Abstract
Purpose
We investigated the incidence of retinal lesions before and after surgery and the percentage of preoperative prophy-lactic laser treatment in patients who underwent corneal refractive surgery or phakic intraocular lens implantation (pIOLi).
Methods
The medical records of patients who underwent refractive surgery from January 2005 to June 2013 were reviewed retrospectively. We investigated the incidence and type of retinal lesions identified during the preoperative examination. Additionally, the percentage of preoperative prophylactic laser treatment and the incidence of postoperative newly developed retinal lesions were analyzed.
Results
A total of 894 eyes of 466 subjects (laser in situ keratomileusis [LASIK] 225 eyes, 117 subjects; laser-assisted sub-epithelial keratectomy [LASEK] or photorefractive keratectomy [PRK] 450 eyes, 231 subjects; pIOLi 219 eyes, 121 subjects) were enrolled in the present study. Retinal lesions were found in 268 eyes (29.98%) and of those, 144 eyes (16.11%) received prophylactic laser treatment. Postoperative newly developed retinal lesions were detected in 8 cases (LASEK or PRK, 5 cases; pIOLi, 3 cases) during the follow-up period. There was a significant correlation between preoperative spherical equivalent and the presence of retinal lesions.
Conclusions
The patient population of refractive surgery is largely myopic and thus particularly vulnerable to retinal lesions. Additionally, a considerable number of patients required preoperative prophylactic laser treatment. Therefore, both surgeons and patients should be aware of the risks of developing postoperative retinal lesions.
Go to : 
References
1. Trokel SL, Srinivasan R, Braren B. Excimer laser surgery of the cornea. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983; 96:710–5.

2. Knorz MC, Liermann A, Seiberth V. . Laser in situ keratomi-leusis to correct myopia of -6.00 to -29.00 diopters. J Refract Surg. 1996; 12:575–84.

3. Ambrósio R Jr, Wilson S. LASIK vs LASEK vs PRK: advantages and indications. Semin Ophthalmol. 2003; 18:2–10.
4. Pallikaris IG, Papatzanaki ME, Stathi EZ. . Laser in situ keratomileusis. Lasers Surg Med. 1990; 10:463–8.

5. Curtin BJ. The Myopias: Basic Science and Clinical Management, 1st ed. Philadelphia: Harpercollins College Division,. 1985; 333–48.
6. Wilkinson CP. Evidence-based analysis of prophylactic treatment of asymptomatic retinal breaks and lattice degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:12–5. discussion 15-8.

7. Wilkinson C. Interventions for asymptomatic retinal breaks and lattice degeneration for preventing retinal detachment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; ((1)):CD003170.

8. Karlin DB, Curtin BJ. Peripheral chorioretinal lesions and axial length of the myopic eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976; 81:625–35.

9. Burton TC. The influence of refractive error and lattice degener-ation on the incidence of retinal detachment. Trans Am Ophthal-mol Soc. 1989; 87:143–55. discussion 155-7.
10. Arevalo JF, Ramirez E, Suarez E. . Incidence of vitreoretinal pathologic conditions within 24 months after laser in situ keratomileusis. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:258–62.

11. Ozdamar A, Aras C, Sener B. . Bilateral retinal detachment as-sociated with giant retinal tear after laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis. Retina. 1998; 18:176–7.

12. Ruiz-Moreno JM, Pérez-Santonja JJ, Alió JL. Retinal detachment in myopic eyes after laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 128:588–94.

13. Charteris DG, Cooling RJ, Lavin MJ, McLeod D. Retinal detach-ment following excimer laser. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997; 81:759–61.

14. Alió JL, de la Hoz F, Pérez-Santonja JJ. . Phakic anterior cham-ber lenses for the correction of myopia: a 7-year cumulative analy-sis of complications in 263 cases. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:458–66.
15. Pesando PM, Ghiringhello MP, Tagliavacche P. Posterior chamber collamer phakic intraocular lens for myopia and hyperopia. J Refract Surg. 1999; 15:415–23.
16. Lee SG, Hwang BN, Her J, Yun IH. Clinical analysis of rhegma-tougenous retinal detachment after laser refractive surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:2769–74.
17. Han HS, Song JS, Kim HM. Long-term results of laser in situ kera-tomileusis for high myopia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2000; 14:1–6.

18. Seiler T, McDonnell PJ. Excimer laser photorefractive keratec-tomy. Surv Ophthalmol. 1995; 40:89–118.

19. Gobbi PG, Carones F, Brancato R. . Acoustic transients follow-ing excimer laser ablation of the cornea. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1995; 5:275–6.

20. Krueger RR, Seiler T, Gruchman T. . Stress wave amplitudes during laser surgery of the cornea. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:1070–4.

21. Haimann MH, Burton TC, Brown CK. Epidemiology of retinal detachment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:289–92.

22. Ruiz-Moreno JM, Alió JL, Pérez-Santonja JJ, de la Hoz F. Retinal detachment in phakic eyes with anterior chamber intraocular lenses to correct severe myopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 127:270–5.

