초록
Purpose:
To assess the usefulness of two spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) instruments (Cirrus®, Spectralis®) for evaluating optic nerve head and peripapillary structures.
Methods:
Images of optic nerve complex were obtained from 136 eyes of 136 patients using enhanced depth imaging technique of 2 SD-OCT instruments. Optic nerve head and peripapillary structures were investigated for their visibility and morphological features in total eyes and glaucomatous eyes. Effect factors for laminar thickness measurement were evaluated and the reproducibility of the lamina cribrosa thickness measured by the 2 OCT instruments was analyzed.
Results:
Lamina cribrosa thickness was better identified using Spectralis® OCT in total and glaucomatous eyes. Short posterior ciliary artery (in total eyes) and peripapillary choroid (in total and glaucomatous eyes) were also better identified using Spectralis® OCT ( p < 0.001). A cup-disc ratio ≤ 0.6 was the significant effect factor for laminar thickness measurement ( p < 0.05). Interobserver reproducibility was excellent using both OCT instruments. Intraobserver reproducibility was excellent using Spectralis® OCT and moderate using Cirrus® OCT.
Go to : 
References
1. Park SC, De Moraes CG, Teng CC, et al. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of deep optic nerve complex structures in glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:3–9.

2. Shin HY, Park HY, Jung KI, Park CK. Glaucoma diagnosis optic disc analysis comparing Cirrus spectral domain optical coherence tomography and Heidelberg retina tomograph II. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2013; 57:41–6.

3. Shpak AA, Sevostyanova MK, Ogorodnikova SN, Shormaz IN. Comparison of measurement error of Cirrus HD-OCT and Heidelberg Retina Tomograph 3 in patients with early glaucomatous visual field defect. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:271–7.

4. Leite MT, Rao HL, Zangwill LM, et al. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracies of the Spectralis, Cirrus, and RTVue optical coherence tomography devices in glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:1334–9.

5. Vilupuru AS, Rangaswamy NV, Frishman LJ, et al. Adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy for in vivo imaging of lamina cribrosa. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2007; 24:1417–25.

6. Kagemann L, Ishikawa H, Wollstein G, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution spectral domain optical coherence tomography imaging of the lamina cribrosa. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2008; 39(4 Suppl):S126–131.

7. Strouthidis NG, Grimm J, Williams GA, et al. A comparison of optic nerve head morphology viewed by spectral domain optical coherence tomography and by serial histology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:1464–74.

8. Yang H, Downs JC, Burgoyne CF. Physiologic intereye differences in monkey optic nerve head architecture and their relation to changes in early experimental glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50:224–34.

9. Lee EJ, Kim TW, Weinreb RN, et al. Visualization of the lamina cribrosa using enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 152:87–95.e1.

10. Park HY, Jeon SH, Park CK. Enhanced depth imaging detects lamina cribrosa thickness differences in normal tension glaucoma and primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:10–20.

11. Chung HS, Sung KR, Lee KS, et al. Relationship between the lamina cribrosa, outer retina, and choroidal thickness as assessed using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2014; 28:234–40.

12. Fleiss JL, Levin B, Paik MC. Statistical methods for rates and pro-portions. 3rd ed.Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.;2003. p. 604.
13. Bambo MP, Garcia-Martin E, Otin S, et al. Influence of cataract surgery on repeatability and measurements of spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014; 98:52–8.

14. Tan BB, Natividad M, Chua KC, Yip LW. Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer measurement between 2 spectral domain OCT instruments. J Glaucoma. 2012; 21:266–73.

15. Yang B, Ye C, Yu M, et al. Optic disc imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: variability and agreement study with Heidelberg retinal tomograph. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1852–7.
16. Kim SY, Park HY, Park CK. The effects of peripapillary atrophy on the diagnostic ability of Stratus and Cirrus OCT in the analysis of optic nerve head parameters and disc size. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:4475–84.

