Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the change in posterior corneal astigmatism and total corneal astigmatism in patients with anterior corneal astigmatism less than 1.0 diopter (D).
Methods
In the present study we evaluated 52 eyes with anterior corneal astigmatism less than 1.0 D. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to steep axis: Group 1 included 33 eyes with within-the-rule (WTR) astigmatism and Group 2 included 19 eyes with against-the-rule (ATR) astigmatism. Anterior, posterior and total corneal astigmatism were measured using Scheimpflug imaging (Pentacam®).
Results
In Group 1, preoperative anterior astigmatism, posterior astigmatism and total astigmatism were 0.55 ± 0.44 D, 0.31 ±0.14 D and 0.30 ± 0.72 D, respectively. At postoperative 2 months, anterior astigmatism, posterior astigmatism and total astig-matism were 0.51 ± 0.67 D, 0.31 ± 0.15 D and 0.35 ± 0.81 D, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference be-tween preoperative and postoperative anterior, posterior and total corneal astigmatism in Group 1. In Group 2, preoperative an-terior astigmatism, posterior astigmatism and total astigmatism were -0.48 ± 0.46 D, 0.26 ± 0.09 D and -0.51 ± 0.65 D, respectively. At postoperative 2 months, anterior astigmatism, posterior astigmatism and total astigmatism were -0.17 ± 0.68 D, 0.25 ± 0.13 D and -0.30 ± 0.55 D, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference between preoperative and post-operative anterior, posterior and total corneal astigmatism in the 2 groups. There was no statistical correlation between pre-operative posterior corneal astigmatism and postoperative 2 months total corneal astigmatism. After vector analysis, surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) of the anterior and total astigmatism in Group 1 were 0.03 D @ 30° and 0.07 D @ 74°, respectively, and in Group 2 were 0.27 D @ 100° and 0.36 D @ 86°, respectively.
References
1. Rubenstein JB, Raciti M. Approaches to corneal astigmatism in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013; 24:30–4.

2. Koch DD, Jenkins RB, Weikert MP. . Correcting astigmatism with toric intraocular lenses: effect of posterior corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1803–9.

3. Cheng LS, Tsai CY, Tsai RJ. . Estimation accuracy of surgi-cally induced astigmatism on the cornea when neglecting the pos-terior corneal surface measurement. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011; 89:417–22.

4. Ho JD, Tsai CY, Liou SW. Accuracy of corneal astigmatism esti-mation by neglecting the posterior corneal surface measurement. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:788–95. 795.e1-2.

5. Koch DD, Ali SF, Weikert MP. . Contribution of posterior cor-neal astigmatism to total corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2080–7.

6. Nemeth G, Berta A, Szalai E. . Analysis of surgically induced astigmatism on the posterior surface of the cornea. J Refract Surg. 2014; 30:604–8.

7. Ferrer-Blasco T, Montés-Micó R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:70–5.

9. Olsen T, Dam-Johansen M. Evaluating surgically induced astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994; 20:517–22.

10. Amesbury EC, Miller KM. Correction of astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009; 20:19–24.

11. Yong Park C, Do JR, Chuck RS. Predicting postoperative astigma-tism using Scheimpflug keratometry (Pentacam) and automated keratometry (IOLMaster). Curr Eye Res. 2012; 37:1091–8.

12. Montalbán R, Piñero DP, Javaloy J, Alió JL. Scheimpflug photog-raphy-based clinical characterization of the correlation of the cor-neal shape between the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces in the normal human eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:1925–33.

13. Ueno Y, Hiraoka T, Beheregaray S. . Age-related changes in anterior, posterior, and total corneal astigmatism. J Refract Surg. 2014; 30:192–7.

14. Kim CS, Ryu JW, Kim HS, Lee YC. Distribution and change of to-tal astigmatism, corneal astigmatism and residual astigmatism with age in patient with emmetropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:485–93.
15. Zhang L, Sy ME, Mai H. . Effect of posterior corneal astigma-tism on refractive outcomes after toric intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:84–9.

