Abstract
Purpose
To compare the corneal higher-order aberrations (HOAs) of normal young subjects using Galilei TM G4 (Zeimer, Port, Switzerland) and Pentacam® (Oculus Inc., Wetzlar, Germany).
Methods
Corneal HOAs were measured using Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam® in 41 healthy individuals (41 eyes). Intraclass corre-lation coefficients (ICCs) were obtained to evaluate the repeatability of the 2 devices. Differences in HOAs between the 2 instru-ments were analyzed with a paired t-test and correlations evaluated.
Results
All ICCs measured using Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam® showed more than moderate repeatability (>0.81) except trefoil, tetrafoil, 4th and 5th HOAs. When comparing the measurements obtained with Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam®, total HOAs, spher-ical aberration (SA), secondary astigmatism and 5th total HOAs were statistically significantly different between the 2 device (all p ≤ 0.001). In addition, Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam® showed discrepancy among all corneal HOAs items. Although the total cor-neal HOAs and the SA were significantly correlated, other HOA measurements generally exhibited a low correlation.
References
1. Lombardo M, Lombardo G. Wave aberration of human eyes and new descriptors of image optical quality and visual performance. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:313–31.

2. Artal P, Guirao A, Berrio E, Williams DR. Compensation of cor-neal aberrations by the internal optics in the human eye. J Vis. 2001; 1:1–8.

3. Campbell CE. A new method for describing the aberrations of the eye using Zernike polynomials. Optom Vis Sci. 2003; 80:79–83.

4. Barkana Y, Gerber Y, Elbaz U. . Central corneal thickness measurement with the Pentacam Scheimpflug system, optical low- coherence reflectometry pachymeter, and ultrasound pachymetry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1729–35.
5. Lee YE, Jun RM. The intra and inter-examiner repeatability of cor-neal parameters obtained by GALILEI(TM) in normal subjects. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1611–16.
6. Burakgazi AZ, Tinio B, Bababyan A. . Higher order aberra-tions in normal eyes measured with three different aberrometers. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:898–903.

7. Yum JH, Choi SK, Kim JH, Lee DH. Comparison of aberrations in Korean normal eyes measured with two different aberrometers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1789–94.

8. Knapp S, Awwad ST, Ghali C, McCulley JP. Ocular aberrations measured by the Fourier-based WaveScan and Zernike-based LADARWave Hartmann-Shack aberrometers. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:201–9.

9. Shin JY, Lee MY, Chung SH. Comparison of keratometry and cor-neal higher order aberrations between Scout videokeratoscope and Pentacam Scheimpflug camera. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1758–64.

10. McGraw KO, Wong SP. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychological Methods. 1996; 1:30.

11. Williams D, Yoon GY, Porter J. . Visual benefit of correcting higher order aberrations of the eye. J Refract Surg. 2000; 16:S554–9.

12. Artal P, Berrio E, Guirao A, Piers P. Contribution of the cornea and internal surfaces to the change of ocular aberrations with age. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2002; 19:137–43.

13. López-Miguel A, Maldonado MJ, Belzunce A. . Precision of a commercial hartmann-shack aberrometer: limits of total wavefront laser vision correction. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012; 154:799–807.e5.

14. Aramberri J, Araiz L, Garcia A. . Dual versus single Scheimpflug camera for anterior segment analysis: precision and agreement. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:1934–49.

15. Cerviño A, Dominguez-Vicent A, Ferrer-Blasco Blasco. . Intrasubject repeatability of corneal power, thickness, and wavefront aberra-tions with a new version of a dual rotating Scheimpflug-Placido system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:186–92.

16. Wang L, Shirayama M, Koch DD. Repeatability of corneal power and wavefront aberration measurements with a dual-Scheimpflug Placido corneal topographer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:425–30.

17. Netto MV, Ambrósio R Jr, Shen TT, Wilson SE. Wavefront analy-sis in normal refractive surgery candidates. J Refract Surg. 2005; 21:332–8.

18. Yoon G, Macrae S, Williams DR, Cox IG. Causes of spherical aberration induced by laser refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:127–35.