Go to : 
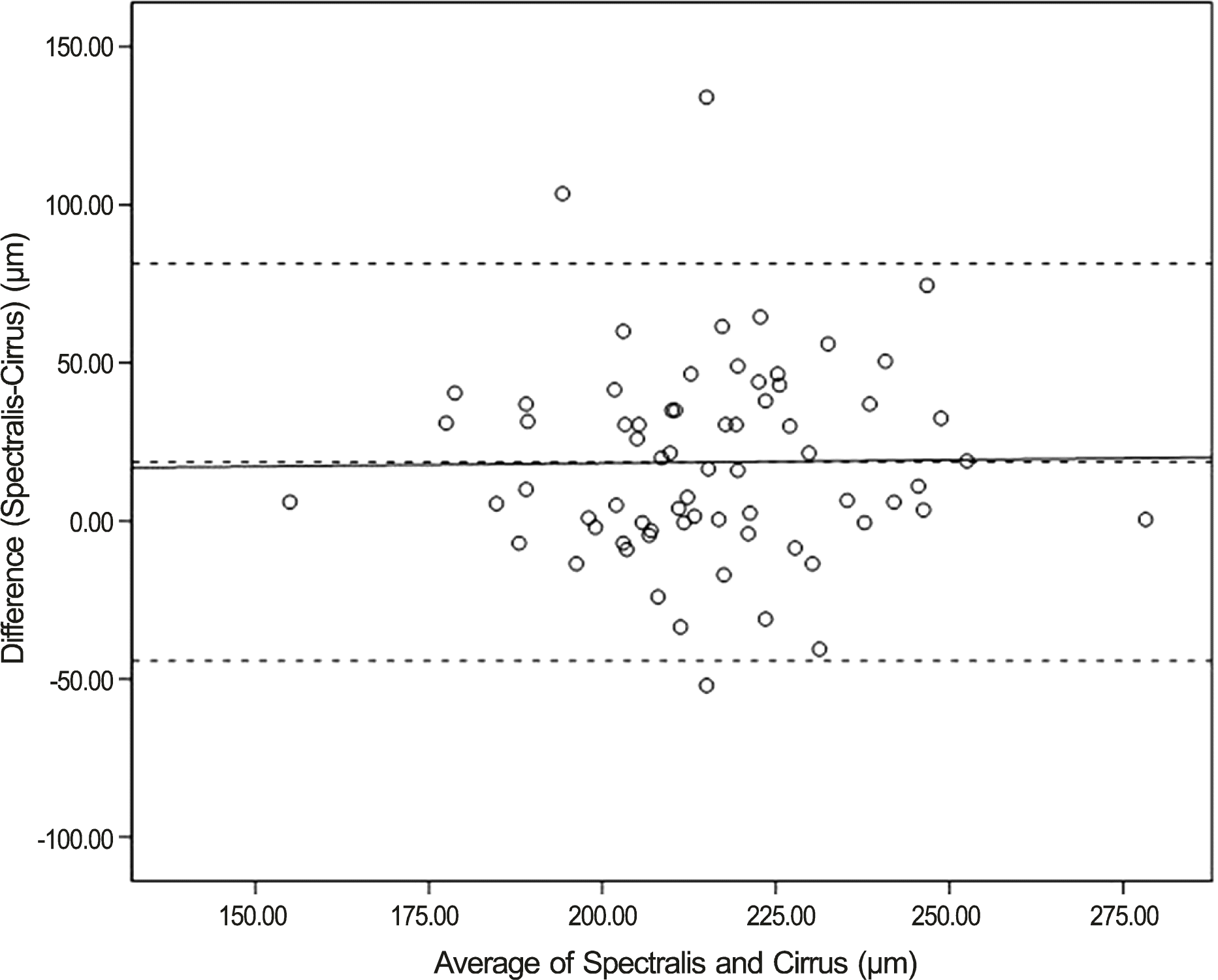 | Figure 1.Bland-Altman plot for lamina cribrosa thickness. Mean difference is 18.61 μm. The 95% limits of agreement for laminal thickness measurements are -40.90 to 80.14 μm. |
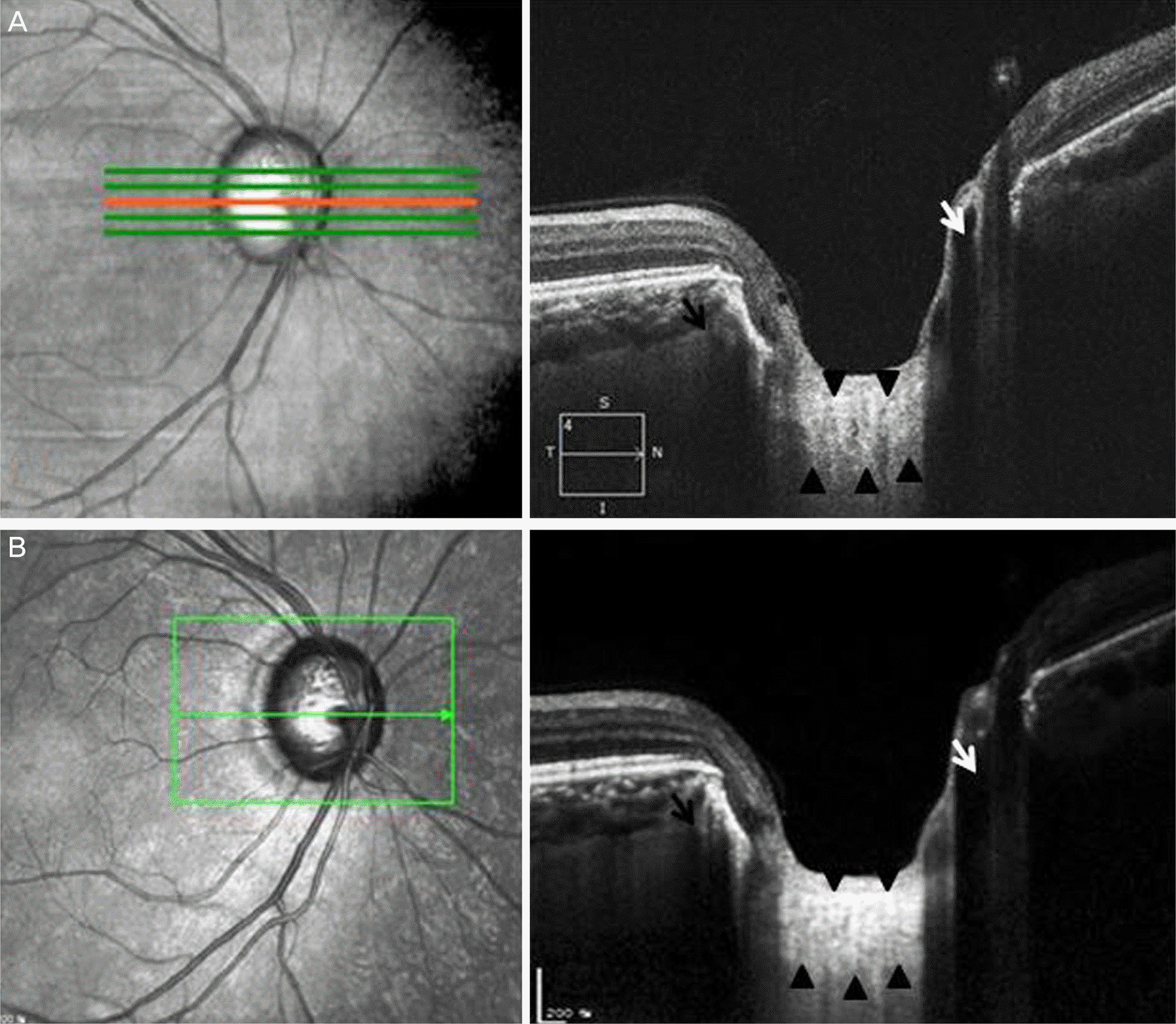 | Figure 2.Optic nerve head complex of cross-sectional images revealed using Cirrus® optical coherence tomography (OCT) (A), Spectralis® OCT (B). Black arrow heads in (A) and (B) denote suspected lamina cribrosa. Lamina cribrosa thickness was 230.77 μm measured by Cirrus® OCT (A) and 297.69 μm measured by Spectralis® OCT (B). Lamina cribrosa pores of various shapes and sizes well identified. Posterior border of lamina cribrosa is relatively less identified in (A). Central retinal vessel trunk (white arrow) passing through the lamina cribrosa identified. Short posterior ciliary artery (black arrow) are shown in the sclera draining into the choroid. |
Table 1.
Patient demographics and clinical information
| Total (n = 136) | Healthy eyes (n = 97) | Glaucomatous eyes (n = 39) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M/F) (n) | 74/62 | 58/39 | 16/23 | 0.139* |
| Age (years) | 56.41 ± 2.98 | 54.05 ± 12.59 | 62.28 ± 12.19 | 0.003† |
