Abstract
Purpose
To assess the degree of agreement of two rotating Scheimpflug cameras, Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR, in measuring corneal refractive power (K), anterior chamber depth (ACD), and central corneal thickness (CCT).
Methods
Measurement agreement was assessed in 40 eyes of 40 outpatients at our hospital. Measurements of anterior and posterior corneal refractive power (K), ACD, and CCT were compared between the Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR.
Results
For Galilei G6 (4 mm), Pentacam HR (3 mm) and Pentacam HR (4 mm), the anterior corneal refractive powers (K) were 44.35 ± 1.38 D, 44.09 ± 1.32 D, and 44.12 ± 1.35 D, respectively, and the posterior corneal refractive powers (K) were 6.39 ±0.23 D, 6.45 ± 0.23 D, 6.45 ±0.22 D. The differences in the results were statistically significant. The average ACD measurements using Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR were 3.26 ± 0.42 mm and 3.17 ± 0.42 mm, respectively, and the average CCT measurements were 556.65 ± 30.12 µm and 553.78 ± 29.42 µm. The differences in the measurements were statistically significant. In addition, ACD 95% limits of agreement (LoA) between Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR were in the range of −0.14∼0.32 mm, and CCT 95% LoA were in the range of −12.54∼18.29 µm.
Go to : 
References
1. Ou RJ, Shaw EL, Glasgow BJ. Keratectasia after laser in situ abdominal (LASIK): evaluation of the calculated residual stromal bed thickness. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 134:771–3.
2. Youn SM, Lim SH, Lee HY. Measurement comparison of anterior segment parameters between AL-Scan(R) and Pentacam(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:801–8.
3. Chen D, Lam AK. Intrasession and intersession repeatability of the Pentacam system on posterior corneal assessment in the normal human eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:448–54.

4. Patel RP, Pandit RT. Comparison of anterior chamber depth abdominals from the Galilei Dual Scheimpflug Analyzer with IOLMaster. J Ophthalmol. 2012; 2012:430249.
5. Aramberri J, Araiz L, Garcia A, et al. Dual versus single abdominal camera for anterior segment analysis: precision and abdominal. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:1934–49.
6. Anayol MA, Güler E, Yağ ci R, et al. Comparison of central corneal thickness, thinnest corneal thickness, anterior chamber depth, and simulated keratometry using Galilei, Pentacam, and Sirius abdominal. Cornea. 2014; 33:582–6.
7. Domínguez-Vicent A, Monsálvez-Romín D, Águila-Carrasco AJD, et al. Measurements of anterior chamber depth, white-to-white distance, anterior chamber angle, and pupil diameter using two Scheimpflug imaging devices. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2014; 77:233–7.

8. Han SH, Hwang HS, Shin MC, Han KE. Comparison of central corneal thickness and anterior chamber depth measured using three different devices. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:694–701.

9. Hernández-Camarena JC, Chirinos-Saldaña P, Navas A, et al. Repeatability, reproducibility, and agreement between three abdominal Scheimpflug systems in measuring corneal and anterior abdominal biometry. J Refract Surg. 2014; 30:616–21.
10. Lee JW, Park SH, Seong MC, et al. Comparison of ocular biometry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients between Galilei-G6(R) and IOL Master(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:515–20.
11. Savini G, Carbonelli M, Barboni P, Hoffer KJ. Repeatability of automatic measurements performed by a dual Scheimpflug analyzer in unoperated and post-refractive surgery eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:302–9.

12. Cı nar Y, Cingü AK, Sahin M, et al. Comparison of optical versus abdominal biometry in keratoconic eyes. J Ophthalmol. 2013; 2013:481238.
13. Saad E, Shammas MC, Shammas HJ. Scheimpflug corneal power measurements for intraocular lens power calculation in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:460–7.e2.

14. Crawford AZ, Patel DV, McGhee CN. Comparison and abdominal of keratometric and corneal power measurements obtained by Orbscan II, Pentacam, and Galilei corneal tomography systems. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:53–60.
15. Engren AL, Behndig A. Anterior chamber depth, intraocular lens position, and refractive outcomes after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:572–7.

16. Miyake T, Shimizu K, Kamiya K. Distribution of posterior corneal astigmatism according to axis orientation of anterior corneal astigmatism. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0117194.

