.001 |
| White-to-white (mm) | 10.9 ± 2.9 | 11.48 ± 0.57 | 0.44 |
| Mean keratometry (diopters) | 44.79 ± 1.50 | 43.92 ± 1.71 | 0.10 |
| Astigmatism magnitude (diopters) | 2.96 ± 1.21 | 3.27 ± 2.42 | 0.87 |
| WTR:ATR | 14:3 | 33:17 | 0.37 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download