Abstract
Purpose
To measure and compare the ocular blood-flow velocity of ophthalmic artery in patients with central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC); affected eyes, asymptomatic fellow eyes, and CSC resolved eyes using transcranial Doppler ultrasonography.
Methods
A total of 31 patients (age 20–52 years) with CSC were evaluated using power motion mode Doppler 150 digital transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. The peak systolic velocity (PSV), peak diastolic velocity (PDV), and resistance index (RI) were measured in the ophthalmic artery of both affected and asymptomatic fellow eyes. After 2 months, 23 patients with resolved serous retinal detachment underwent repeated measurement of the above hemodynamic indices.
Results
The PSV and PDV of the ophthalmic artery were 30.05 ± 5.34 cm/sec and 14.07 ± 2.90 cm/sec in affected eyes and 33.03 ± 2.00 cm/sec and 17.17 ± 2.76 cm/sec in asymptomatic fellow eyes, respectively. Both indices were significantly lower in affected eyes (p = 0.004, p < 0.001, respectively). The RI was 0.52 ± 0.08 in affected eyes and 0.43 ± 0.04 in fellow eyes, a significant difference (p < 0.001). After 2 months, in 23 eyes with resolved CSC, the PSV and PDV were 32.94 ± 6.24 cm/sec and 15.54 ± 2.88 cm/sec, respectively. Both indices were significantly higher than at baseline (p = 0.031, p = 0.045, respectively). However, RI was 0.48 ± 0.04 and was not significantly different (p = 0.073).
Conclusions
The CSC-affected eyes showed lower ocular blood-flow velocity and higher RI than the asymptomatic fellow eyes. The ocular blood-flow velocity was increased as CSC was resolved. These findings provide insights into the ophthalmic arterial vascular factors related to the pathogenesis of CSC.
Go to : 
References
1. Von Graefe A. Ueber centrale recidivierende retinitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1866; 12:211–5.
2. Donald J, Gass M. Pathogenesis of disciform detachment of the neuroepithelium: II. Idiopathic central serous choroidopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967; 63:587–15.
3. Gelber GS, Schatz H. Loss of vision due to central serous abdominal following psychological stress. Am J Psychiatry. 1987; 144:46–50.
5. Yap EY, Robertson DM. The long-term outcome of central serous chorioretinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996; 114:689–92.

6. Scheider A, Nasemann JE, Lund OE. Fluorescein and indocyanine green angiographies of central serous choroidopathy by scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:50–6.

7. Kitaya N, Nagaoka T, Hikichi T, et al. Features of abnormal abdominal circulation in central serous chorioretinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:709–12.
8. Aaslid R, Markwalder TM, Nornes H. Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg. 1982; 57:769–74.

9. Chen Q, Haeri S, Van Veen T, et al. Power M-mode transcranial Doppler examination of the ophthalmic artery in pregnancy: abdominal operating procedure and review of the literature. J Ultrasound Med. 2013; 32:1671–5.
10. Erickson SJ, Hendrix LE, Massaro BM, et al. Color Doppler flow imaging of the normal and abnormal orbit. Radiology. 1989; 173:511–6.

11. Kim YY, Huh K, Lee TS. Color Doppler imaging in diagnose abdominal disorders. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:261–6.
12. Youn JW, Lee HB, Lee KW, Youn DH. The measurement of ocular blood flow velocity using Doppler ultrasound in primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension patents. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1651–6.
13. Hamidi C, Türkcü FM, Göya C, et al. Evaluation of retrobulbar blood flow with color doppler ultrasonography in patients with central serous chorioretinopathy. J Clin Ultrasound. 2014; 42:481–5.

14. Gass JD. Pathogenesis of disciform detachment of the neuroepithelium. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967; 63(Suppl):1–139.
15. Spitznas M. Pathogenesis of central serous retinopathy: a new working hypothesis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1986; 224:321–4.

16. Iida T, Kishi S, Hagimura N, Shimizu K. Persistent and bilateral choroidal vascular abnormalities in central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 1999; 19:508–12.

17. Spaide RF, Hall L, Haas A, et al. Indocyanine green videoangiography of older patients with central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 1996; 16:203–13.