17. Salouti R, Nowroozzadeh MH, Zamani M, et al. Comparison of abdominal and posterior elevation map measurements between 2 abdominal imaging systems. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:856–62.
18. Menassa N, Kaufmann C, Goggin M, et al. Comparison and abdominal of corneal thickness and curvature readings obtained by the Galilei and the Orbscan II analysis systems. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1742–7.
Go to : 
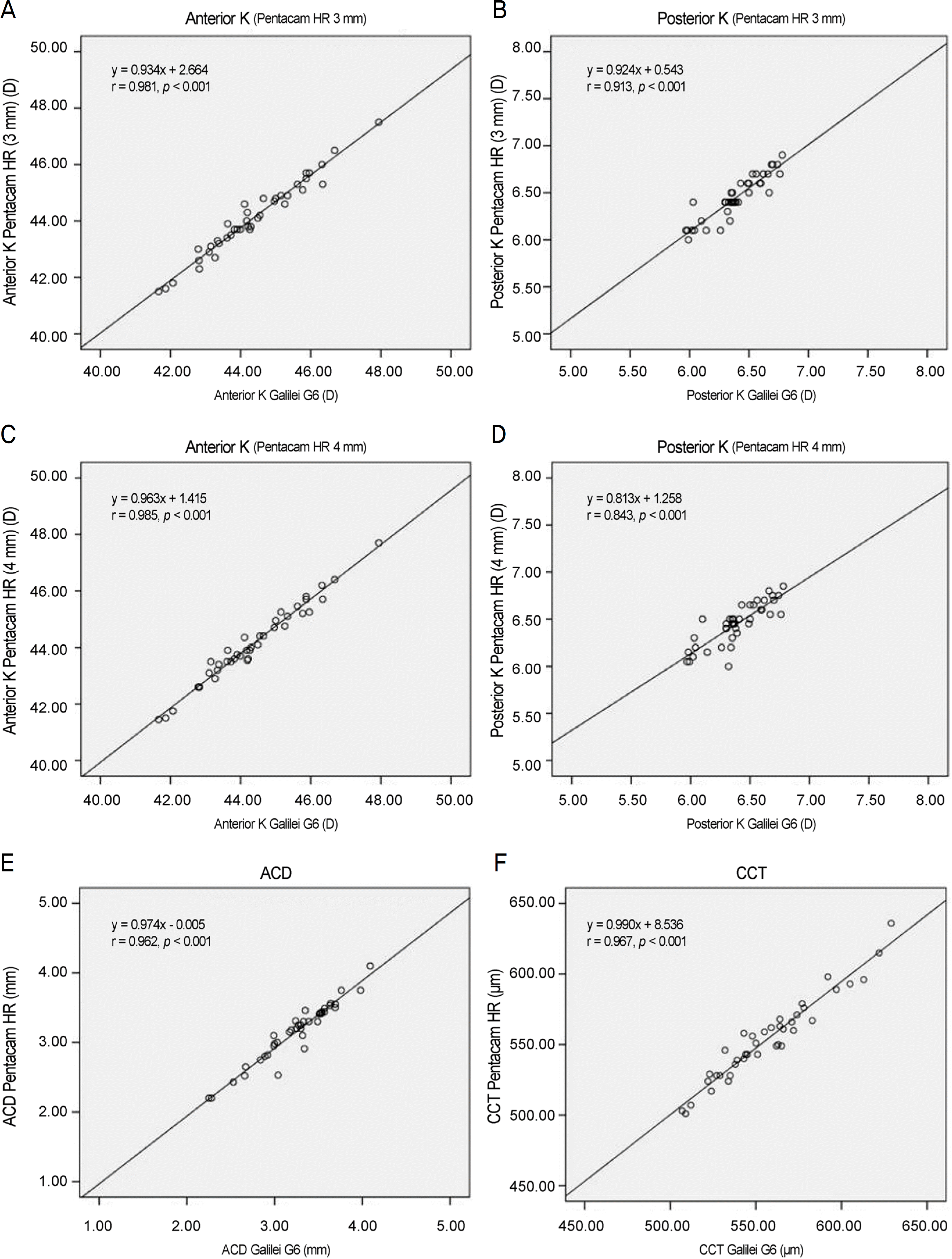 | Figure 1.Pearson correlation of Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR in anterior segment parameters. (A) Anterior mean keratometric diopter (K mean) (Pentacam HR 3 mm), (B) Posterior K mean (Pentacam HR 3 mm), (C) Anterior K mean (Pentacam HR 4 mm), (D) Posterior K mean (Pentacam HR 4 mm), (E) anterior chamber depth (ACD), (F) central corneal thickness (CCT). K = keratometric diopter. |
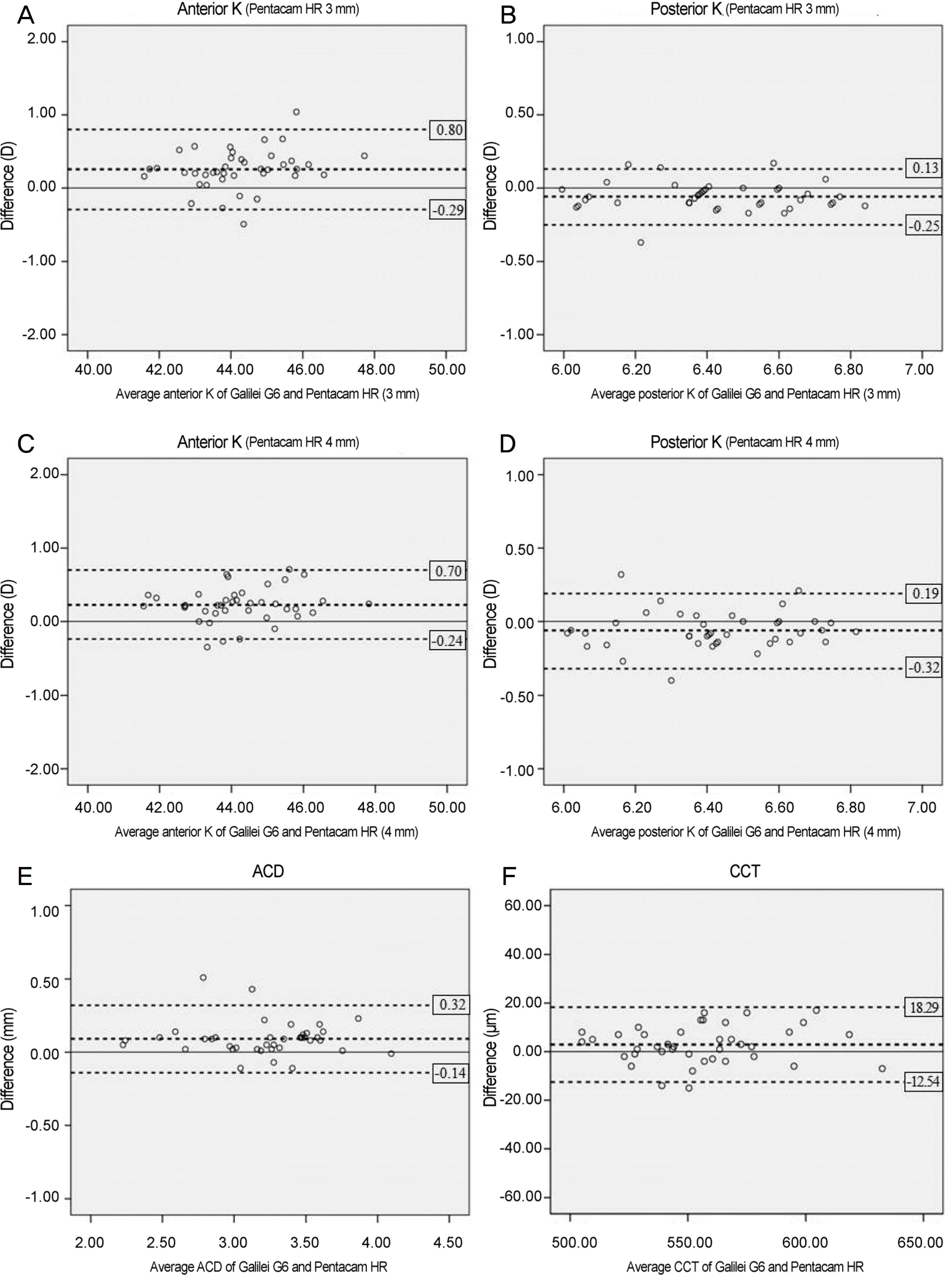 | Figure 2.Bland-Altman plots of Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR in anterior segment parameters. (A) Anterior mean keratometric diopter (K mean) (Pentacam HR 3 mm), (B) Posterior K mean (Pentacam HR 3 mm), (C) Anterior K mean (Pentacam HR 4 mm), (D) Posterior K mean (Pentacam HR 4 mm), (E) anterior chamber depth (ACD), (F) central corneal thickness (CCT). K = keratometric diopter. |
