초록
Purpose:
To observe the change in the measured thickness of ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness before and after cataract surgery.
Methods:
Forty-six eyes of 32 patients, scheduled to have cataract surgery, were imaged with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) (Cirrus HD OCT) before and 5 weeks after the surgery to measure GCIPL and RNFL thickness repeatly. Results: All GCIPL and RNFL thickness parameters were significantly higher postoperatively compared with preoperative measurements ( p < 0.001). RNFL thickness changed more than GCIPL; the increased amount of mean RNFL thickness (14.16%) was higher than GCIPL thickness (7.36%; p < 0.001). GCIPL and RNFL thicknesses and, GCIPL signal strength changes were significantly increased in all types of cataracts ( p < 0.05). RNFL signal strength change was significantly increased in posterior subcapsular cataracts ( p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
Cataracts may affect GCIPL and RNFL thicknesses. After cataract surgery, GCIPL thickness, similar to the RNFL thickness, was increased significantly. As GCIPL thickness may be less affected by cataracts than RNFL thickness, GCIPL thickness may be a more meaningful indicator for the diagnosis of glaucoma with cataract.
Go to : 
References
1. Mwanza JC, Bhorade AM, Sekhon N, et al. Effect of cataract and its removal on signal strength and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer optical coherence tomography measurements. J Glaucoma. 2011; 20:37–43.

2. DeBuc DC, Somfai GM, Ranganathan S, et al. Reliability and reproducibility of macular segmentation using a custom-built optical coherence tomography retinal image analysis software. J Biomed Opt. 2009; 14:064023.
3. Koh VT, Tham YC, Cheung CY, et al. Determinants of ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness measured by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:5853–9.

4. Mwanza JC, Oakley JD, Budenz DL, et al. Macular ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer: automated detection and thickness reproducibility with spectral domain-optical coherence tomography in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:8323–9.

5. Tham YC, Cheung CY, Koh VT, et al. Relationship between ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer and optic disc/retinal nerve fibre layer parameters in non-glaucomatous eyes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:1592–7.

6. Tan O, Chopra V, Lu AT, et al. Detection of macular ganglion cell loss in glaucoma by Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2305–14.e1-2.

7. Shin HY, Park HY, Jung KI, et al. Glaucoma diagnostic ability of ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness differs according to the location of visual field loss. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:93–9.

8. Mwanza JC, Durbin MK, Budenz DL, et al. Glaucoma diagnostic accuracy of ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness: comparison with nerve fiber layer and optic nerve head. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1151–8.

9. Takayama K, Hangai M, Durbin M, et al. A novel method to detect local ganglion cell loss in early glaucoma using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:6904–13.

10. van Velthoven ME, van der Linden MH, de Smet MD, et al. Influence of cataract on optical coherence tomography image quality and retinal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:1259–62.

11. Esmaeelpour M, Povazay B, Hermann B, et al. Three-dimensional 1060-nm OCT: choroidal thickness maps in normal subjects and improved posterior segment visualization in cataract patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:5260–6.

12. Cagini C, Fiore T, Iaccheri B, et al. Macular thickness measured by optical coherence tomography in a healthy population before and after uncomplicated cataract phacoemulsification surgery. Curr Eye Res. 2009; 34:1036–41.

13. von Jagow B, Ohrloff C, Kohnen T. Macular thickness after uneventful cataract surgery determined by optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007; 245:1765–71.

14. Ghosh S, Roy I, Biswas PN, et al. Prospective randomized comparative study of macular thickness following phacoemulsification and manual small incision cataract surgery. Acta Ophthalmol. 2010; 88:e102–6.

15. El-Ashry M, Appaswamy S, Deokule S, Pagliarini S. The effect of phacoemulsification cataract surgery on the measurement of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness using optical coherence tomography. Curr Eye Res. 2006; 31:409–13.

16. Nakatani Y, Higashide T, Ohkubo S, et al. Effect of cataract and its removal on ganglion cell complex thickness and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements by fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2013; 22:447–55.

17. Lee Y, Sung KR, Hong JT, Na JH. Glaucoma diagnostic performance of macular and retinal nerve fiber layer by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:1250–7.

18. Mwanza JC, Budenz DL, Godfrey DG, et al. Diagnostic performance of optical coherence tomography ganglion cell--inner plexiform layer thickness measurements in early glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:849–54.

19. Cheung CY, Leung CK, Lin D, et al. Relationship between retinal nerve fiber layer measurement and signal strength in optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:1347–51. 1351.e1-2.

20. Na JH, Sung KR, Lee Y. Factors associated with the signal strengths obtained by spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2012; 26:169–73.

21. Wu Z, Huang J, Dustin L, Sadda SR. Signal strength is an important determinant of accuracy of nerve fiber layer thickness measurement by optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2009; 18:213–6.

