Abstract
Purpose
To determine the risk factors and incidence of cataract formation over a long-term mean follow-up of 7.5 years after type V4 implantable collamer lens (ICL) implantation.
Methods
We analyzed the preoperative, 3-month postoperative, 3-year postoperative, and last follow-up data of 228 eyes (118 patients) with mean preoperative spherical equivalent of -12.7 D and minimum postoperative follow-up of 3 years. Additionally, we determined the risk factors for cataract formation and calculated the 10.3 year cumulative cataract formation rate and 10.3 year cumulative cataract surgery rate using a survival curve.
Results
After type V4 ICL implantation with minimum follow-up of 3 years, the calculated 10.3 year cumulative cataract formation rate was 20% and actual cataracts developed in 34 eyes (14.9%). The 10.3 year cumulative cataract surgery rate was 12% based on a survival curve and actual cataract surgery was performed in 12 eyes (5.3%). The risk factors for cataract formation were age (odds ratio [OR] = 1.10, p = 0.00), preoperative spherical equivalent (OR = 0.90, p = 0.00), crystalline lens thickness (OR = 9.54, p = 0.00), axial length (OR = 1.33, p = 0.00), 3 months postoperative vault (OR = 0.50, p = 0.03), and existence of peripheral touch between ICL optic margin and crystalline lens at last follow-up (OR = 7.84, p = 0.00).
Go to : 
References
1. Sanders DR, Vukich JA, Doney K, et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration clinical trial of the implantable contact lens for moderate to high myopia. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:255–66.

2. Sanders DR, Doney K, Poco M; ICL in Treatment of Myopia Study Group. United States Food and Drug Administration clinical trial of the Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) for moderate to high myopia: three-year follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1683–92.
3. Alfonso JF, Baamonde B, Fernández-Vega L, et al. Posterior chamber collagen copolymer phakic intraocular lenses to correct myopia: five-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:873–80.

4. Fernandes P, González-Méijome JM, Madrid-Costa D, et al. Implantable collamer posterior chamber intraocular lenses: a review of potential complications. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:765–76.

5. Jiménez-Alfaro I, Benítez del Castillo JM, García-Feijoó J, et al. Safety of posterior chamber phakic intraocular lenses for the correction of high myopia: anterior segment changes after posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:90–9.
6. Pérez-Santonja JJ, Iradier MT, Benítez del Castillo JM, et al. Chronic subclinical inflammation in phakic eyes with intraocular lenses to correct myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:183–7.

7. Sanders DR. Anterior subcapsular opacities and cataracts 5 years after surgery in the visian implantable collamer lens FDA trial. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:566–70.

8. Sanders DR; ICL in Treatment of Myopia Study Group. Postoperative inflammation after implantation of the implantable contact lens. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:2335–41.

9. Hoffer KJ. Ultrasound axial length measurement in biphakic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:961–5.

10. Sanders DR, Vukich JA; ICL in Treatment of Myopia (ITM) Study Group. Incidence of lens opacities and clinically significant cataracts with the implantable contact lens: comparison of two lens designs. J Refract Surg. 2002; 18:673–82.

11. Kubo E, Kumamoto Y, Tsuzuki S, Akagi Y. Axial length, myopia, and the severity of lens opacity at the time of cataract surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:1586–90.

12. Jeon S, Kim HS. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of cataract surgery in highly myopic Koreans. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:84–9.

13. Younan C, Mitchell P, Cumming RG, et al. Myopia and incident cataract and cataract surgery: the blue mountains eye study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43:3625–32.
14. Wong TY, Klein BE, Klein R, et al. Refractive errors and incident cataracts: the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001; 42:1449–54.
15. Leske MC, Wu SY, Nemesure B, et al. Risk factors for incident nuclear opacities. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1303–8.

16. Khalifa YM, Moshirfar M, Mifflin MD, et al. Cataract development associated with collagen copolymer posterior chamber phakic intraocular lenses: clinicopathological correlation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1768–74.

17. Fujisawa K, Shimizu K, Uga S, et al. Changes in the crystalline lens resulting from insertion of a phakic IOL (ICL) into the porcine eye. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007; 245:114–22.

18. Kawamorita T, Uozato H, Shimizu K. Fluid dynamics simulation of aqueous humour in a posterior-chamber phakic intraocular lens with a central perforation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:935–9.

19. Uozato H, Shimizu K, Kawamorita T, Ohmoto F. Modulation transfer function of intraocular collamer lens with a central artifi-cial hole. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011; 249:1081–5.

20. Maeng HS, Chung TY, Lee DH, Chung ES. Risk factor evaluation for cataract development in patients with low vaulting after phakic intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:881–5.

