초록
Purpose:
To investigate the efficacy and safety of intravitreal dexamethasone implant for controlling postoperative inflammation among uveitis patients undergoing cataract extraction.
Methods:
Ten eyes with noninfectious uveitis underwent phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation followed by intravitreal injection of 0.7-mg dexamethasone implant (implant group) between February 2011 and January 2014. Twenty age- and gender-matched controls who received cataract surgery without implantation during the same period were recruited (non-im-plant group). Medical records of the subjects were retrospectively reviewed and 6-month postoperative clinical outcomes were compared between the 2 groups.
Results:
The mean age was 42.30 15.81 years in the implant group and 45.65 13.63 years in the non-implant group. The 2 groups were similar in terms of age, gender, preoperative inflammatory status, and preoperative visual acuity ( p = 0.552, 1.000, 0.133 and 0.767, respectively). After surgery, oral steroid was used in the non-implant group (8.8 1.5 mg/day on average) and the implant group (3.5 1.3 mg/day; p = 0.029). Visual acuity (log MAR) improved significantly in both groups ( p = 0.789) with no significant difference between the 2 groups. Postoperative recurrence rates of uveitis were reduced more (40%) in the implant group than in the non-implant group (50%) but without significance ( p = 0.709). Elevated intraocular pressure ≥25 mm Hg occurred in 3 eyes (30%) in the implant group and 4 eyes (20%) in the non-implant group ( p = 0.657), of which 1 in each group re-quired a filtering surgery. Otherwise, no significant complications developed in either group.
Go to : 
References
1. Kim JC, Ham DI. Clinical characteristics and treatments of intermediate uveitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:85–91.

2. Foster CS, Fong LP, Singh G. Cataract surgery and intraocular lens implantation in patients with uveitis. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:281–8.

3. Krishna R, Meisler DM, Lowder CY, et al. Long-term follow-up of extracapsular cataract extraction and posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation in patients with uveitis. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:1765–9.

4. Okhravi N, Lightman SL, Towler HM. Assessment of visual outcome after cataract surgery in patients with uveitis. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:710–22.

5. Kim YW, Seo KY. The Results of Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery in Patients with Behcet's Disease. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1943–7.
6. Estafanous MF, Lowder CY, Meisler DM, Chauhan R. Phacoemulsification cataract extraction and posterior chamber lens implantation in patients with uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:620–5.

7. Ram J, Gupta A, Kumar S, et al. Phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation in patients with uveitis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1283–8.

8. Kosker M, Sungur G, Celik T, et al. Phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation in patients with anterior uveitis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1002–7.

9. Laurell CG, Zetterström C. Effects of dexamethasone, diclofenac, or placebo on the inflammatory response after cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:1380–4.

10. Foster CS, Rashid S. Management of coincident cataract and uveitis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2003; 14:1–6.

11. Han HC, Bang JW, Yum JH, et al. A case of acute endophthalmitis following a dexamethasone intravitreal implant. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1939–44.

12. Chang-Lin JE, Attar M, Acheampong AA, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a sustained-release dexamethasone intravitreal implant. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:80–6.

13. Holladay JT. Proper method for calculating average visual acuity. J Refract Surg. 1997; 13:388–91.

14. Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RB, Rosenbaum JT; Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group. Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the First International Workshop. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:509–16.
15. Okhravi N, Morris A, Kok HS, et al. Intraoperative use of intravitreal triamcinolone in uveitic eyes having cataract surgery: pilot study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1278–83.

16. Dada T, Dhawan M, Garg S, et al. Safety and efficacy of intraoperative intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide injection after phacoemulsification in cases of uveitic cataract. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1613–8.

17. Paganelli F, Cardillo JA, Melo LA Jr, et al. A single intraoperative subTenon's capsule triamcinolone acetonide injection for the treatment of post-cataract surgery inflammation. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:2102–8.

18. Chang DT, Herceg MC, Bilonick RA, et al. Intracameral dexamethasone reduces inflammation on the first postoperative day after cataract surgery in eyes with and without glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2009; 3:345–55.

19. Chieh JJ, Carlson AN, Jaffe GJ. Combined fluocinolone acetonide intraocular delivery system insertion, phacoemulsification, and intraocular lens implantation for severe uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 146:589–94.

20. Gupta A, Ram J, Gupta A, Gupta V. Intraoperative dexamethasone implant in uveitis patients with cataract undergoing phacoemulsification. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2013; 21:462–7.

21. van Kooij B, Rothova A, de Vries P. The pros and cons of intravitreal triamcinolone injections for uveitis and inflammatory cystoid macular edema. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2006; 14:73–85.

22. Ram J, Kaushik S, Brar GS, et al. Phacoemulsification in patients with Fuchs' heterochromic uveitis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1372–8.

