Abstract
Purpose
To compare electroretinogram (ERG) waveforms acquired using a ganzfeld stimulator and a Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator.
Methods
ERGs were recorded with a ganzfeld stimulator and a Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator from both eyes of 25 volunteers. Peak-to-trough amplitudes and peak implicit times were compared between both eyes and between a ganzfeld stimulator and a Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator. ERGs taken from the sitting and supine positions were also compared using the Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference between the Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator and dome-shaped ganzfeld stimulator in amplitude and implicit time of dark adapted 0.01, 3.0 ERG, photopic 3.0 ERG, photopic 3.0 flicker. The differences in amplitude and implicit time between the right and left eyes were not influenced by the Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator. Additionally, no differences were observed in ERGs obtained from the sitting and supine positions using the Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator.
Go to : 
References
1. Marmor MF, Fulton AB, Holder GE. . ISCEV Standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2008 update). Doc Ophthalmol. 2009; 118:69–77.

2. Gunkel RD, Bergsma DR, Gouras P. A Ganzfeld stimulator for electroretinography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976; 94:669–70.

3. Rabin AR, Berson EL. A full-field system for clinical electro- retinography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974; 92:59–63.
4. Gouras P. Electroretinography: some basic principles. Invest Ophthalmol. 1970; 9:557–69.
5. Metzger W. Optical investigations of the Ganzfeld. Psychological Research. 1930; 13:6–29.
6. Gibson JJ, Waddell D. Homogeneous retinal stimulation and visual perception. Am J Psychol. 1952; 65:263–70.

9. Cohen W. Comparisons of homogeneous Ganzfelds with Ganzfelds containing simple figures. Dissertation Abstracts. 1956; 16:1510–1.
10. Kritchman EM, Friesem AA, Yekutieli G. Highly concentrating Fresnel lenses. Appl Opt. 1979; 18:2688–95.

11. Besch D, Kurtenbach A, Apfelstedt-Sylla E. . Visual field con-striction and electrophysiological changes associated with vigabatrin. Doc Ophthalmol. 2002; 104:151–70.
12. Huang S, Wu D, Jiang F. . The multifocal electroretinogram in X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Doc Ophthalmol. 2003; 106:251–5.
Go to : 
 | Figure 2.The shape of Fresnel lens. Fresnel lens is made by removing the non-refractive part of a conventional lens, leaving the lens with a thin profile. (A) Side. (B) Front. |
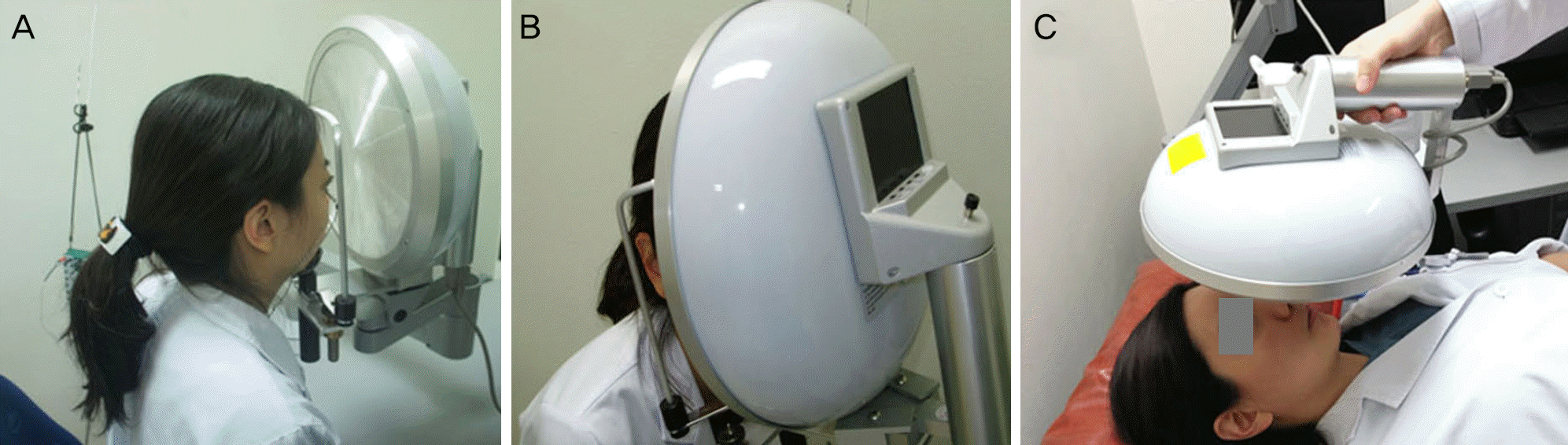 | Figure 3.Comparision of dome-shaped ganzfeld stimulator and Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator. (A) Conventional ganzfeld. (B) Fresnel ganzfeld. |
 | Figure 4.Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator. Its lightweight construction, built-in infra-red video display, and stimulus trigger make it an ideal handheld stimulator for the reclining or supine subject. (A) Front side. (B) Back side. (C) Supine position. |
Table 1.
Comparison of b-wave amplitude and the implicit time of each response using Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator between the right and left eye (n = 25)
Table 2.
Comparison of a-wave amplitude and the implicit time of each response between Ganzfeld stimulator and Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator (n = 25)
Table 3.
Comparison of b-wave amplitude and the implicit time of each response between Ganzfeld stimulator and Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator (n = 25)
Table 4.
Comparison of b-wave amplitude and the implicit time of each response using Fresnel ganzfeld stimulator between sitting and supine position (n = 25)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download