21. Gonvers M, Bornet C, Othenin-Girard P. Implantable contact lens for moderate to high myopia: relationship of vaulting to cataract formation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:918–24.
22. Schmidinger G, Lackner B, Pieh S, Skorpik C. Long-term changes in posterior chamber phakic intraocular collamer lens vaulting in myopic patients. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:1506–11.

23. de Castro A, Siedlecki D, Borja D, et al. Age-dependent variation of the Gradient Index profile in human crystalline lenses. Journal of Modern Optics. 2011; 58:1781–7.

24. Nongpiur ME, He M, Amerasinghe N, et al. Lens vault, thickness, and position in Chinese subjects with angle closure. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:474–9.

25. Oh WH, Kim TW, Park KH, Kim DM. Location of the tube tip in the anterior chamber and change in corneal endothelium after Ahmed valve implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:469–74.

26. Takahashi A, Ito Y, Iguchi Y, et al. Axial length increases and related changes in highly myopic normal eyes with myopic complications in fellow eyes. Retina. 2012; 32:127–33.

27. Olsen T, Jeppesen P. The incidence of retinal detachment after cataract surgery. Open Ophthalmol J. 2012; 6:79–82.

28. Ripandelli G, Scassa C, Parisi V, et al. Cataract surgery as a risk factor for retinal detachment in very highly myopic eyes. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:2355–61.