22. Pareja-Esteban J, Teus-Guezala MA, Drake-Casanova P, Dapena-Sevilla I. [Retinal nerve fiber layer changes after cataract surgery measured by OCT: a pilot study]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2009; 84:305–9.
Go to : 
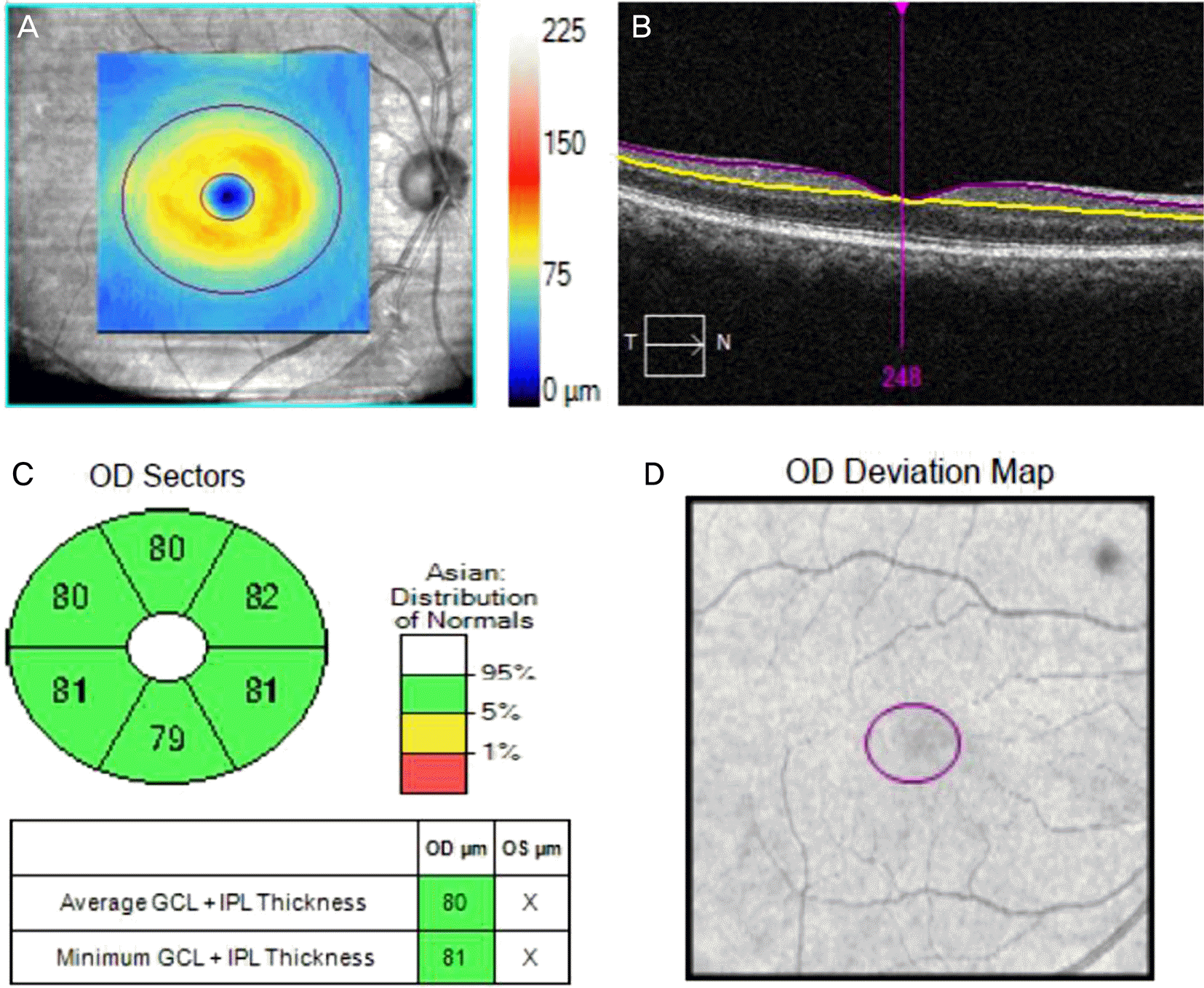 | Figure 1.Cirrus HD-OCT images of the macula of the right eye. (A) GCIPL thickness maps (the denser the orange/yellow ring, the thicker the GCIPL) (B) Boundary lines drawn to measure GCIPL thickness. The pur-ple line indicates the boundary between the RNFL and GCL. And the yellow line indicates the boundary between the IPL and INL. (C) GCIPL division map. The significance map shows (clockwise) thickness of the superior, superonasal, inferonasal, inferior, inferotemporal, and superotemporal sectors of the annulus and the average and minimum GCIPL (box) (D) GCIPL deviation map. GCIPL = ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer; RNFL = retinal nerve fiber layer; HD-OCT = high definition-OCT; GCL = ganglion cell layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; INL = inner nuclear layer. |
