초록
Purpose:
To evaluate rotational stability of Toric Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) implantation to correct myopic astigmatism.
Methods:
We estimated the degree of Toric ICL rotation together with change in visual acuity and astigmatism in 118 eyes of 66 patients who underwent Toric ICL implantation and had a long-term mean follow-up period of 37 months.
Results:
After Toric ICL implantation, 107 (91%) out of 118 eyes showed uncorrected visual acuity of 0.8 or better. The mean postoperative astigmatism decreased to -0.64 ± 0.61 D from a mean preoperative astigmatism of -2.96 ± 1.13 D. The mean axis change of Toric ICL was 2.4 ± 3.8 degrees during follow-up period. Two (1.7%) out of 118 eyes showed the axis change of more than 10 degrees. These two eyes had a decrease in visual acuity, rotational axis change of 18 degrees and 30 degrees, respectively, and increases in astigmatism of 1.50 D and 1.00 D, respectively. The remaining 116 eyes (98.3%) showed excellent rotational stability without visual acuity decreasing Toric ICL rotation during the follow-up period.
Go to : 
References
1. Geggel HS, Talley AR. Delayed onset keratectasia following laser in situ keratomileusis and photorefractive keratectomy. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:640–52.
2. Göker S, Er H, Kahvecioglu C. Laser in situ keratomileusis to correct hyperopia from +4.25 to +8.00 diopters. J Refract Surg. 1998; 14:26–30.

3. Nagy ZZ, Munkácsy G, Popper M. Photorefractive keratectomy using the meditec MEL 70 G-scan laser for hyperopia and hyperopic astigmatism. J Refract Surg. 2002; 18:542–50.

4. Lee SY, Cheon HJ, Baek TM, Lee KH. Implantable contact lens to correct high myopia (Clinical Study with 24 Months Follow-up). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1515–22.
5. Chun YS, Lee JH, Lee JM, et al. Outcomes after implantable contact lens for moderate to high myopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:480–9.
6. Sanders DR, Brown DC, Martin RG, et al. Implantable contact lens for moderate to high myopia: phase 1 FDA clinical study with 6 month follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:607–11.

7. Sanders DR, Vukich JA, Doney K, Gaston M; Implantable Contact Lens in Treatment of Myopia Study Group. U.S. Food and Drug Administration clinical trial of the Implantable Contact Lens for moderate to high myopia. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:255–66.

8. Sanders DR, Schneider D, Martin R, et al. Toric Implantable Collamer Lens for moderate to high myopic astigmatism. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:54–61.

9. Sanders DR, Doney K, Poco M; ICL in Treatment of Myopia Study Group. United States Food and Drug Administration clinical trial of the Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) for moderate to high myopia: three-year follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1683–92.
10. Dejaco-Ruhswurm I, Scholz U, Pieh S, et al. Long-term endothelial changes in phakic eyes with posterior chamber intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1589–93.

11. Edelhauser HF, Sanders DR, Azar R, Lamielle H; ICL in Treatment of Myopia Study Group. Corneal endothelial assessment after ICL implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:576–83.

12. Jiménez-Alfaro I, Benítez del Castillo JM, García-Feijoó J, et al. Safety of posterior chamber phakic intraocular lenses for the correction of high myopia: anterior segment changes after posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:90–9.
13. Sanders DR, Grabow HB, Shepherd J, Raanan MR. Staar AA 4203T Toric Silicone IOL. Martin RG, Gillis JP, Sanders DR, editors. Foldable Intraocular Lenses. Thorofare, NJ: SLACK Inc.;1993. v. 1:chap. 14.
14. Han SY, Lee KH. Long term effect of ICL implantation to treat high myopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:465–72.
15. Chang J, Lau S. Toric Implantable Collamer Lens for high myopic astigmatic Asian eyes. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2340–7.

16. Bhikoo R, Rayner S, Gray T. Toric implantable collamer lens for patients with moderate to severe myopic astigmatism: 12-month follow-up. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2010; 38:467–74.