23. Martinez-Castillo V, Boixadera A, Verdugo A. . Rhegmatogen-ous retinal detachment in phakic eyes after posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation for severe myopia. Ophthal-mology. 2005; 112:580–5.
Go to : 
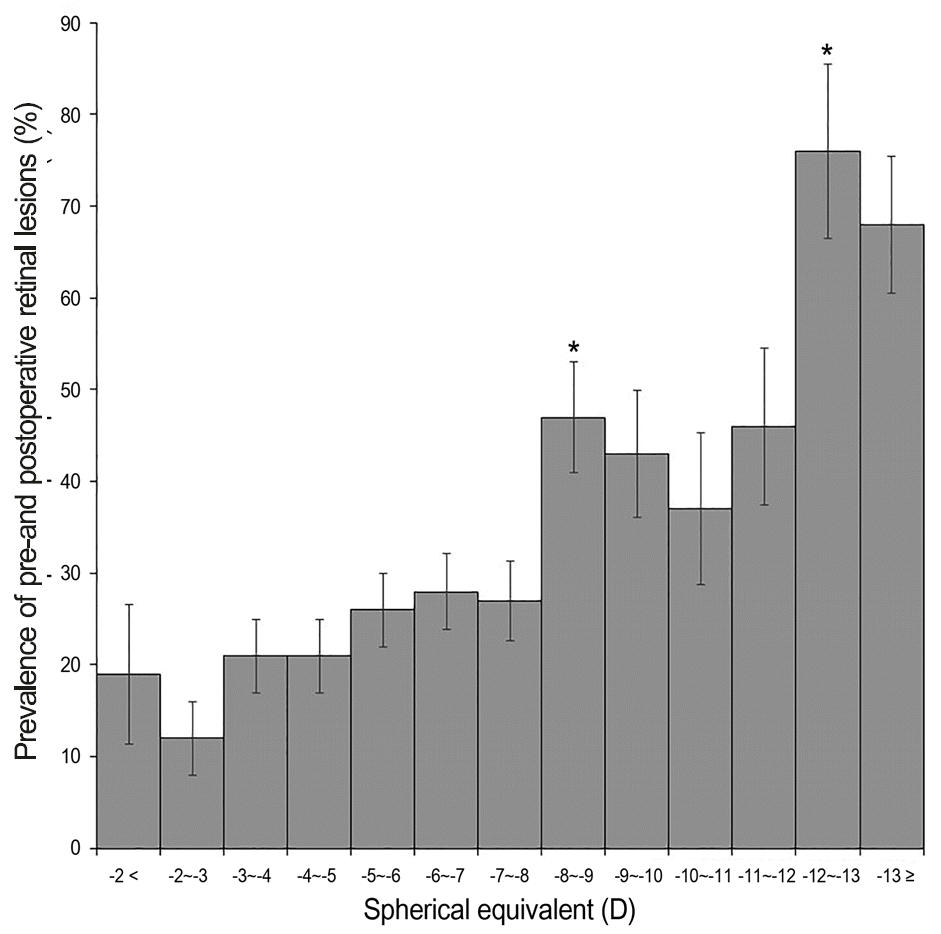 | Figure 1.Changes in prevalence of pre- and postoperative reti-nal lesions according to spherical equivalent. * p < 0.05 com-pared with previous subgroup, independent t-test. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of patients based on different type of surgery
| LASIK | LASEK or PRK | pIOLi | Total | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes (subjects, n) | 225 (117) | 450 (231) | 219 (121) | 894 (466) | |
| Age (years) | 26.76 ± 6.16 | 26.92 ± 6.30 | 28.32 ± 6.16 | 27.24 ± 6.25 | 0.09* |
| Men:women | 34:82 | 71:158 | 37:84 | 142:324 | 0.95† |
| SE (D) | -5.49 ± 2.17 | -5.18 ± 1.96 | -10.78 ± 3.33 | -6.61 ± 3.42 | <0.05* |
| ACD (mm) | 3.43 ± 0.36 | 3.14 ± 0.27 | 3.47 ± 0.37 | 3.29 ± 0.36 | <0.05* |
| Retinal lesions (n, %) | 40 (17.78) | 129 (28.67) | 99 (45.21) | 268 (29.98) | <0.05† |
Table 2.
The correlation between characteristics of patients and presence of pre- and postoperative retinal lesions
|
Presence of pre- and postoperative retinal lesions |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-value* | |
| Age | 1.01 | 0.98-1.03 | 0.54 |
| Sex | |||
| Men vs. women | 0.92 | 0.66-1.27 | 0.61 |
| Type of surgery | |||
| Corneal refractive surgery vs. pIOLi | 0.97 | 0.60-1.56 | 0.89 |
| SE | 0.83 | 0.78-0.88 | <0.05 |
| ACD | 0.79 | 0.51-1.23 | 0.31 |
Table 3.
Type of preoperative retinal lesions
| Types of lesion (n) |
No. of eyes |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LASIK | LASEK or PRK | pIOLi | Total | |
| Lattice degeneration | 28 | 87 | 57 | 172 |
| Retinal thinning | 3 | 12 | 5 | 20 |
| Lattice with retinal hole | 3 | 7 | 18 | 28 |
| PVD | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Retinal hole | 1 | 4 | 8 | 13 |
| Retinal tear | 4 | 4 | 8 | |
| Other retinal lesions | 4* | 14† | 7‡ | 25 |
| Total | 40 | 129 | 99 | 268 |
LASIK = laser in situ keratomileusis; LASEK = laser-assisted subepithelial keratectomy; PRK = photorefractive keratectomy; pIOLi = phakic intraocular lens implantation; PVD = posterior vitreous detachment.
Table 4.
The number of eyes with preoperative prophylactic laser treatment and the ratio of that to the number of retinal lesions
| Types of lesion (n) |
No. of eyes (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LASIK | LASEK or PRK | pIOLi | Total | |
| Lattice degeneration | 23 | 36 | 34 | 93 (54.07) |
| Retinal thinning | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 (15) |
| Lattice with retinal hole | 3 | 6 | 17 | 26 (92.86) |
| PVD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Retinal hole | 1 | 3 | 8 | 12 (92.31) |
| Retinal tear | 0 | 4 | 4 | 8 (100) |
| Other retinal lesions | 1* | 1† | 0 | 2 (8) |
| Total | 29 (72.5) | 52 (40.31) | 64 (64.64) | 144 (53.73) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download