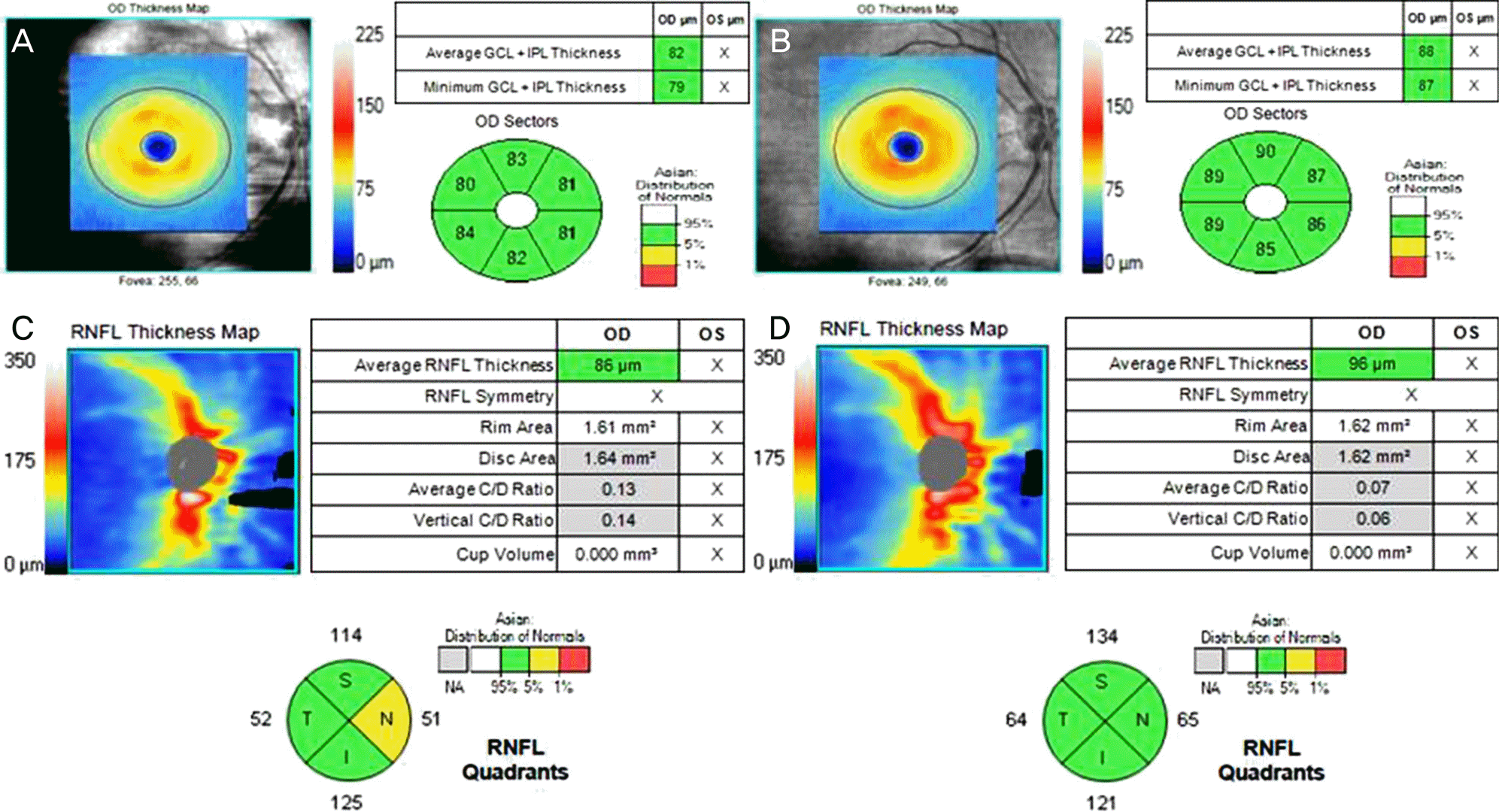 | Figure 2.GCIPL and RNFL thickness measurement before (A) and after (B) cataract surgery. RNFL thickness measurement before (C) and after (D) cataract surgery. After cataract surgery, both GCIPL and RNFL thickness were increased. GCIPL thickness was less changed than RNFL. GCIPL = ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer; RNFL = retinal nerve fiber layer; GCL = ganglion cell layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; C/D = cup/disc; N = nasal; S = superior; T = temporal; I = inferior. |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of study participants
Table 2.
Preoperative and postoperative GCIPL and RNFL measurements in eyes
Table 3.
Comparison between GCIPL and RNFL measurements in eyes
Table 4.
Mean and standard deviation (SD) of SS, average GCIPL and RNFL thickness analysis in types of cataract
Table 5.
Pearson correlation between change in signal strength (GCIPL, RNFL) and other factors
Table 6.
Pearson correlation between change in average thickness measurement (GCIPL, RNFL) and other factors




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download