17. Mori T, Yokoyama S, Kojima T, et al. Factors affecting rotation of a posterior chamber collagen copolymer toric phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:568–73.

18. Oh J, Shin HH, Kim JH, et al. Direct measurement of the ciliary sulcus diameter by 35-megahertz ultrasound biomicroscopy. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1685–8.

19. Reinstein DZ, Archer TJ, Silverman RH, et al. Correlation of anterior chamber angle and ciliary sulcus diameters with white-to-white corneal diameter in high myopes using artemis VHF digital ultrasound. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:185–94.

20. Sheng XL, Rong WN, Jia Q, et al. Outcomes and possible risk factors associated with axis alignment and rotational stability after implantation of the Toric implantable collamer lens for high myopic astigmatism. Int J Ophthalmol. 2012; 5:459–65.
Go to : 
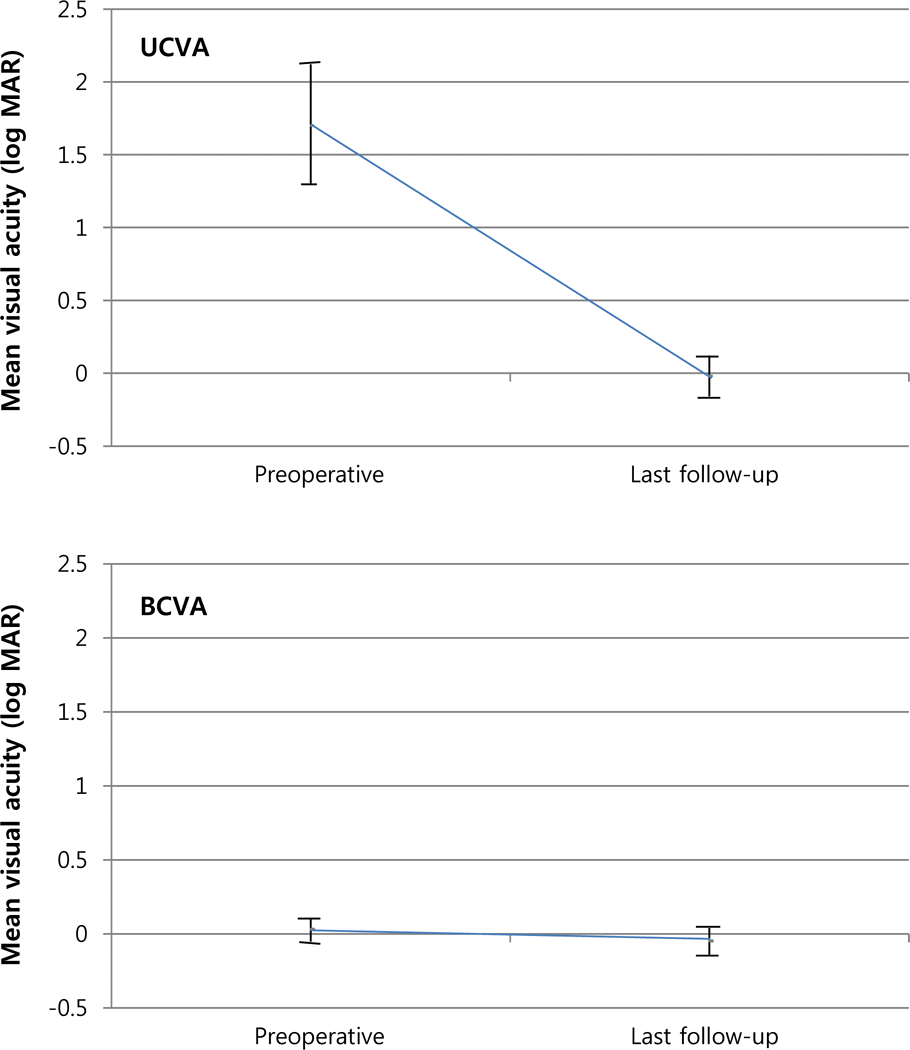 | Figure 1.Mean log MAR uncorrected distance visual acuity (UCVA) and log MAR best-corrected distance visual acuity before and after Toric ICL implantation. The preoperative mean log MAR UCVA of +1.71 ± 0.41 changed to -0.02 ±0.41 at last follow-up. And the preoperative mean log MAR corrected visual acuity of +0.03 ± 0.08 changed to -0.05 ±0.09 at last follow-up. ICL = implantable collamer lens; BCVA = best-corrected distance visual acuity. |
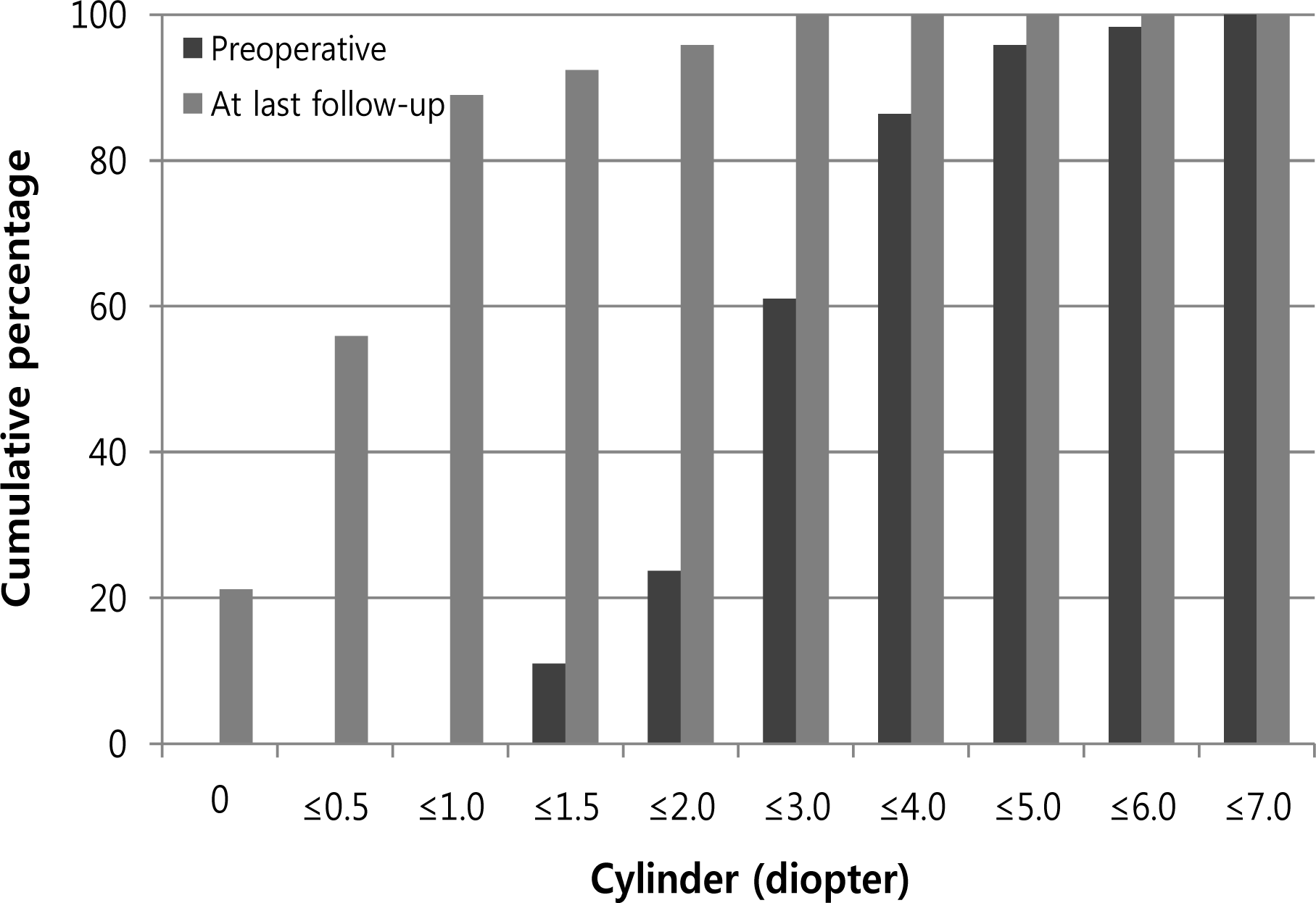 | Figure 2.Comparison between preoperative cylinder and postoperative last follow-up cylinder after Toric ICL implantation. The postoperative cylinder at last follow-up was within 0.50 D in 66 eyes (56%) and within 1.00 D in 105 eyes (89%). ICL = implantable collamer lens. |
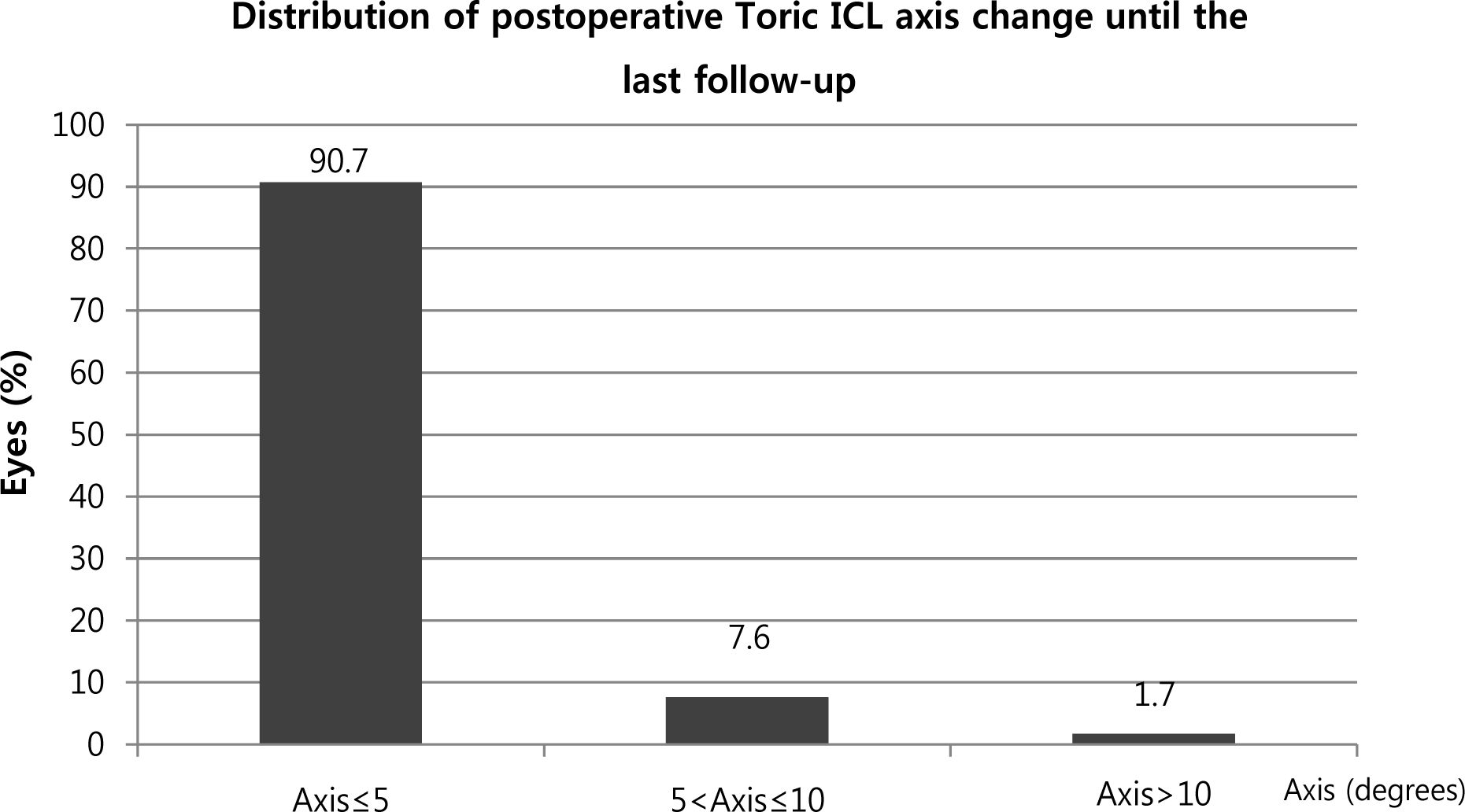 | Figure 3.Toric ICL axis change after the surgery. The Toric ICL axis changes until the last follow-up were within 5 degrees in 107 eyes (90.7%), between more than 5 degrees and 10 degrees or less in 9 eyes (7.6%), and over 10 degrees in 2 eyes (1.7%). ICL = implantable collamer lens. |
Table 1.
Preoperative profile
