초록
Purpose:
To determine the correlation between intraocular pressure (IOP) and the bottle heights during vitrectomy using TONO-PENⓇ XL applanation tonometer and IcareⓇ PRO rebound tonometer.
Methods:
Twenty-four eyes of 24 patients who underwent 23-gauge sutureless vitrectomy were evaluated. After complete vitrectomy, the IOP was gradually increased by lifting the irrigation bottle height from the trocar insertion site by 40 cm, 45 cm, 50 cm, and 55 cm. The distance between the floor and patient's eye was consistent in all cases (105.5 cm). Before the removal of 23-gauge microcannulas, IOP was measured five times using each of the two methods, Tono-PenⓇ XL and IcareⓇ PRO.
Results:
The mean IOPs were 8.25 ± 0.35 mm Hg for TONO-PENⓇ XL and 8.96 ± 0.32 mm Hg for IcareⓇ PRO at 40 cm bottle height. As the bottle height increased, the differences in IOP was also increased, 10.71 ± 0.37 mm Hg at 45 cm, 14.18 ± 0.39 mm Hg at 50 cm and 17.93 ± 0.40 mm Hg at 55 cm for TONO-PENⓇ XL and 11.48 ± 0.31 mm Hg at 45 cm, 14.64 ± 0.31 mm Hg at 50 cm and 18.13 ± 0.38 mm Hg at 55 cm for IcareⓇ PRO. In TONO-PENⓇ XL, the linear equation was Y = 0.65 X - 18.108 (R2 = 0.794, p = 0.000) and the quadratic equation was Y = 0.013 X2 - 0.569 X + 10.446 (R2 = 0.801, p = 0.000). In IcareⓇ PRO, the linear equation was Y = 0.614 X - 15.842 (R2 = 0.820, p = 0.000) and the quadratic equation was Y = 0.010 X2 - 0.306 X + 5.688 (R2= 0.825, p = 0.000). The results show correlation of the quadratic equation was stronger than the linear equation in both tonometers.
Go to : 
References
1. Tranos P, Bhar G, Little B. Postoperative intraocular pressure spikes: the need to treat. Eye (Lond). 2004; 18:673–9.

2. Geijer C, Bill A. Effects of raised intraocular pressure on retinal, prelaminar, laminar, and retrolaminar optic nerve blood flow in monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1979; 18:1030–42.
3. Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Jimenez-Santos M, Saenz-Frances F, et al. Performance of the rebound, noncontact and Goldmann applanation tonometers in routine clinical practice. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011; 89:676–80.

4. Abraham LM, Epasinghe NC, Selva D, Casson R. Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann applanation tonometer by experienced and inexperienced tonometrists. Eye (Lond). 2008; 22:503–6.

5. Findl O, Strenn K, Wolzt M, et al. Effects of changes in intraocular pressure on human ocular haemodynamics. Curr Eye Res. 1997; 16:1024–9.

6. Sugiura Y, Okamoto F, Okamoto Y, et al. Ophthalmodynamometric pressure in eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy measured during pars plana vitrectomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:624–9.e1.

7. Okamoto F, Sugiura Y, Okamoto Y, et al. Measurement of ophthalmodynamometric pressure with the vented-gas forced-infusion system during pars plana vitrectomy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:4195–9.

8. Jonas JB. Retinal arterial collapse pressure in eyes with retinal arterial occlusive diseases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:589.

9. Jonas JB, Harder B. Ophthalmodynamometric differences between ischemic vs nonischemic retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:112–6.

10. Kim SH, Choi KS. Changes of intraocular pressure during experimental vitrectomy. Curr Eye Res. 2012; 37:698–703.

11. Liu J, He X. Corneal stiffness affects IOP elevation during rapid volume change in the eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50:2224–9.

12. Elsheikh A, Wang D, Brown M, et al. Assessment of corneal biomechanical properties and their variation with age. Curr Eye Res. 2007; 32:11–9.

13. Leiva M, Naranjo C, Peña MT. Comparison of the rebound tonometer (ICare) to the applanation tonometer (Tonopen XL) in nor-motensive dogs. Vet Ophthalmol. 2006; 9:17–21.
14. Nakamura M, Darhad U, Tatsumi Y, et al. Agreement of rebound tonometer in measuring intraocular pressure with three types of applanation tonometers. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:332–4.

Go to : 
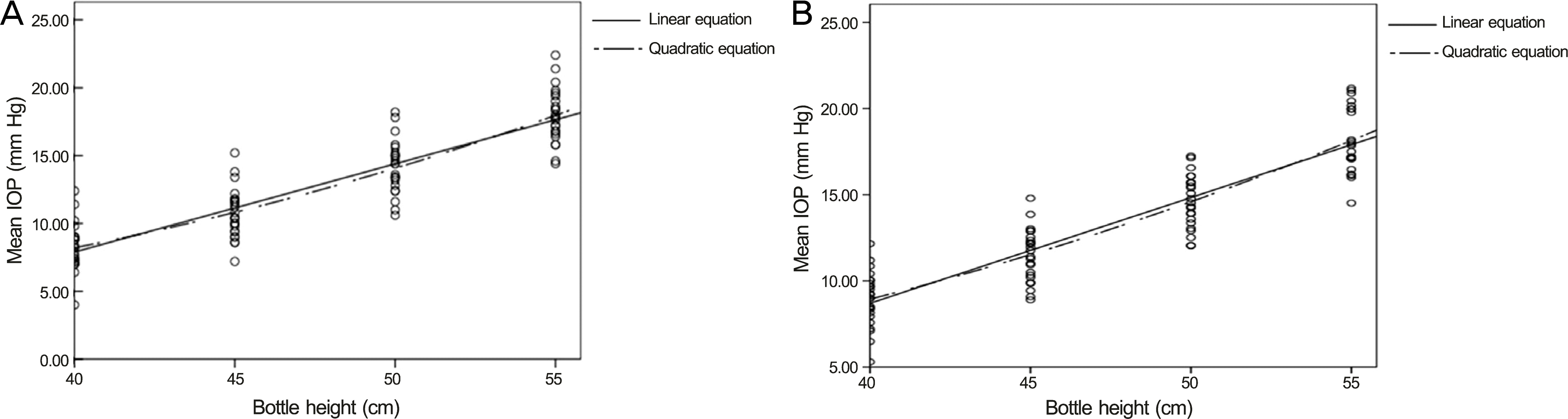 | Figure 1.Scatter plots showing intraocular pressure measurements with TONO-PENⓇ XL (A) and IcareⓇ PRO (B). In, nonlinear regression analysis, the correlation of quadratic equation is more stronger than that of the linear equation. In TONO-PENⓇ XL, the linear equation is Y = 0.65 X - 18.108 (R2 = 0.794, p = 0.000) and the quadratic equation is Y = 0.013 X2 - 0.569 X + 10.446 (R2= 0.801, p = 0.000). In IcareⓇ PRO, the linear equation is Y = 0.614 X - 15.842 (R2 = 0.820, p = 0.000) and the quadratic equation is Y = 0.010 X2 - 0.306 X + 5.688 (R2 = 0.825, p = 0.000). IOP = intraocular pressure. |
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of study subjects
Table 2.
Summary of mean IOP measurements and differences between the 2 methods




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download