| Visual field test | ||||
| MD (dB) | -2.35 ± 3.06 | -1.54 ± 2.22 | -4.44 ± 6.14 | <0.001† |
| PSD (dB) | 2.37 ± 2.12 | 1.87 ± 1.49 | 3.70 ± 3.24 | <0.001† |
| Cup-disc ratio | 0.71 ± 0.13 | 0.68 ± 0.14 | 0.81 ± 0.16 | 0.003† |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) | -0.96 ± 2.42 | -0.98 ± 2.45 | -0.75 ± 2.38 | 0.980† |
Table 2.
Lamina cribrosa and ONH Structures measured by Spectralis® OCT and Cirrus® OCT in all eyes (n = 136)
| Spectralis® OCT | Cirrus® OCT | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lamina cribrosa | |||
| Thickness (μm) | 218.1 ± 27.7 | 206.6 ± 25.5 | 0.002* |
| Anterior surface (n, %) | 129 (94.9) | 109 (82.6) | 0.002† |
| Posterior surface (n, %) | 125 (91.9) | 71 (55.0) | <0.001† |
| Pore (n, %) | 132 (97.1) | 124 (93.9) | 0.250† |
| Deep ONH structures (n, %) | |||
| Central retinal vessel trunk | 123 (90.4) | 115 (87.1) | 0.441† |
| Central retinal artery | 18 (13.2) | 11 (8.3) | 0.239† |
| Central retinal vein | 20 (14.7) | 10 (7.6) | 0.081† |
| Short posterior ciliary artery | 40 (29.4) | 8 (6.1) | <0.001† |
| Peripapillary choroid | 135 (99.3) | 129 (97.7) | 0.365† |
