Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effects of benzalkonium chloride (BAC), mitomycin C (MMC) and dexamethasone (DEX) on cellular stress in cultured human trabecular meshwork cell (HTMC) monolayers.
Methods
HTMCs were cultured in the inner Transwell chamber until confluence and then were exposed to BAC, MMC or DEX for 6 hours. The carboxyfluorescein permeability through the HTMC monolayer was measured using a spectrofluorometer at 532 nm after 2 hours in the outer chamber. The 3-[4, 5 -dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was used to evaluate cellular viabilities.
Results
The carboxyfluorescein permeability through the HTMC monolayer increased and cell survival decreased with 0.002% BAC (p < 0.05). Increased permeability without decreasing cell survival occurred with 0.05 μ g/mL MMC. No effect on the permeability or cell survival was observed at 0.1 or 1.0 μ m DEX (p > 0.05).
Go to : 
References
1. Alvarado J, Murphy C, Juster R. Trabecular meshwork cellularity in primary open-angle glaucoma and nonglaucomatous normals. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:564–79.

2. Rohen JW, Lütjen-Drecoll E, Flügel C. . Ultrastructure of the trabecular meshwork in untreated cases of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG). Exp Eye Res. 1993; 56:683–92.
3. Hamard P, Blondin C, Debbasch C. . In vitro effects of preserved and unpreserved antiglaucoma drugs on apoptotic marker expression by human trabecular cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2003; 241:1037–43.

4. Yee RW. The effect of drop vehicle on the efficacy and side effects of topical glaucoma therapy: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007; 18:134–9.

6. Doucet O, Lanvin M, Thillou C. . Reconstituted human corneal epithelium: a new alternative to the Draize eye test for the assessment of the eye irritation potential of chemicals and cosmetic products. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006; 20:499–512.

7. Khoh-Reiter S, Jessen BA. Evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of ophthalmic solutions containing benzalkonium chloride on corneal epithelium using an organotypic 3-D model. BMC Ophthalmol. 2009; 9:5.

8. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983; 65:55–63.

9. Freimoser FM, Jakob CA, Aebi M, Tuor U. The MTT [3-(4,5-di-methylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay is a fast and reliable method for colorimetric determination of fungal cell densities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999; 65:3727–9.

10. Grimes PA, Stone RA, Laties AM, Li W. Carboxyfluorescein. A probe of the blood-ocular barriers with lower membrane permeability than fluorescein. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:635–9.
11. Araie M. Carboxyfluorescein. A dye for evaluating the corneal endothelial barrier function in vivo. Exp Eye Res. 1986; 42:141–50.

12. Araie M. Barrier function of corneal endothelium and the intra-ocular irrigating solutions. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:435–8.

13. Tsuboi S, Pederson JE. Permeability of the isolated dog retinal pigment epithelium to carboxyfluorescein. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986; 27:1767–70.
14. Blair NP, Rusin MM. Blood-retinal barrier permeability to carbox-yfluorescein and fluorescein in monkeys. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1986; 224:419–22.

15. Grimes PA. Carboxyfluorescein transfer across the blood-retinal barrier evaluated by quantitative fluorescence microscopy: comparison with fluorescein. Exp Eye Res. 1988; 46:769–83.

16. Grimes PA. Carboxyfluorescein distribution in ocular tissues of normal and diabetic rats. Curr Eye Res. 1988; 7:981–8.

17. Kimura M, Araie M, Koyano S. Movement of carboxyfluorescein across retinal pigment epithelium-choroid. Exp Eye Res. 1996; 63:51–6.

18. Lei Y, Stamer WD, Wu J, Sun X. Oxidative stress impact on barrier function of porcine angular aqueous plexus cell monolayers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013; 54:4827–35.

19. Burke AG, Zhou W, O'Brien ET. . Effect of hydrostatic pressure gradients and Na2EDTA on permeability of human Schlemm's canal cell monolayers. Curr Eye Res. 2004; 28:391–8.