16. Royston JM, Dunne MC, Barnes DA. Measurement of posterior corneal surface toricity. Optom Vis Sci. 1990; 67:757–63.

17. Royston JM, Dunne MC, Barnes DA. Measurement of the posteri-or corneal radius using slit lamp and Purkinje image techniques. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1990; 10:385–8.

18. Dunne MC, Royston JM, Barnes DA. Posterior corneal surface tor-icity and total corneal astigmatism. Optom Vis Sci. 1991; 68:708–10.

19. Aujla JS, Vincent SJ, White S, Panchapakesan J. Cataract surgery in eyes with low corneal astigmatism: implantation of the Acrysof IQ toric SN6AT2 intraocular lens. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2014; 9:324–8.
20. Ernest P, Potvin R. Effects of preoperative corneal astigmatism ori-entation on results with a low-cylinder-power toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:727–32.

21. Magdum RM, Gahlot A, Maheshgauri RD, Patel K. A comparative study of surgically induced astigmatism in superior and temporal scleral incision in manual small incision cataract surgery. Natl J Med Res. 2012; 2:497–500.
Figure 1.
Double-angle plots of surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) of anterior corneal astigmatism (SIA-A) and total corneal as-tigmatism (SIA-T) in (A) WTR group and (B) ATR group. WTR = within-the-rule; ATR = against-the-rule.
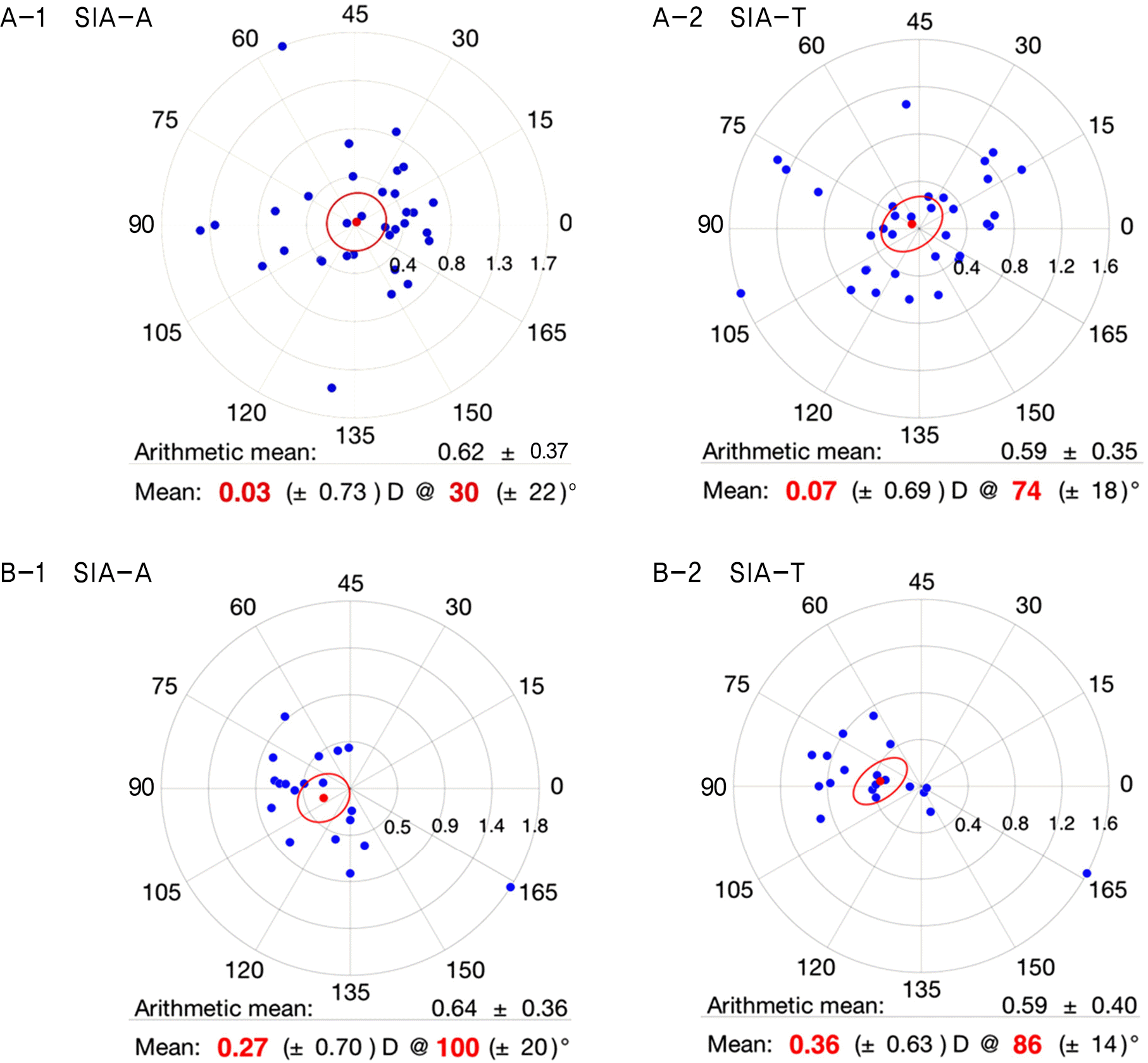
Figure 2.
Correlation analysis between preoperative anterior astigmatism and posterior astigmatism in (A) total group, (B) WTR group and (C) ATR group. WTR = within-the-rule; ATR = against-the-rule.
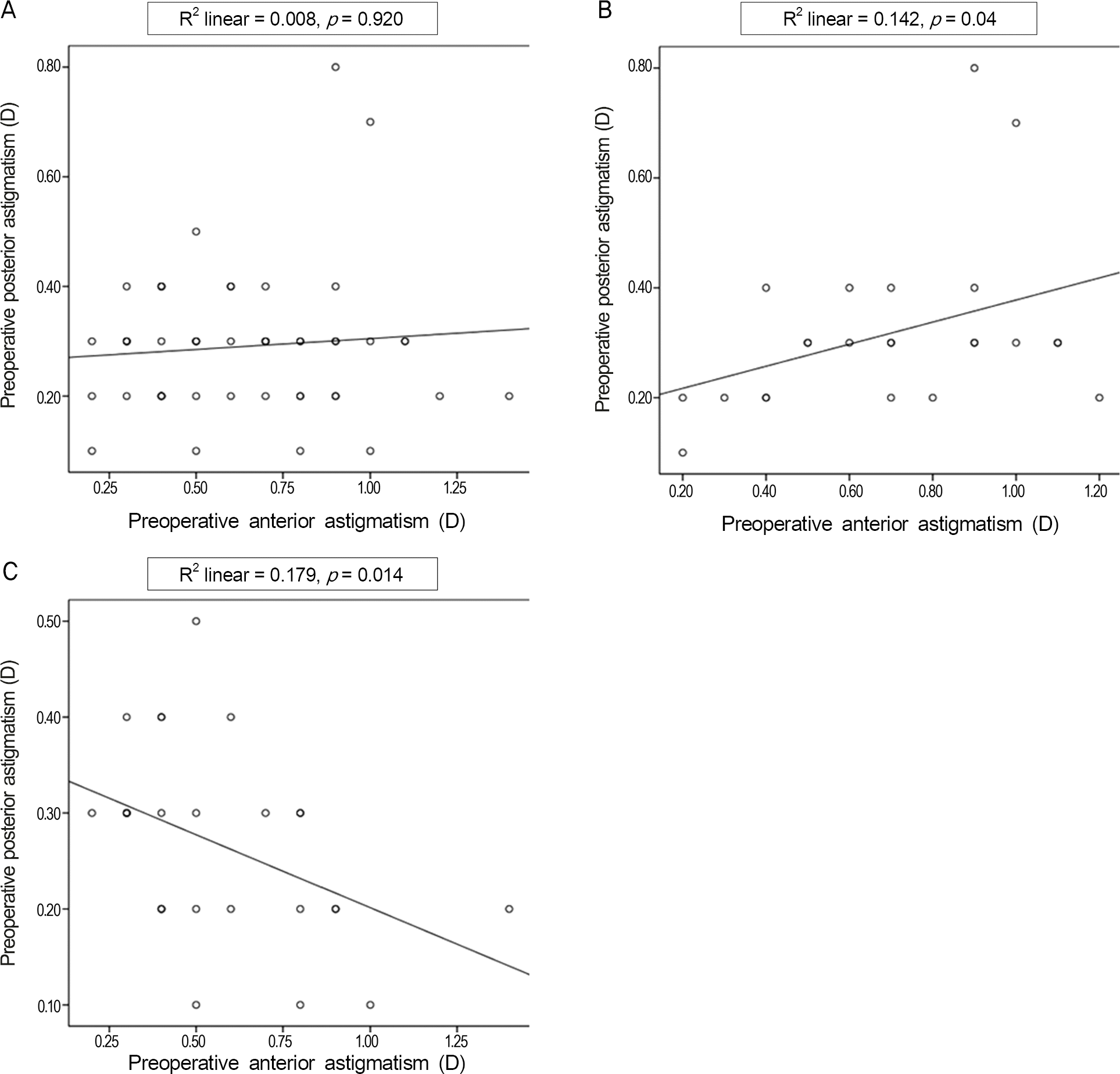
Figure 3.
Correlation analysis between preoperative posterior astigmatism and postoperative total astigmatism in (A) WTR group and (B) ATR group. WTR = within-the-rule; ATR = against-the-rule.
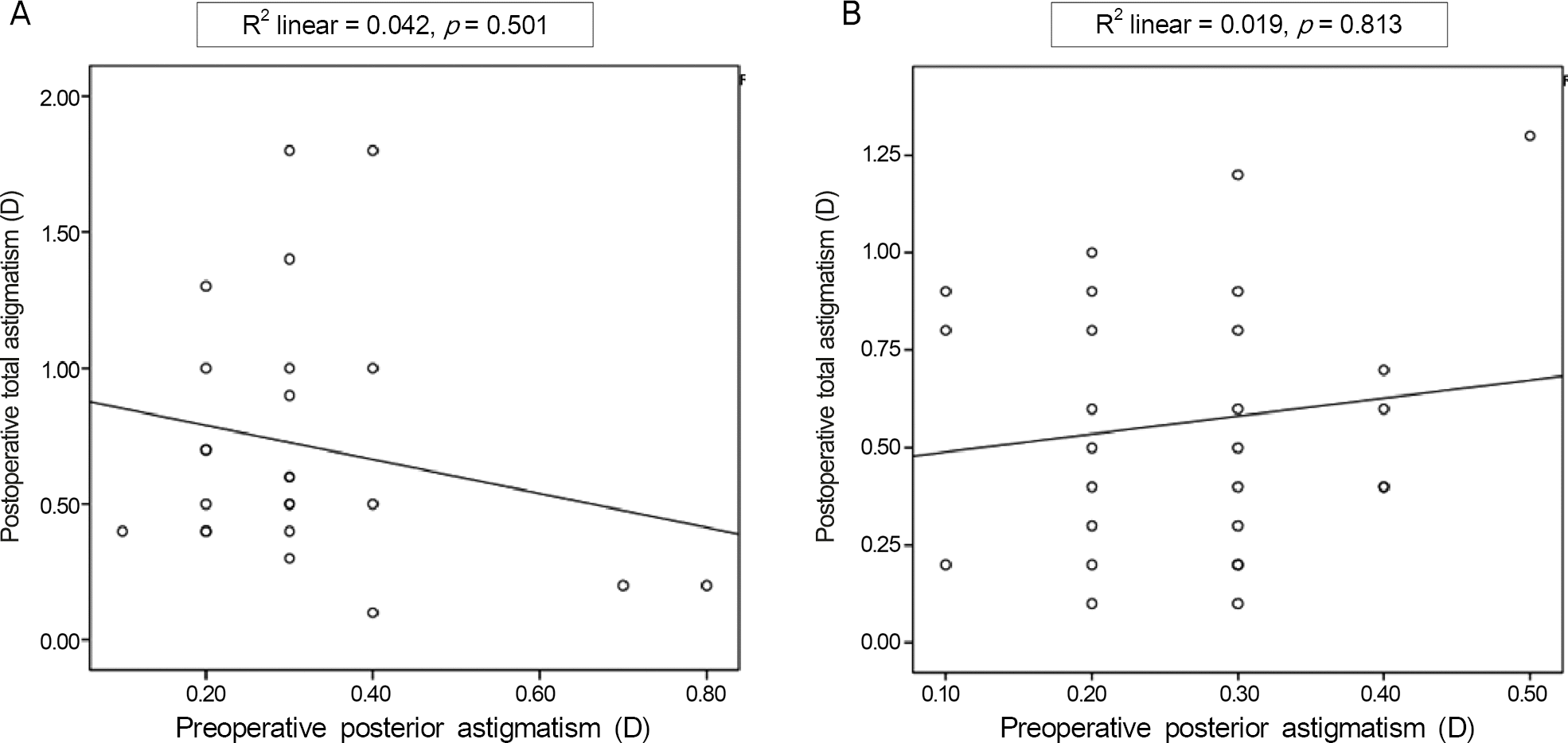
Table 1.
Preoperative clinical characteristics of each group