| Parameter | Number | Mean ± SD | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 66 | ||
| Eyes | 118 | ||
| Sex | |||
| Male | 22 | ||
| Female | 44 | ||
| Age (years) | 28.5 ± 7.10 | 19-50 | |
| Refractive sphere (diopter) | -8.47 ± 2.94 | -1.25~-17.5 | |
| Refractive cylinder (diopter) | -2.96 ± 1.13 | -1.0~-7.0 | |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) | -9.95 ± 3.12 | -4.0~-19.5 | |
| K power (diopter) | 44.36 ± 1.29 | 41.00-48.35 | |
| Axial length (mm) | 27.08 ± 1.31 | 23.12-30.14 | |
| Anterior chamber depth (mm) | 3.33 ± 0.24 | 2.80-3.91 | |
| Horizontal white-to-white diameter (mm)* | 11.84 ± 0.34 | 11.0-12.9 | |
| Corneal thickness (μ m) | 519 ± 36 | 422-598 | |
| ICL size (mm) | 12.26 ± 0.32 | 11.5-13.0 | |
| ICL sphere (diopter) | -16.65 ± 3.88 | -8.5~-23.0 | |
| ICL cylinder (diopter) | +3.79 ± 1.21 | +1.5~+6.0 | |
| Mean follow-up (month) | 37.1 ± 24.1 | 3-80 |
Table 2.
Cycloplegic refractive spherical equivalent (SE) on 1 month and last follow-up after Toric ICL implantation
| Refractive SE (diopter)* |