29. Williams MA, McGimpsey S, Abugreen S, et al. The incidence and rate of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment seven years after cataract surgery in patients with high myopia. Ulster Med J. 2009; 78:99–104.
30. Colin J, Robinet A, Cochener B. Retinal detachment after clear lens extraction for high myopia: seven-year follow-up. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2281–4. discussion 2285.
Go to : 
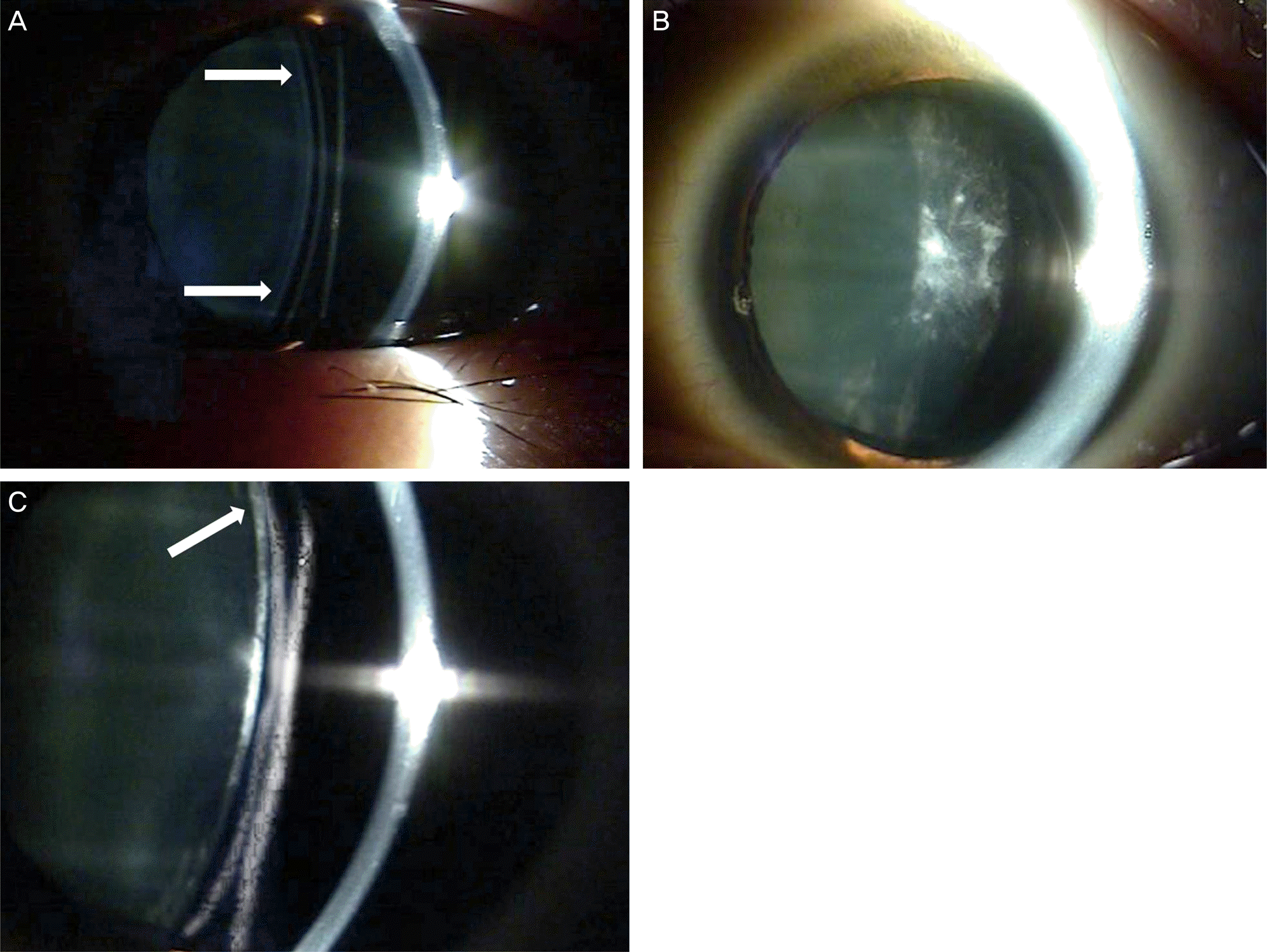 | Figure 1.Superior or inferior peripheral crystalline lenticular touch by superior or inferior periphery of implantable collamer lens (ICL). (A) The arrows indicate the superior or inferior periphery of ICL is not touching the crystalline lens and there is no cataract formation. (B) It shows visually significant anterior subcapsular opacity. (C) The same eye with (B) shows the superior periphery of ICL is touching the crystalline lens (arrow). |
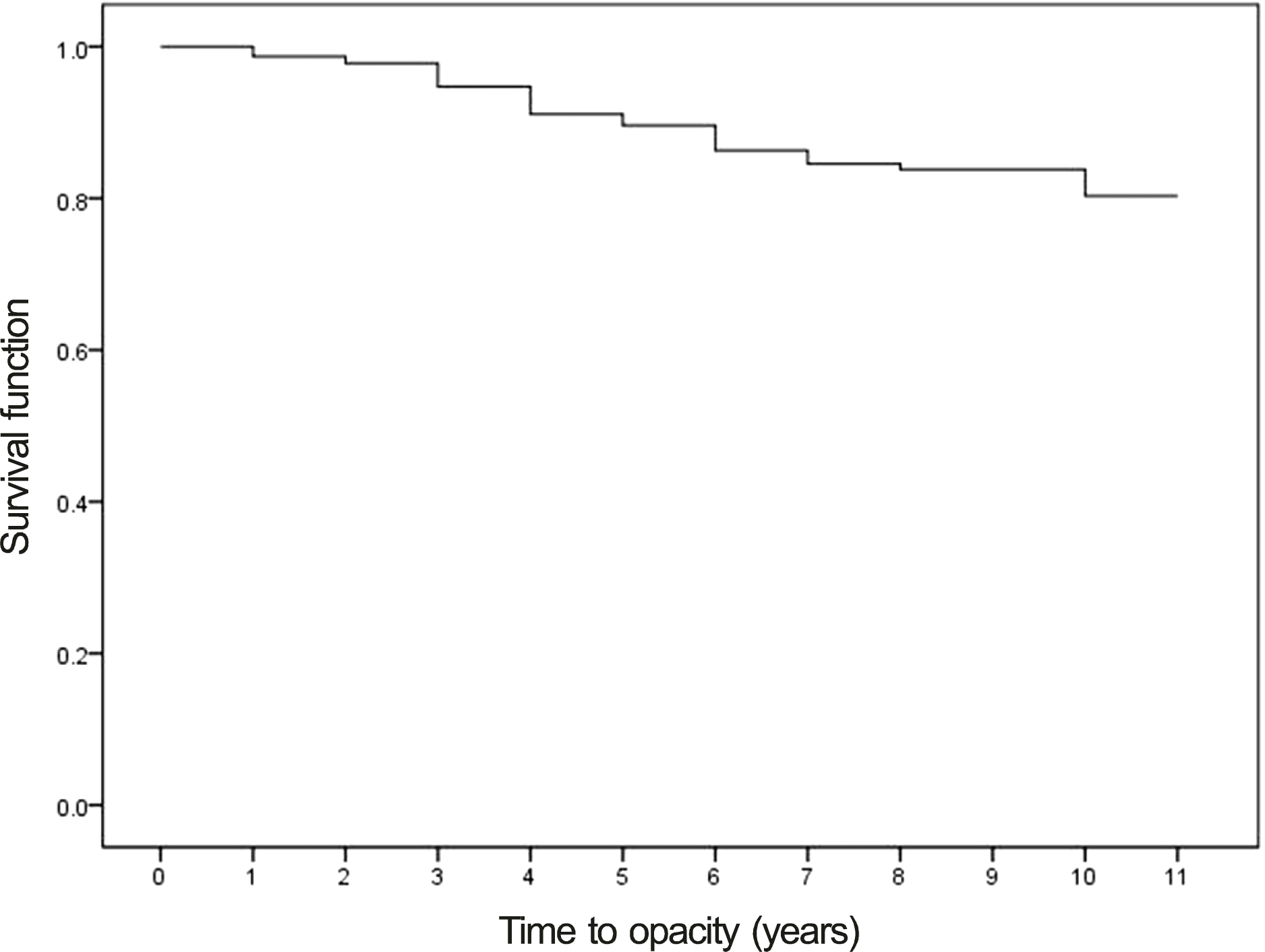 | Figure 2.Life table for cataract formation after implantable collamer lens (ICL) implantation. The moments when the initial cataract developed in group A or B patients after ICL implantation were regarded as “censored” in this survival curve. |
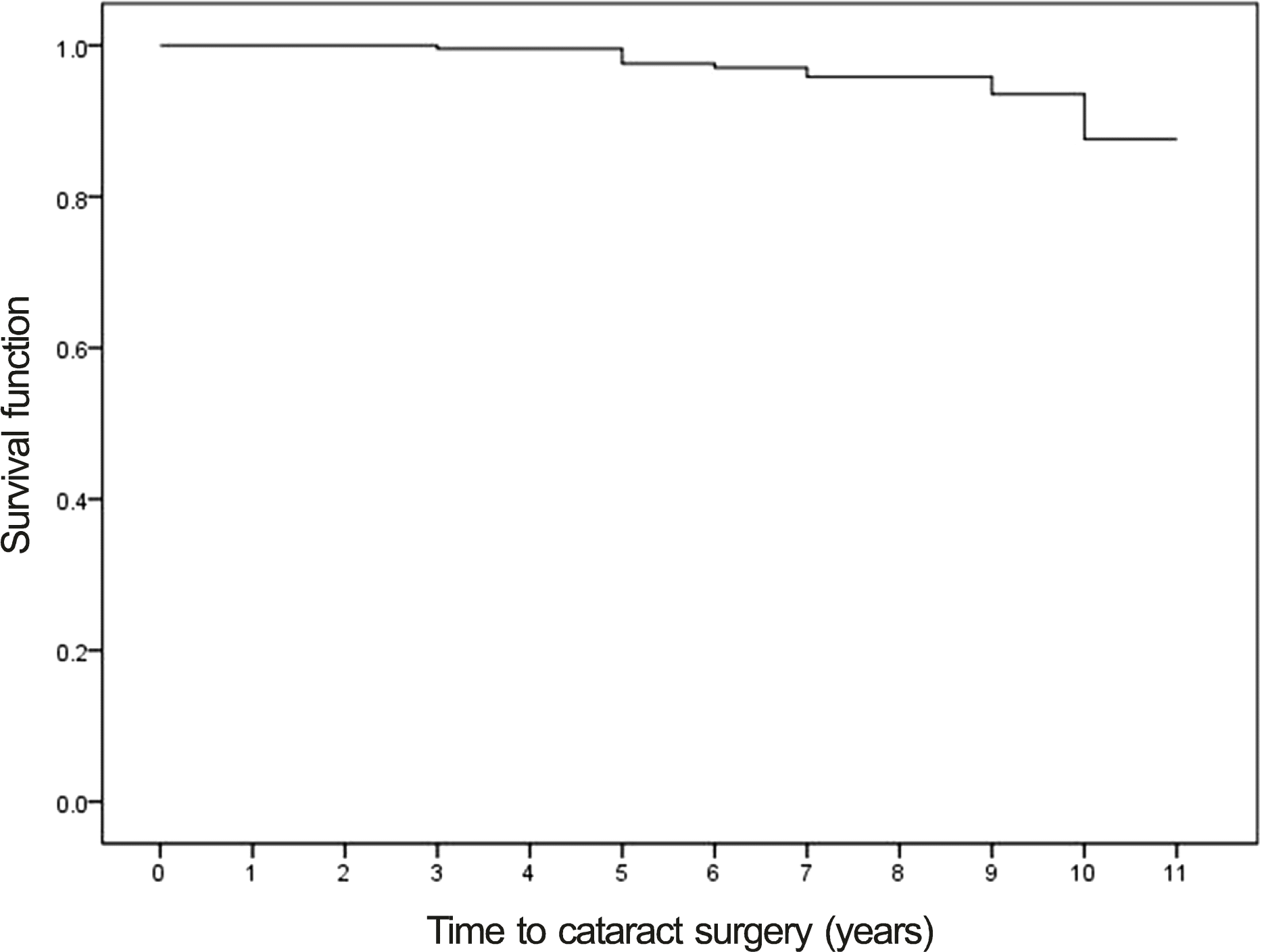 | Figure 3.Life table for cataract surgery after implantable collamer lens (ICL) implantation. The moments when the patients in group A underwent cataract surgery were regarded as “censored” in this survival curve. |
Table 1.
Preoperative patient demographics