Figure 1.
Bland-Altman plots showing the agreement between mean corneal aberrometers (μ m) obtained by the 2 tomography de-vices: Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam®. (A-F) graphs plot the difference against the average of two measurements of corneal HOAs, with 95% limits of agreement (broken lines) and the mean difference (black line). (A) Total corneal HOAs, (B) Coma, (C) Trefoil, (D) Spherical aberration, (E) Secondary astigmatism, (F) Tetrafoil. HOAs = higher-order aberrations; SA = spherical aberration; 2° astig = secondary astigmatism.
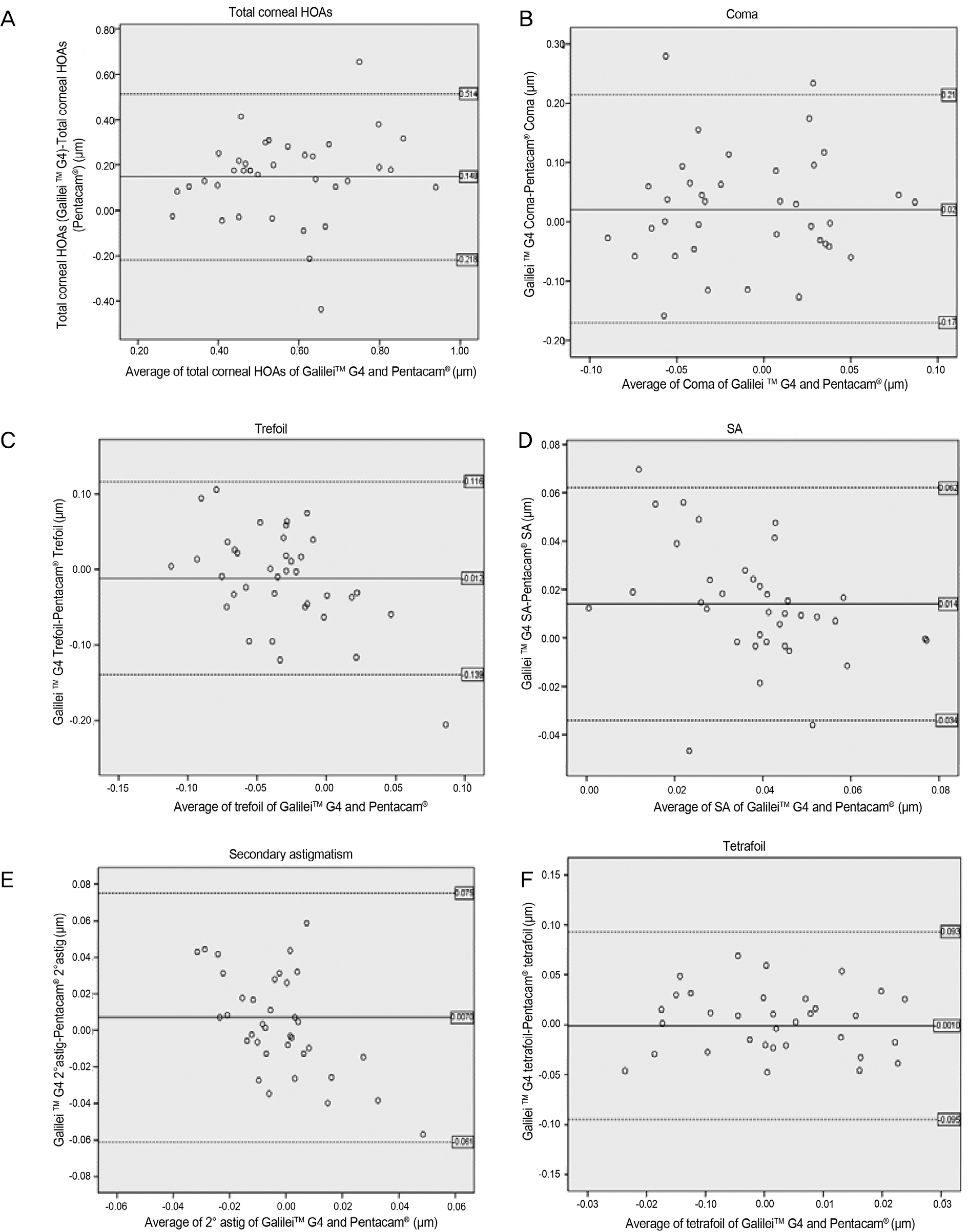
Figure 2.
Correlations of measurements of corneal aberration using Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam®. (A-F) Shows measurements of total corneal HOAs using Galilei TM G4 against Pentacam® measurements. (A) Total corneal HOAs, (B) Coma, (C) Trefoil, (D) Spherical aberration, (E) Secondary astigmatism, (F) Tetrafoil. HOAs = higher-order aberrations; SA = spherical aberration; 2° astig = sec-ondary astigmatism; r = Pearson correlation coefficient. * Statistically significant ( p-value < 0.05, based on t-test).
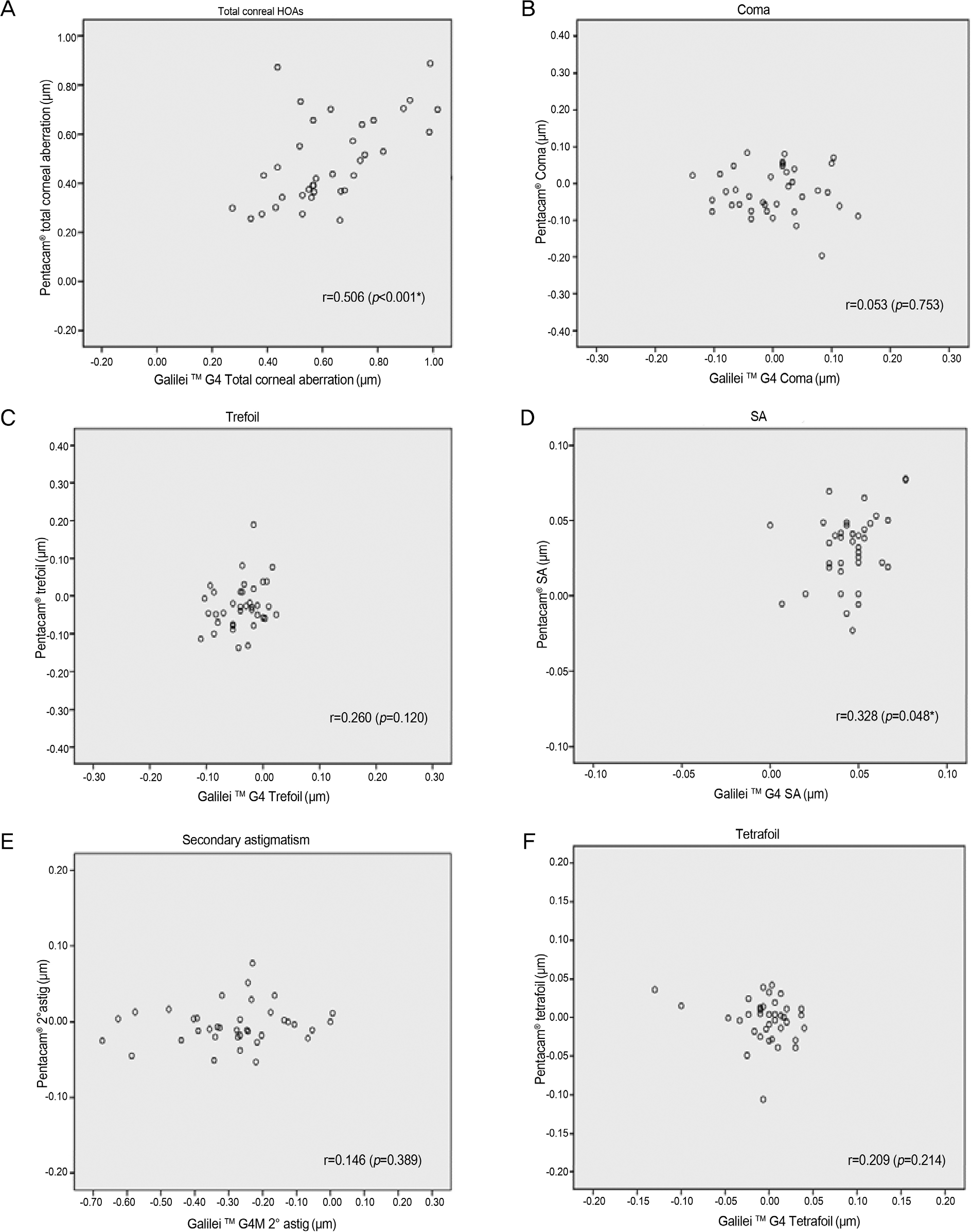
Table 1.
Demographics of subjects
| Data | |
|---|---|