18. Bujarborua D, Chatterjee S, Choudhury A, et al. Fluorescein abdominal features of asymptomatic eyes in central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 2005; 25:422–9.
Go to : 
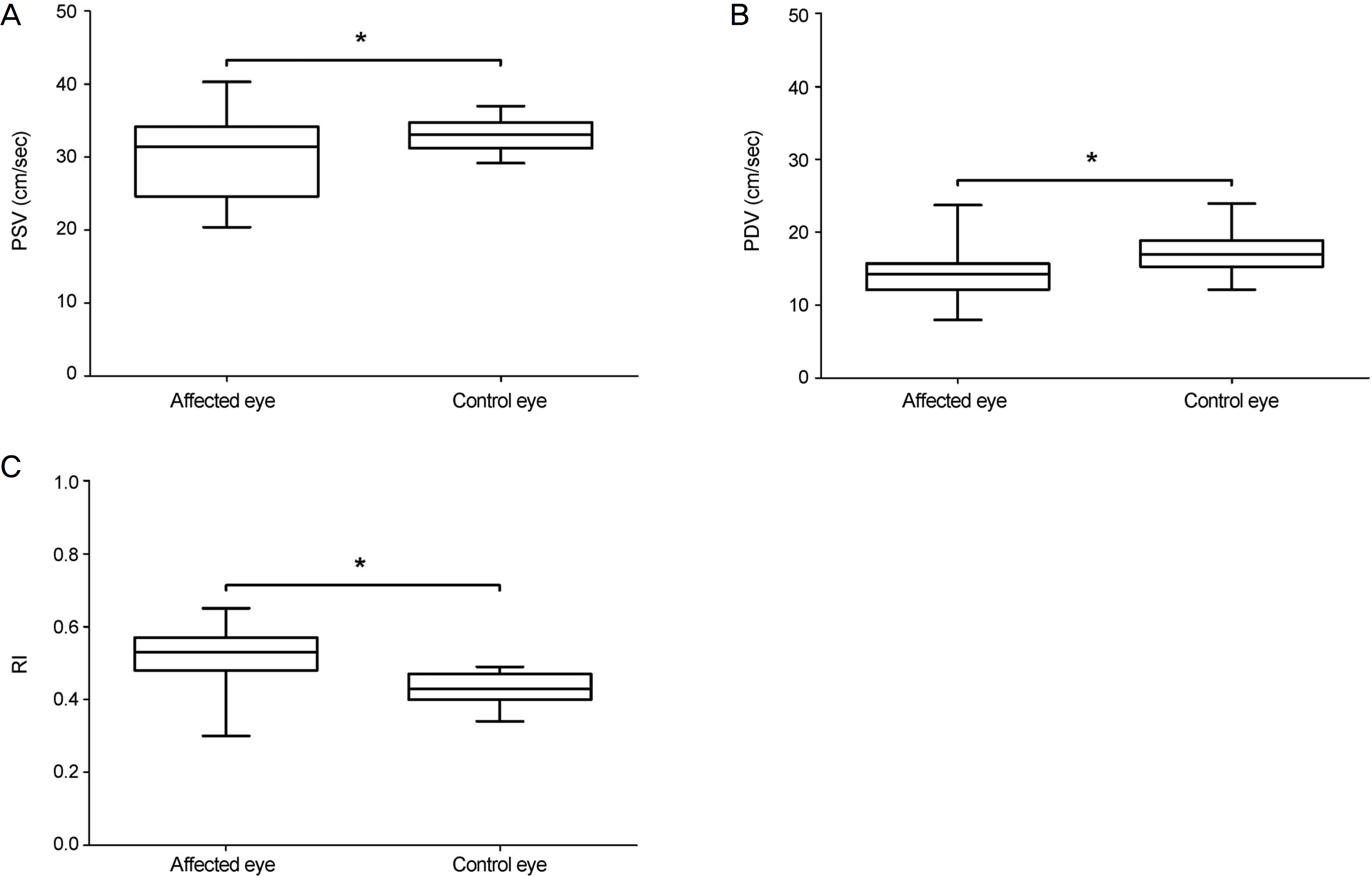 | Figure 1.Difference of ophthalmic artery Doppler variables between affected eye and control eye. (A) peak systolic velocity (PSV), (B) peak diastolic velocity (PDV), (C) RI. Note that 3 indices are significantly different (paired t-test). RI = resistive index ([PSV-PDV]/PSV). * p < 0.05. |
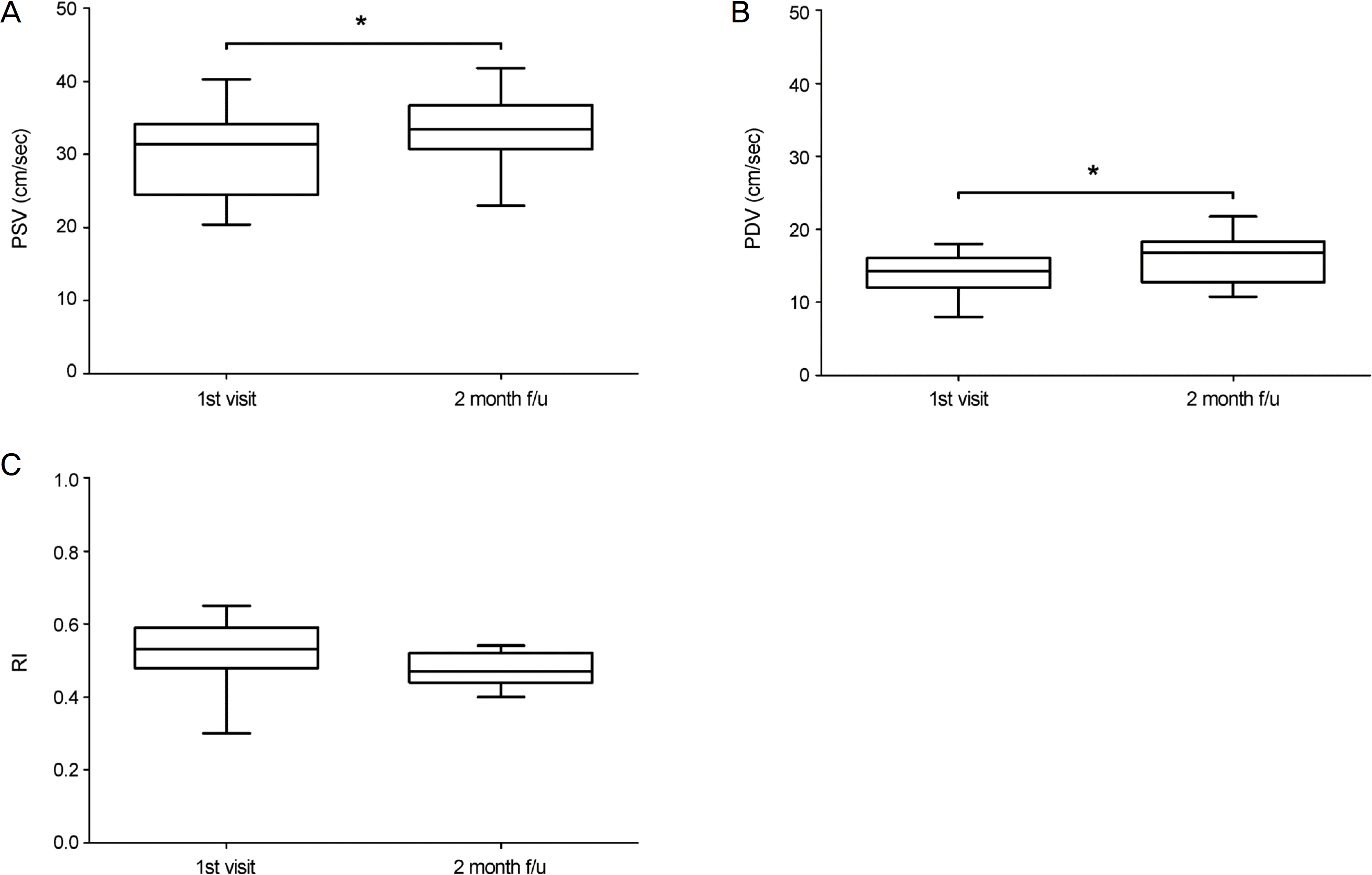 | Figure 2.Difference of ophthalmic artery Doppler variables of