Eyes (n, %) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | Month 1 | Last follow-up | |
| 0.0 | 0 | 7 (5.9) | 13 (11.1) |
| 0.0 < D ≤ 0.5 | 0 | 35 (29.7) | 66 (55.9) |
| 0.5 < D ≤ 1.0 | 0 | 54 (45.8) | 29 (24.6) |
| 1.0 < D ≤ 2.0 | 0 | 20 (16.9) | 9 (7.6) |
| 2.0 < D | 118 (100) | 2 (1.7) | 1 (0.8) |
| Mean SE ± SD | -9.95 ± 3.12 | +0.66 ± 0.57 | +0.03 ± 0.66 |
Table 3.
Cycloplegic refractive cylinder at 1 month and last follow-up after Toric ICL implantation
| Refractive cylinder (diopter)* |
Eyes (n, %) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | Month 1 | Last follow-up | |
| 0.0 | 0 | 32 (27.1) | 25 (21.2) |
| 0.0 < D ≤ 0.5 | 0 | 40 (33.9) | 41 (34.7) |
| 0.5 < D ≤ 1.0 | 0 | 34 (28.8) | 39 (33.1) |
| 1.0 < D ≤ 2.0 | 28 (24) | 10 (8.5) | 8 (6.8) |
| 2.0 < D | 90 (76) | 2 (1.7) | 5 (4.2) |
| Mean cylinder ± SD | -2.96 ± 1.13 | -0.54 ± 0.49 | -0.64 ± 0.61 |
Table 4.
Toric ICL vault on 1 month and last follow-up after Toric ICL implantation




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download