Go to : 
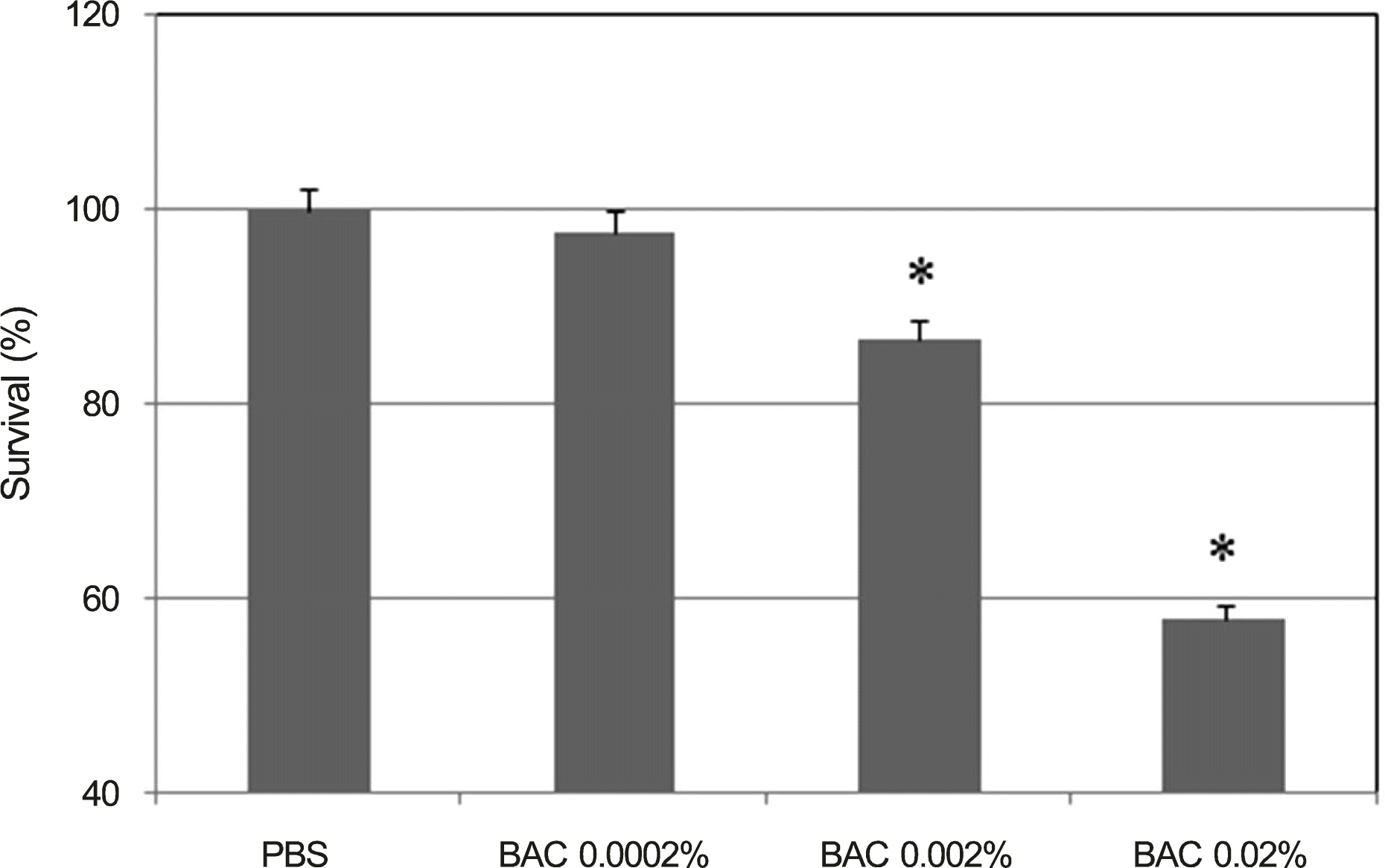 | Figure 1.Effects of benzalkonium chloride (BAC) on the survival of trabecular meshwork cells. BAC concentrations more than 0.002% decreased cellular viability significantly (* p < 0.05). PBS = phosphate buffered saline. |
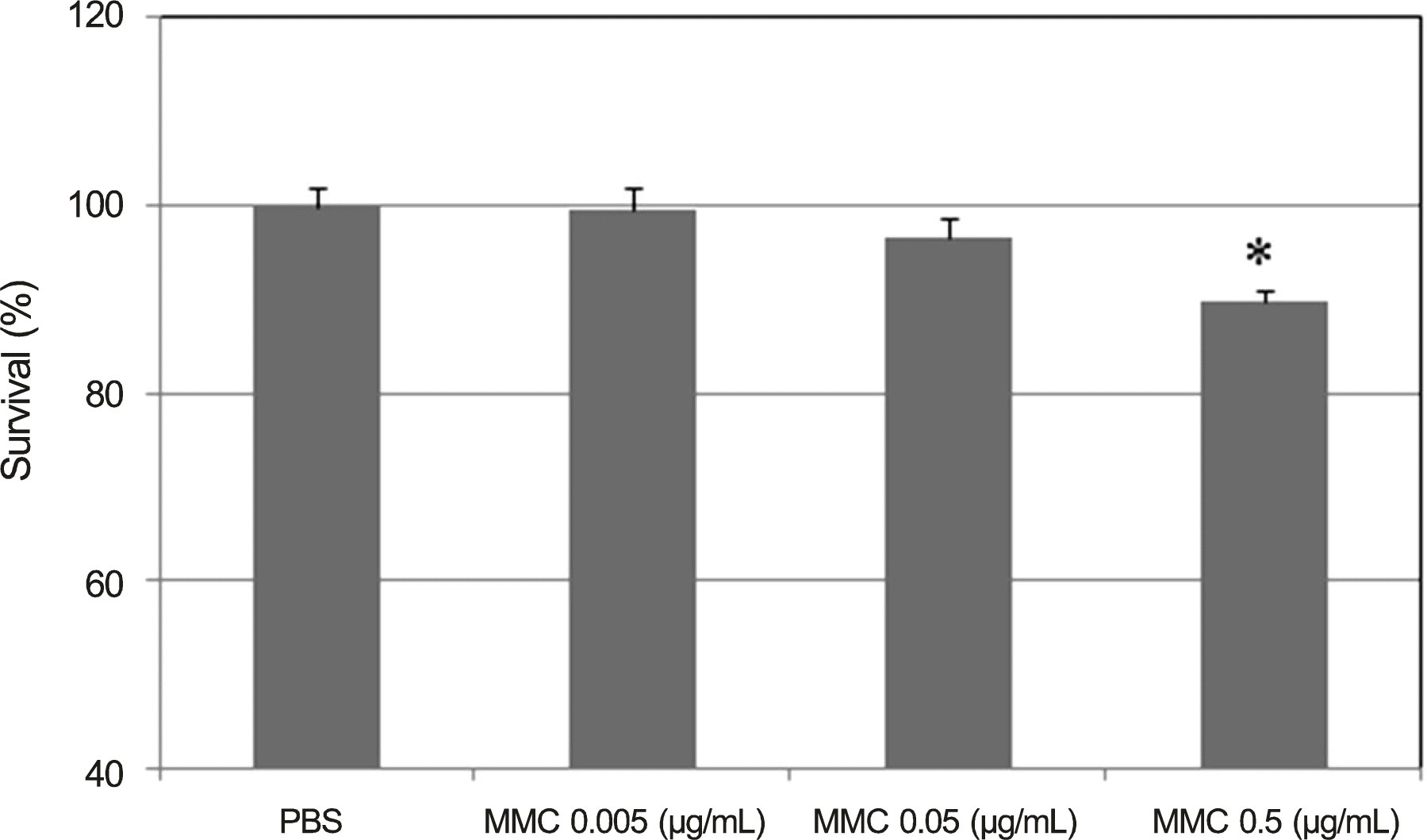 | Figure 2.Effects of mitomycin C (MMC) on the survival of trabecular meshwork cells. 