Values are presented as mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated. Age = age at implantable collamer lens implantation; SE = spherical equivalent; IOP = intraocular pressure; LT = crystalline lens thickness; ACD = anterior chamber depth; AXL = axial length; WWD = white to white diameter measured with caliper; CCT = central corneal thickness; BCVA = best corrected visual acuity; UCVA = uncorrected visual acuity.
Table 2.
Time to develop initial late onset cataract*
| Time to initial cataract (years) | Range (years) | |
|---|---|---|
| Group A (n = 13) | 2.6 ± 2.0 | 0.3-4.5 |
| Group B (n = 21) | 4.7 ± 1.3 | 0.9-9.1 |
Table 3.
Patterns of cataract after ICL implantation (number of eyes)
| ASCO only | PSCO only | NS only | ASCO + PSCO | ASCO + NS | ASCO +NS + PSCO | NS + PSCO | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | 4 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 13 |
| Group B | 10 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 21 |
Table 4.
Touch between ICL optic periphery and crystalline lens at last follow up*
| Group A (n = 13) | Group B (n = 21) | Group C (n = 194) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of eyes (%) | 6 (46) | 2 (10) | 4 (2) |
Table 5.
Risk factors for cataract formation after ICL implantation by univariate Cox’s propotional hazards
| Parameter | Group A + B (34 eyes)(Cataract group) | Group C (194 eyes)(No cataract group) | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 38.0 ± 8.3 | 29.8 ± 7.6 | 1.10 (1.06-1.14) | 0.00 |
| Preoperative SE (diopters) | -15.2 ± 4.6 | -12.2 ± 4.2 | 0.90 (0.84-0.96) | 0.00 |
| Preoperative LT (mm) | 3.92 ± 0.36 | 3.71 ± 0.26 | 9.54 (3.19-28.51) | 0.00 |
| Preoperative AXL (mm) | 29.2 ± 1.70 | 27.9 ± 1.84 | 1.33 (1.13-1.57) | 0.00 |