Table 1.
Patient demographics
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| No. of eyes (patients) | 40 (40) |
| Age (years) | 62.28 ± 10.20 |
| Sex (male:female) | 13:27 |
| Laterality (right:left) | 17:23 |
| Spherical equivalent (D) | –0.12 ± 2.22 |
Table 2.
Comparison of corneal refractive power (K) measured by Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR
|
Anterior corneal surface |
Posterior corneal surface |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kmean (D) | Difference (D) | p-value* | Kmean (D) | Difference (D) | p-value* | |
| Galilei G6 (4 mm) | 44.35 ± 1.38 | 6.39 ± 0.23 | ||||
| Pentacam HR (3 mm) | 44.09 ± 1.32 | 0.26 ± 0.27† | <0.001 | 6.45 ± 0.23 | –0.06 ± 0.10† | <0.001 |
| Pentacam HR (4 mm) | 44.12 ± 1.35 | 0.23 ± 0.23‡ | <0.001 | 6.45 ± 0.22 | –0.06 ± 0.13‡ | 0.004 |
Table 3.
Comparison of anterior chamber depth (ACD) and central corneal thickness (CCT) measured by Galilei G6 and Pentacam HR
| Galilei G6 | Pentacam HR | Difference | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACD (mm) | 3.26 ± 0.42 | 3.17 ± 0.42 | 0.09 ± 0.12 | <0.001 |
| CCT (µm) | 556.65 ± 30.12 | 553.78 ± 29.42 | –2.88 ± 7.71 | 0.023 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download