0.5 μ g/mL MMC decreased cellular viability significantly (* p < 0.05). PBS = phosphate buffered saline. |
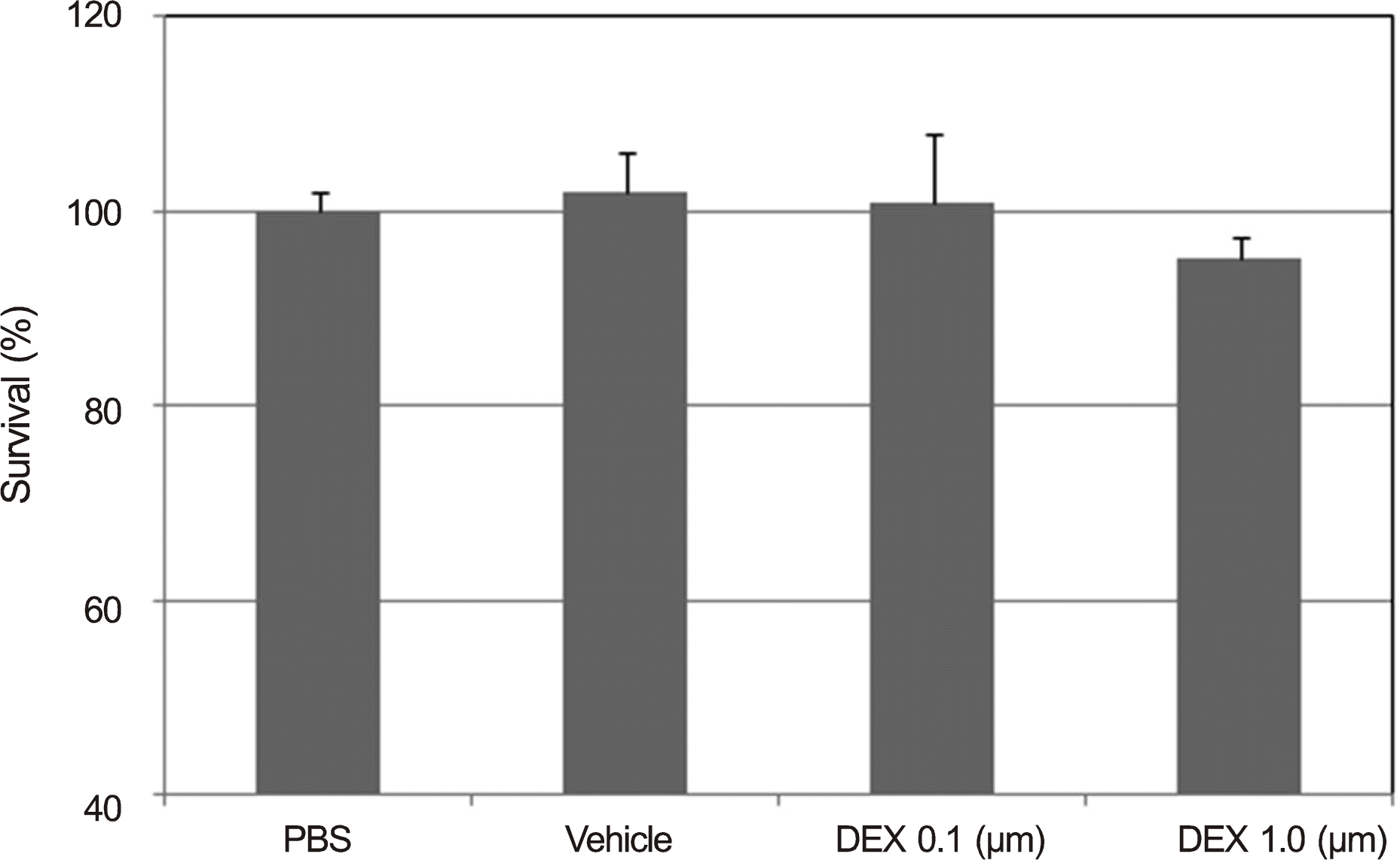 | Figure 3.Effects of dexamethasone (DEX) or 0.06% ethanol (vehicle) on the survival of trabecular meshwork cells. Both 0.1 or 1.0 μ m DEX showed no