Go to : 
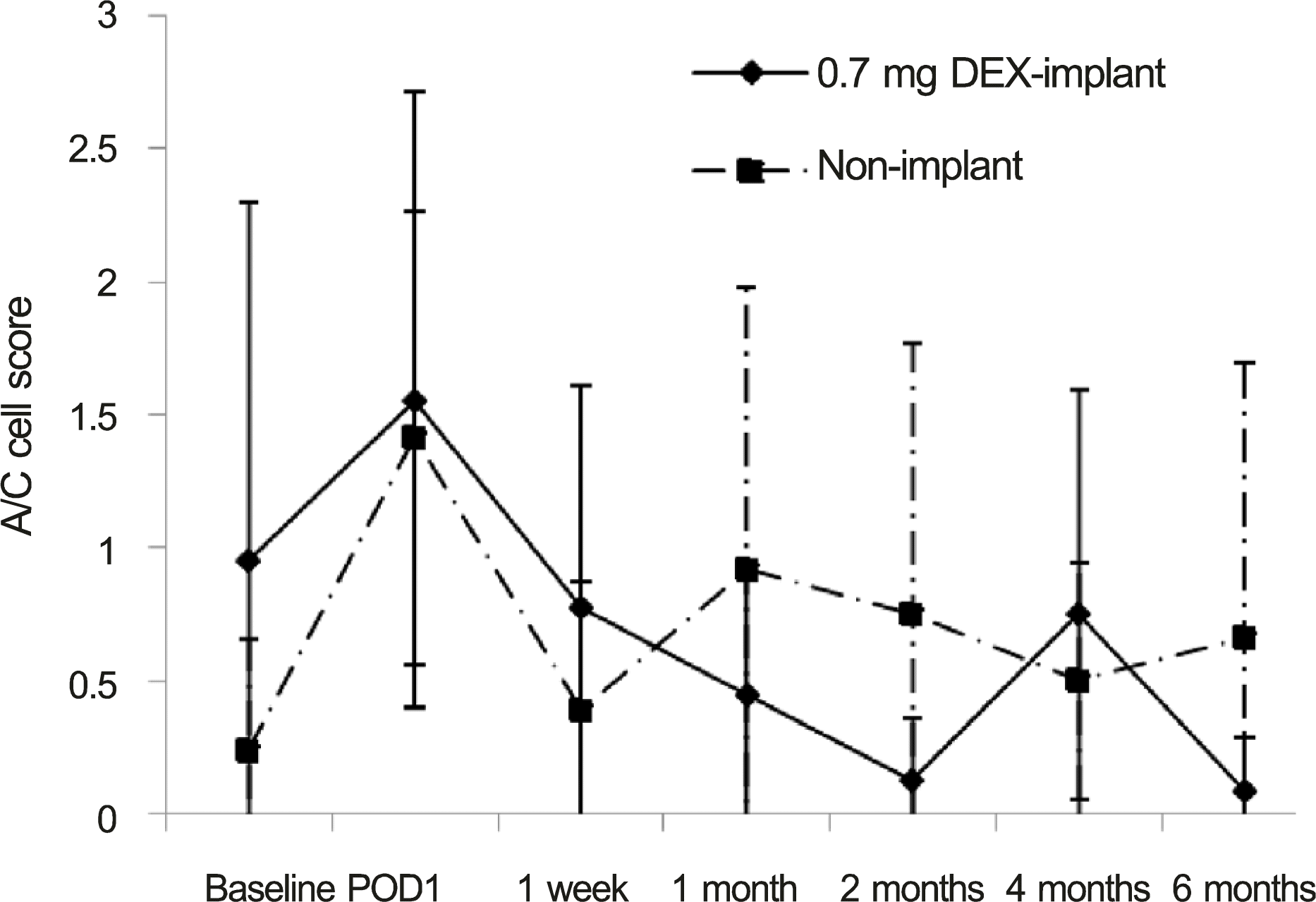 | Figure 1.Uveitis activity presented as anterior chamber cell grade before and after cataract surgery between 0.7 mg dex-amehasone implant and non-implant group. No significant differences are found at all points. A/C = anterior chamber; DEX = dexamethasone; POD = postoperative day. |
 | Figure 2.Systemic steroid dose before and after cataract surgery with independent-samples t-test. (A) Preoperative dose. (B) Postoperative dose. No significant differences are found before surgery ( p = 0.136). Significant differences are found after surgery ( p = 0.029). |
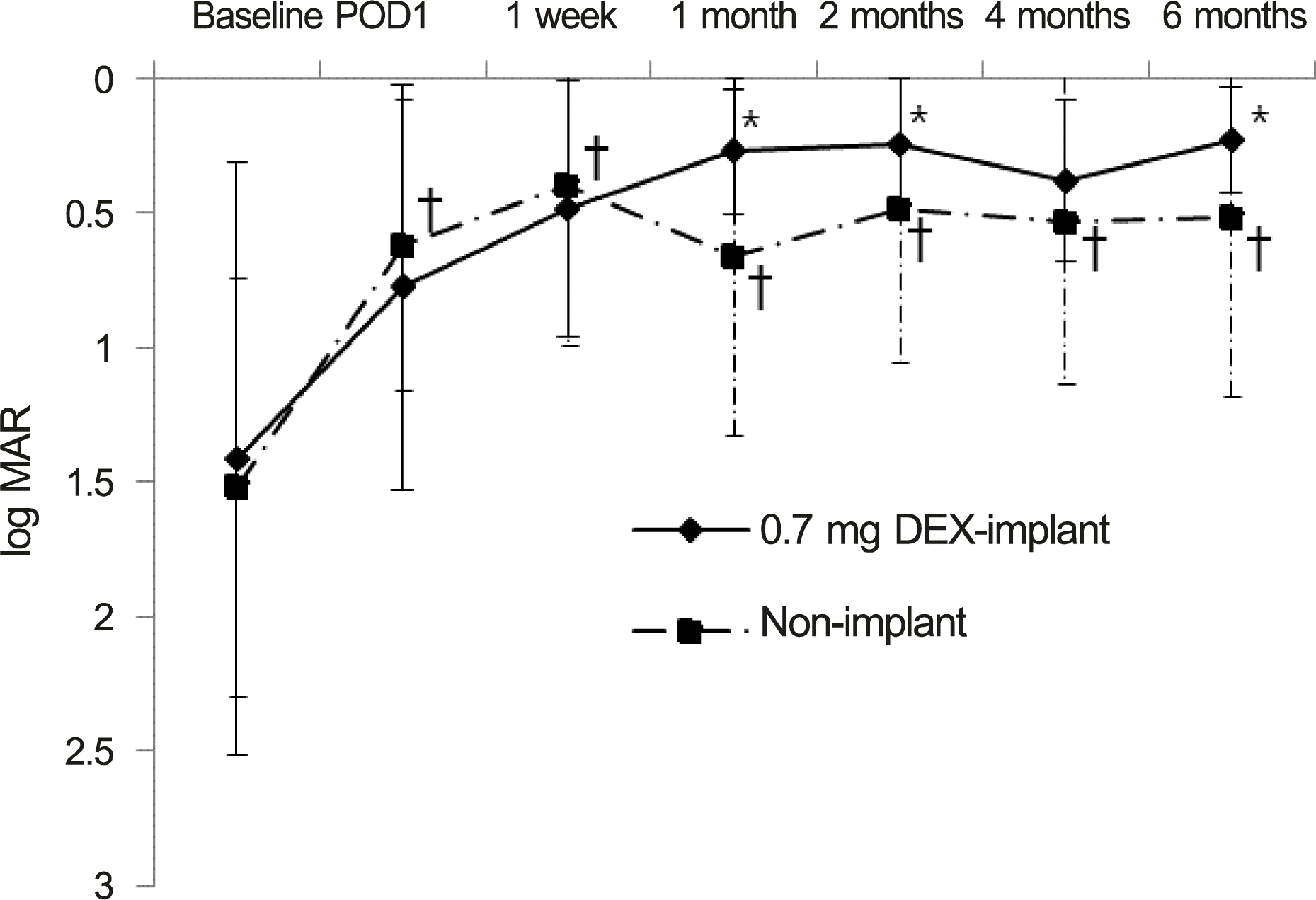 | Figure 3.Consecutive changes of visual acuities (log MAR) after cataract surgery in patients with noninfectious uveitis. Visual acuities were improved significantly with Bonferroni correction in both groups. POD =postoperative day; DEX = dexamethasone. * p < 0.05 compared to baseline visual acuity of DEX-implant group; †p < 0.05 compared to baseline visual acuity of Non-implant group. |
Table 1.
Demographics and diagnosis of uveitis patients who underwent cataract extraction surgery
| 0.7 mg DEX-implant group (n = 10) | Non-implant group (n = 20) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age* | 42.30 ± 15.81 | 45.65 ± 13.63 | 0.552 |
| Sex (M:F)† | 6:4 | 12:8 | 1.000 |
| Diagnosis | |||
| Behcet’s disease | 5 | 13 | |
| Ankylosing spodylitis | 0 | 1 | |
| Juvenile rheumatic arthritis | 1 | 0 | |
| Idiopathic | 4 | 6 |
Table 2.
Results of postoperative steroid injection in uveitis patients undergoing cataract surgery




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download