초록
Purpose:
To compare pain levels in cataract surgery under topical anesthesia only and topical anesthesia under monitored anesthesia care.
Methods:
We recruited 243 patients who were scheduled to undergo cataract surgery under topical anesthesia only or topical anesthesia with monitored anesthesia care (MAC) using fentanyl and midazolam. Anesthesia methods were selected based on the patient’s preference. All patients completed an anxiety and information scale survey preoperatively. Vital signs during the operations were recorded. A 0-to-10 visual analog scale pain score survey was conducted immediately and at 2 hours, 6 hours, and 1 day after surgery.
Results:
Of the 237 patients who completed the study, 183 patients selected topical anesthesia, and 54 patients selected MAC. Mean pain scores according to the aforementioned time points after surgery were 0.50, 0.58, 0.29, and 0.12 in the topical anesthesia group, and 0.22, 0.16, 0.06, and 0.09 in the MAC group, respectively. The differences in pain score between the two groups was statistically significant at 2 hours ( p = 0.019) and 6 hours ( p = 0.040) after surgery. The mean patient anxiety score for anesthesia was 10.50 in the topical anesthesia group and 11.41 in the MAC group ( p = 0.280). Mean systolic blood pressure at the start of surgery was 140.6 mm Hg in the topical anesthesia group, and 158.2 mmHg in the MAC group.
Go to : 
References
1. Apil A, Kartal B, Ekinci M, et al. Topical anesthesia for cataract surgery: the patients' perspective. Pain Res Treat. 2014; 2014:827659.

2. Yoon KC, Cho CW, Seo MS, Yang KJ. Comparision of ocular pain between topical and retrobulbar anesthesia for cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:2041–7.
3. Ryu JH, Kim M, Bahk JH, et al. A comparison of retrobulbar block, sub-Tenon block, and topical anesthesia during cataract surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2009; 19:240–6.

4. Wagle AA, Wagle AM, Bacsal K, et al. Practice preferences of ophthalmic anaesthesia for cataract surgery in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2007; 48:287–90.
5. Paik HJ, Song HJ, Shyn KH. 2007 Survey for KSCRS members: current trends in cataract surgery in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1624–31.
6. Fichman RA. Use of topical anesthesia alone in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:612–4.

7. Seo JB, Byun SW, Kim JH, Joo CK. Comparison of effects of topical, pinpoint and retrobulbar anesthesin in cataract surgery using clear corneal incision. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1716–22.
8. Lee JS, Chung SK, Baek NH. Topical versus retrobulbar anesthesia in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3031–7.
9. Lee JH, Yoo JH, Cho SH, et al. Thyroid surgery under monitored anesthesia care (MAC). Korean J Anesthesiol. 2009; 56:284–9.

10. Lee Y, Chang HW, Shim JY. The effect of combined fentanyl and ketamine administration in the monitored anesthetic care of ambu-latory strabismus surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2006; 50:434–8.

11. Rosenfeld SI, Litinsky SM, Snyder DA, et al. Effectiveness of monitored anesthesia care in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:1256–60. discussion 1261.

12. Zakrzewski PA, Banashkevich AV, Friel T, Braga-Mele R. Monitored anesthesia care by registered respiratory therapists during cataract surgery: an update. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:897–902.

13. Moerman N, van Dam FS, Muller MJ, Oosting H. The Amsterdam preoperative anxiety and information scale (APAIS). Anesth Analg. 1996; 82:445–51.

14. Porela-Tiihonen S, Kaarniranta K, Kokki M, et al. A prospective study on postoperative pain after cataract surgery. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013; 7:1429–35.
15. Ko JS, Ahn JM, Seo KY, et al. Relationship between cataract matu-ration and pain scale during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:437–42.

16. Ursea R, Feng MT, Zhou M, et al. Pain perception in sequential cataract surgery: comparison of first and second procedures. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1009–14.