significant effects on the cellular viability (p > 0.05). PBS = phosphate buffered saline. |
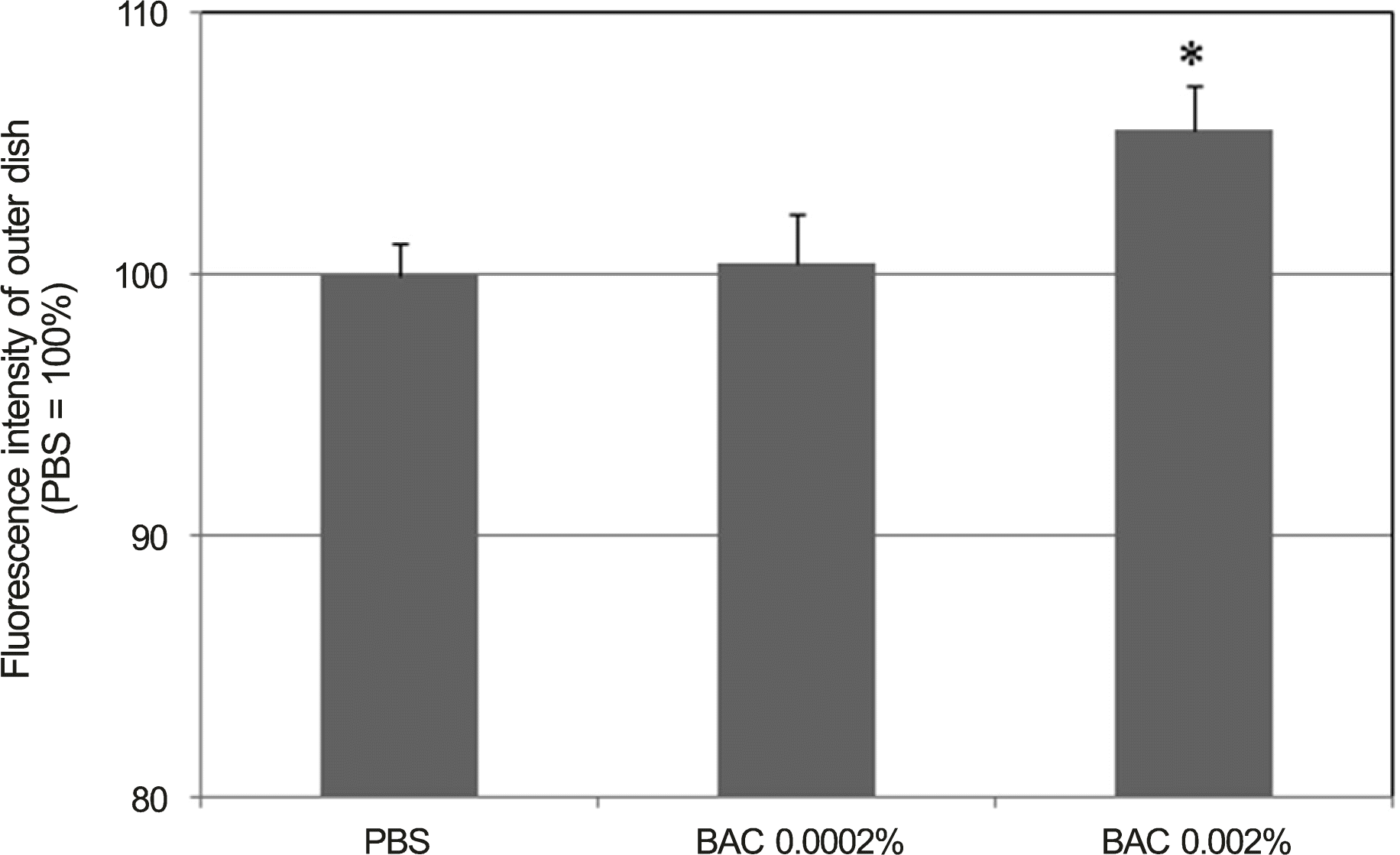 | Figure 4.Effects of benzalkonium chloride (BAC) on the permeability of carboxyfluorescin through the trabecular mesh-work cell monolayer. 0.002% BAC increased permeabilty of carboxyfluorescein significantly (* p < 