| Group 1 (n = 33) | Group 2 (n = 19) | p-value | Total group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (female:male) | 24:9 | 13:6 | 0.692 | 37:15 |
| Age (years) | 65.7 ± 12.4 | 69.1 ± 7.5 | 0.290† | 66.91 ± 10.93 |
| Laterality (right eye:left eye) | 14:19 | 7:12 | 0.606* | 21:31 |
| BCVA (log MAR) | 0.31 ± 0.23 | 0.31 ± 0.57 | 1.000‡ | 0.31 ± 0.38 |
| IOP (mm Hg) | 13.3 ± 2.8 | 14.4 ± 2.8 | 0.153† | 13.6 ± 3.1 |
| Axial length (mm) | 24.27 ± 2.06 | 23.70 ± 1.85 | 0.324‡ | 24.06 ± 1.99 |
| ACD (mm) | 2.63 ± 0.60 | 2.59 ± 0.43 | 0.822† | 2.62 ± 0.54 |
| Central corneal thickness (μ m) | 546 ± 41 | 545 ± 29 | 0.923† | 545 ± 37 |
| Corneal endothelium cell density (cells/mm2) | 2,706 ± 485 | 2,880 ± 343 | 0.174† | 2,768 ± 444 |
| Corneal astigmatism (algebraic value, D) | ||||
| Anterior | 0.55 ± 0.44 | -0.48 ± 0.46 | 0.000† | 0.18 ± 0.67 |
| Posterior | 0.31 ± 0.14 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.124‡ | 0.29 ± 0.13 |