affected eyes between in 1st visit and 2 month follow up (f/u). (A) peak systolic velocity (PSV), (B) peak diastolic velocity (PDV), (C) RI. Note that 2 indices are significantly different (W ilcoxon signed rank test). RI = resistive index ([PSV-PDV]/PSV). * p < 0.05. |
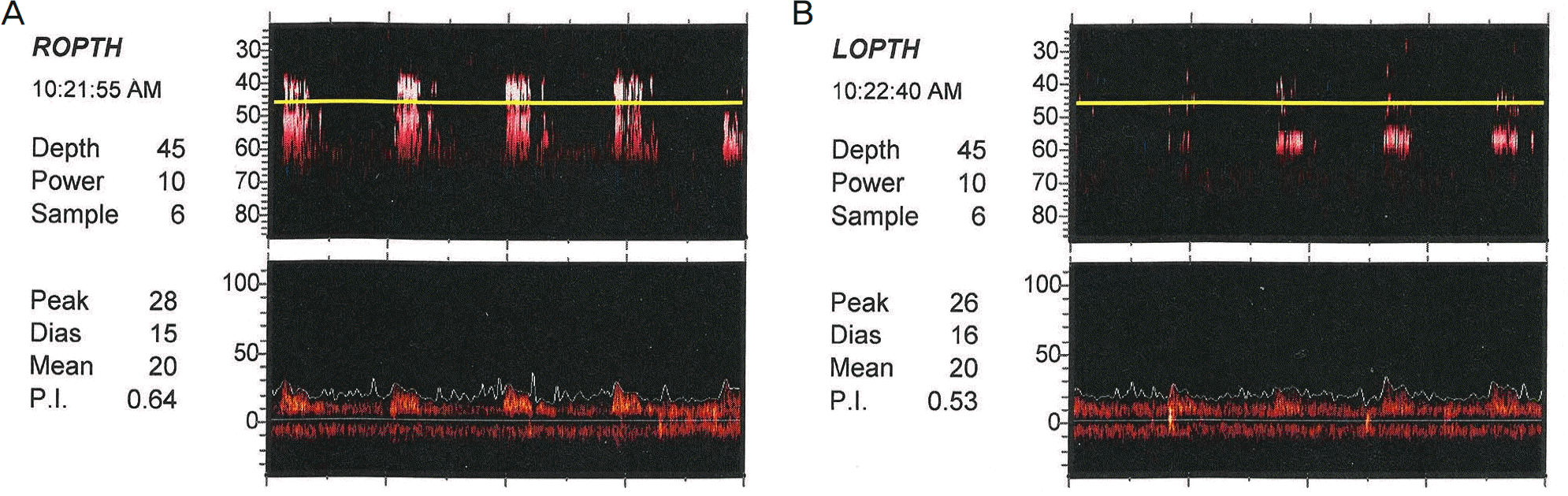 | Figure 3.Images obtained from a patient with central serous chorioretinopathy. Doppler spectra in the ophthalmic artery of a healthy control eye (A) and an affected eye (B). P.I. = pulsatility index. |
Table 1.
Ophthalmic artery Doppler variables of affected eyes and healthy control eyes
| Affected eyes | Control eyes | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSV (cm/sec) | 30.05 ± 5.34 | 33.03 ± 2.00 | 0.004 |
| PDV (cm/sec) | 14.07 ± 2.90 | 17.17 ± 2.76 | <0.001 |
| RI | 0.52 ± 0.08 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | <0.001 |
Table 2.
Ophthalmic artery Doppler variables of affected eyes in 1st visit and 2 month follow up
| 1st visit | 2 month follow up | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSV (cm/sec) | 30.32 ± 5.52 | 32.94 ± 6.24 | 0.031 |
| PDV (cm/sec) | 14.32 ± 3.06 | 15.54 ± 2.88 | 0.045 |
| RI | 0.52 ± 0.09 | 0.48 ± 0.04 | 0.073 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download