| Vault 3m (CCT) | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.50 (0.27-0.94) | 0.03 |
| (range 0-3.0) | (range 0.3-4.0) | |||
| Last peripheral touch* (eyes) | 8/34 (24%) | 4/194 (2%) | 7.84 (3.53-17.39) | 0.00 |
Table 6.
Comparison of crystalline lens thickness between cataract group and no cataract group*
| Group A + B (Cataract group) | Group C (No cataract group) | |
|---|---|---|
| Preoperative LT >4 mm (eyes) | 13 (38) | 23 (12) |
|
Preoperative LT ≤4 mm (eyes) |
21 (62) |
171 (88) |
| Total | 34 (100) | 194 (100) |
Table 7.
Comparison of age between cataract group and no cataract group in eyes with thick crystalline lens*
| Group A + B (Cataract group) | Group C (No cataract group) | |
|---|---|---|
| Preoperative LT >4 mm, Age ≤35 (eyes) | 2 (15) | 11 (48) |
|
Preoperative LT >4 mm, Age >35 (eyes) |
11 (85) |
12 (52) |
| Total | 13 (100) | 23 (100) |
Table 8.
Risk factors for clinically significant cataract formation by univariate Cox’s propotional hazards
| Parameter | Group A (13 eyes) | Group B (21 eyes) | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vault 3mo (CCT) | 0.9 ± 0.3 (range 0.4-1.3) | 1.5 ± 0.7 (range 0-3.0) | 0.29 (0.11-0.75) | 0.01 |
| Last peripheral touch* (eyes) | 6/13 (46%) | 2/21 (10%) | 4.19 (1.27-13.79) | 0.02 |
Table 9.
Changes of postoperative values over time after ICL implantation
Table 10.
Adverse events after ICL implantation
| Adverse event | No. of eyes |
|---|---|
| Retinal detachment | 2 (0.9) |
| Myopic CNV | 3 (1.3) |
| Pigment dispersion glaucoma | 2 (0.9) |
| Turbid ICL | 2 (0.9) |
|
Immediate postoperative sterile hypopyon |
2 (0.9) |
| Total | 11 (4.8) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download