17. Cakmak H, Kocaturk T, Dundar SO, et al. The effects of diazepam on blood pressure levels in cataract surgery. Saudi Med J. 2014; 35:669–73.
Go to : 
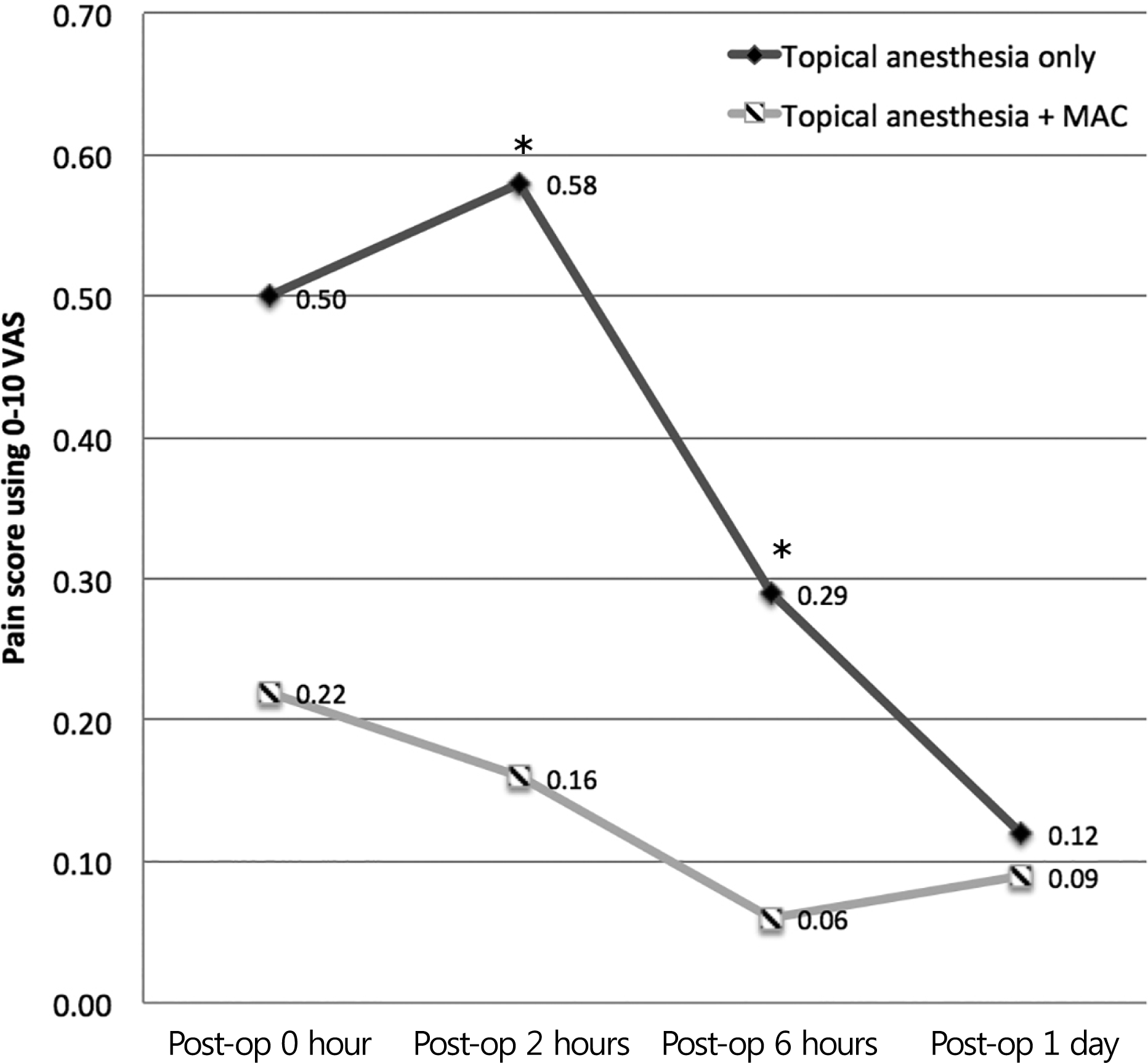 | Figure 1.Subjective postOperative pain score using 0-to-10 Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) Cataract surgery using MAC consistently offered less pain throughout the postOperative period and the difference was statistically significant at postop 2 hour and 6 hour. MAC = monitored anesthesia care; op = operation. * Statistically significant ( p < 0.05). |
Table 1.
Questionnaire based on the Amsterdam Preoperative Anxiety and Information Scale (APAIS)
Table 2.
Demographics of the patients
Table 3.
Patient anxiety scale
Table 4.
Vital signs measured during the operation
| Group | Topical anesthesia only | Topical anesthesia + MAC | t-test between group (Significance) |
|---|---|---|---|
| When operation started | |||
| HR | 68.49 ± 10.86 | 67.03 ± 11.66 | p=0.080 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 140.63 ± 16.12 | 158.24 ± 21.24 | p<0.001* |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 80.04 ± 8.97 | 78.30 ± 9.69 | p=0.366 |
| When operation ended | |||
| HR | 67.55 ± 10.43 | 62.58 ± 10.00 | p=0.011* |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 139.14 ± 18.17 | 140.21 ± 20.39 | p=0.947 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 79.10 ± 9.74 | 72.00 ± 10.89 | p<0.001* |
Table 5.
Bivariate correlation analysis of postOperative pain score with various preoperative and intraoperative factors
| Factors | Age | Gender | NO | Anes. Anxiety | Proc. Anxiety | NPO time | OP order | OP time | HR at start | SBP at start | DBP at start | HR at end | SBP at end | DBP at end | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain at 0 hour | Pearson | -0.005 | -0.021 | -0.059 | 0.086 | 0.099 | -0.052 | -0.053 | 0.341 | 0.140 | -0.077 | -0.045 | 0.096 | -0.055 | -0.035 |
| Sig. | 0.936 | 0.744 | 0.368 | 0.186 | 0.129 | 0.423 | 0.419 | 0.000* | 0.031* | 0.235 | 0.490 | 0.141 | 0.402 | 0.587 | |
| Pain at 2 hours | Pearson | -0.072 | 0.008 | -0.076 | 0.119 | 0.153 * | -0.031 | -0.016 | 0.233* | 0.109 | -0.065 | -0.061 | 0.097 | -0.033 | 0.059 |
| Sig. | 0.269 | 0.899 | 0.246 | 0.067 | 0.018* | 0.637 | 0.803 | 0.000* | 0.094 | 0.321 | 0.353 | 0.135 | 0.615 | 0.363 | |
| Pain at 6 hours | Pearson | -0.130 | -0.056 | -0.081 | -0.025 | -0.028 | -0.113 | -0.038 | 0.131 | 0.049 | 0.04 | -0.057 | 0.072 | 0.022 | 0.018 |
| Sig | 0.045* | 0.392 | 0.214 | 0.697 | 0.669 | 0.082 | 0.563 | 0.044* | 0.455 | 0.539 | 0.385 | 0.27 | 0.741 | 0.784 | |
| Pain at 1 day | Pearson | -0.135 | 0.030 | 0.011 | 0.071 | 0.068 | -0.06 | 0.011 | 0.283 | 0.076 | 0.026 | 0.023 | 0.014 | -0.027 | -0.043 |
| Sig | 0.038* | 0.647 | 0.865 | 0.275 | 0.299 | 0.359 | 0.870 | 0.000* | 0.243 | 0.693 | 0.72 | 0.833 | 0.683 | 0.506 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download