0.05). Carboxyfluorescein intensity of outer chamber normalized to the mean value obtained using PBS (permeability 100%). PBS = phosphate buffered saline. |
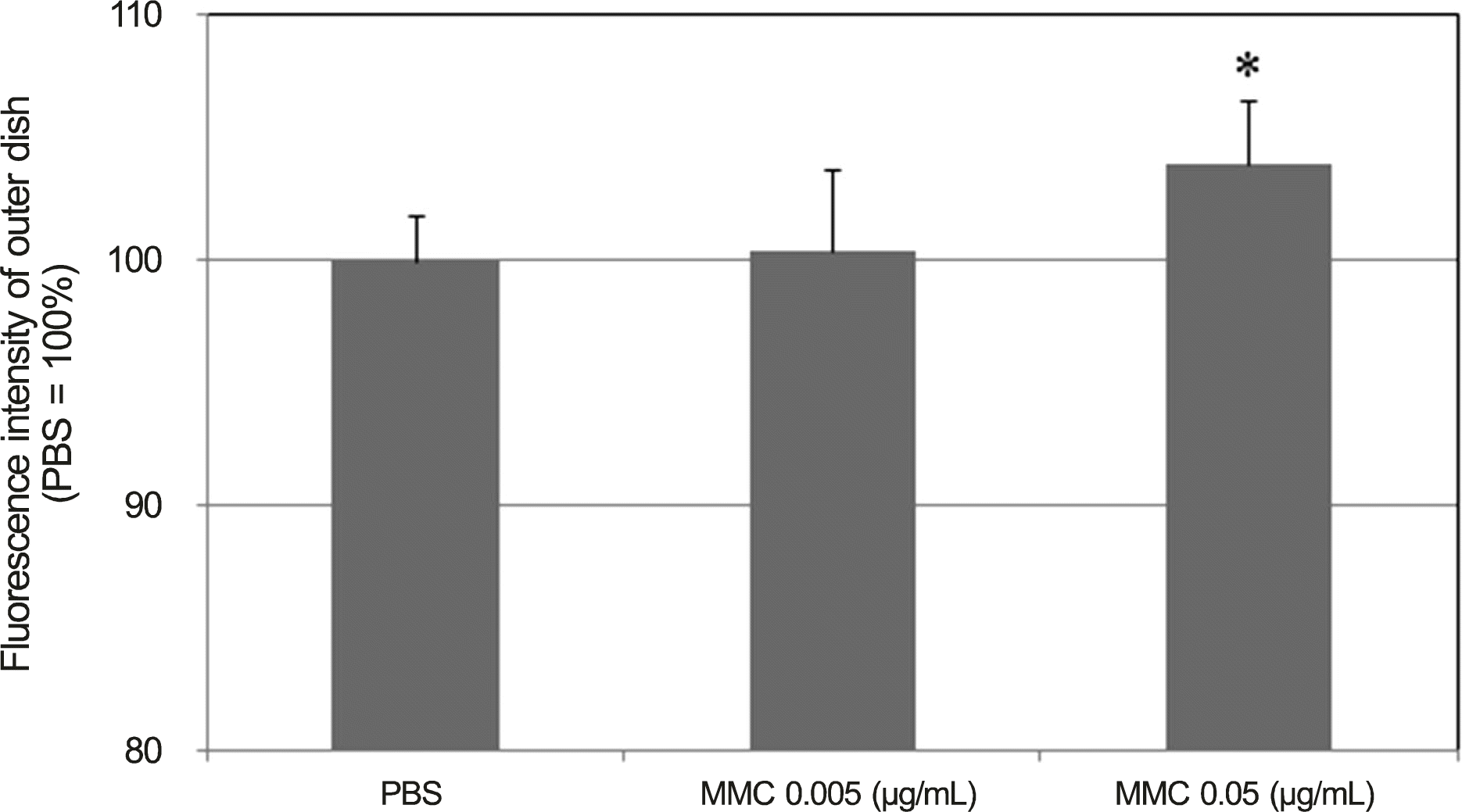 | Figure 5.Effects of mitomycin C (MMC) on the permeability of carboxyfluorescin through the trabecular meshwork cell monolayer. 