| No. of subjects (eyes) | 41 (41) |
| Age (years) | 27.76 ± 4.04 (19-35) |
| Male:female | 14:27 |
| SE (diopter) | -1.87 ± 2.33 (-6.0 ± 5.0) |
Table 2.
Intra-examiner ICC of corneal HOAs using Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam®
Table 3.
The comparison of corneal HOAs between the Galilei TM G4 and Pentacam®
| Pentacam® | Galilei TM G4 | p-value* | Mean difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total corneal HOAs (μ m) | 0.490 ± 0.175 | 0.638 ± 0.200 | <0.001 | 0.148 ± 0.366 |
| 3rd order HOA (μ m) | 0.114 ± 0.047 | 0.131 ± 0.052 | 0.141 | 0.016 ± 0.129 |
| Coma Z (3, 1) (μ m) | -0.022 ± 0.063 | 0.002 ± 0.068 | 0.141 | -0.024 ± 0.190 |
| Trefoil Z (3, 3) (μ m) | -0.027 ± 0.063 | -0.039 ± 0.036 | 0.272 | -0.012 ± 0.128 |
| 4th order HOA (μ m) | 0.074 ± 0.026 | 0.083 ± 0.027 | 0.170 | -0.009 ± 0.073 |
| SA Z (4, 0) (μ m) | 0.032 ± 0.024 | 0.045 ± 0.016 | 0.001 | -0.014 ± 0.048 |
| 2° astig Z (4, 2) (μ m) | -0.004 ± 0.026 | -0.003 ± 0.025 | 0.219 | -0.007 ± 0.068 |
| Tetrafoil Z (4, 4) (μ m) | -0.029 ± 0.028 | -0.004 ± 0.033 | 0.872 | -0.001 ± 0.094 |
| 5th order HOA (μ m) | 0.025 ± 0.012 | 0.037 ± 0.018 | <0.001 | -0.013 ± 0.037 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download