| Total | 0.30 ± 0.72 | -0.51 ± 0.65 | 0.000† | 0.04 ± 0.79 |
Table 2.
Preoperative and postoperative corneal astigmatism (algebraic value)
Table 3.
Comparison of preoperative and postoperative 2 month corneal astigmatism (algebraic value)
| Pre-op | Post-op 2 months | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Anterior (D) | 0.55 ± 0.44 | 0.51 ± 0.67 | 0.706* |
| Posterior (D) | 0.31 ± 0.14 | 0.31 ± 0.15 | 1.000† | |
| Total (D) | 0.30 ± 0.72 | 0.35 ± 0.81 | 0.701* | |
| Group 2 | Anterior (D) | -0.48 ± 0.46 | -0.17 ± 0.68 | 0.036† |
| Posterior (D) | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.25 ± 0.13 | 0.867* | |
| Total (D) | -0.51 ± 0.65 | -0.30 ± 0.55 | 0.216* | |
| Total group | Anterior (D) | 0.18 ± 0.67 | 0.26 ± 0.75 | 0.335* |
| Posterior (D) | 0.29 ± 0.13 | 0.29 ± 0.14 | 0.926* | |
| Total (D) | -0.01 ± 0.80 | 0.11 ± 0.78 | 0.293* |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download