0.05 μ g/mL MMC increased permeabilty of car-boxyfluorescein significantly (* p < 0.05). Carboxyfluorescein intensity of outer chamber normalized to the mean value obtained using PBS (permeability 100%). PBS = phosphate buffered saline. |
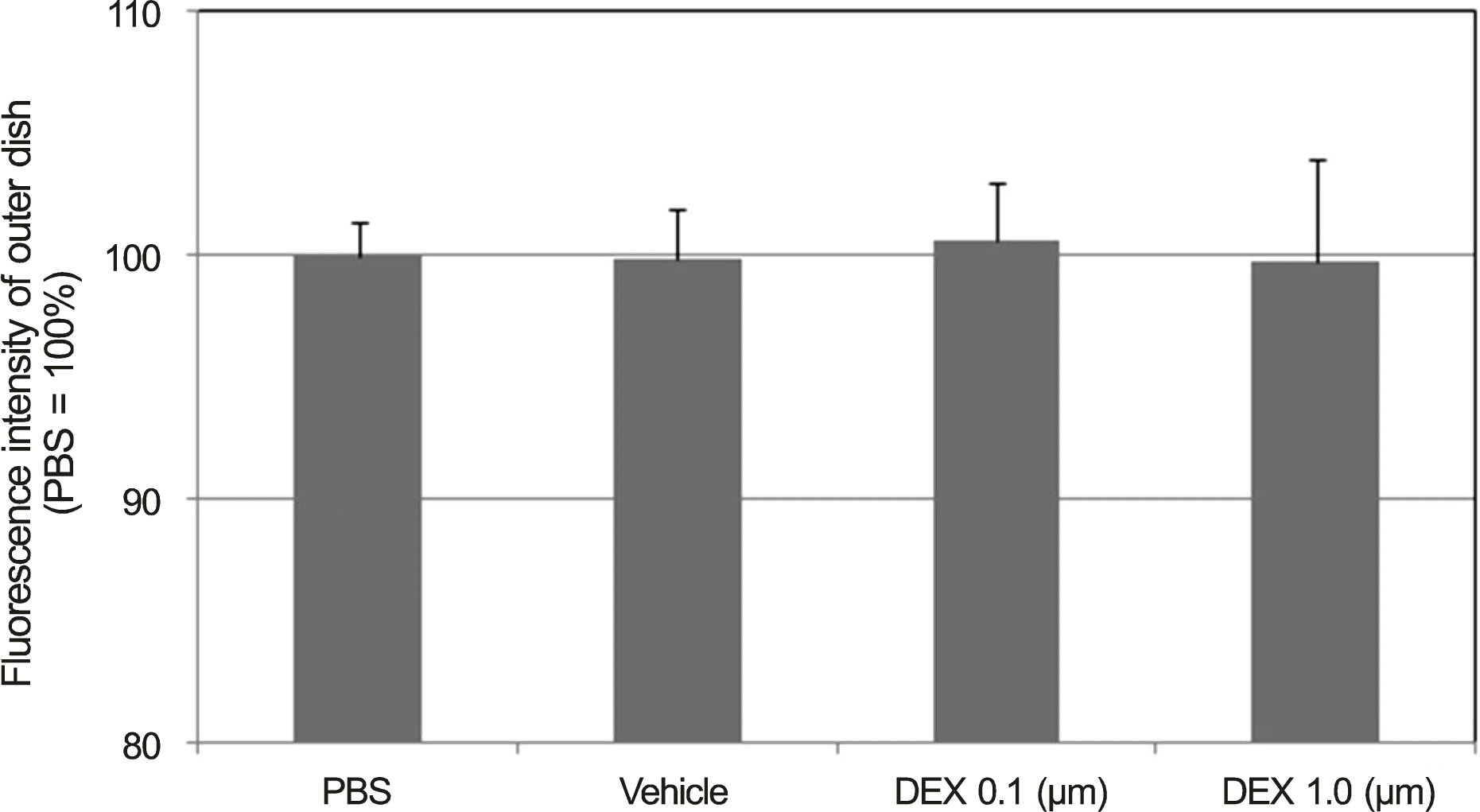 | Figure 6.Effects of dexamethasone (DEX) on the permeability of carboxyfluorescin through the trabecular meshwork cell monolayer. Both 0.1 or 1.0 μ m DEX showed no significant effects on the permeabilty of carboxyfluorescein (p > 0.05). Carboxyfluorescein intensity of outer chamber normalized to the mean value obtained using PBS (permeability 100%). PBS = phosphate buffered saline. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download