| Peripapillary sclera | 129 (94.9) | 91 (68.9) | <0.001† |
Table 3.
Lamina cribrosa and ONH Structures measured by Spectralis® OCT and Cirrus® OCT in eyes with glaucoma (n = 39)
| Spectralis® OCT | Cirrus® OCT | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lamina cribrosa | |||
| Thickness (μm) | 215.7 ± 27.9 | 204.2 ± 31.8 | 0.235* |
| Anterior surface (n, %) | 39 (100) | 31 (81.6) | 0.005† |
| Posterior surface (n, %) | 37 (94.9) | 15 (41.7) | <0.001† |
| Pore (n, %) | 37 (94.9) | 35 (92.1) | 0.675† |
| Deep ONH structures (n, %) | |||
| Central retinal vessel trunk | 39 (100) | 37 (97.4) | 0.494† |
| Central retinal artery | 7 (17.9) | 4 (10.5) | 0.517† |
| Central retinal vein | 9 (23.1) | 4 (10.5) | 0.224† |
| Short posterior ciliary artery | 9 (23.1) | 4 (10.5) | 0.224† |
| Peripapillary choroid | 38 (97.4) | 37 (97.4) | 1.000† |
| Peripapillary sclera | 34 (87.2) | 16 (42.1) | <0.001† |
Table 4.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis for risk factor of lamina cribrosa thickness measurement
Table 5.
Reproducibility of the lamina cribrosa thickness measured by Spectralis® OCT and Cirrus® OCT




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download