1. Woodward MA, Randleman JB, Stulting RD. Dissatisfaction after multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:992–7.

2. Mester U, Hunold W, Wesendahl T, Kaymak H. Functional outcomes after implantation of Tecnis ZM900 and Array SA40 multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1033–40.

3. de Vries NE, Nuijts RM. Multifocal intraocular lenses in cataract surgery: literature review of benefits and side effects. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:268–78.

4. McAlinden C, Moore JE. Multifocal intraocular lens with a sur-face-embedded near section: Short-term clinical outcomes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:441–5.

5. Alió JL, Plaza-Puche AB, Piñero DP, et al. Comparative analysis of the clinical outcomes with 2 multifocal intraocular lens models with rotational asymmetry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1605–14.

6. Muñoz G, Albarrán-Diego C, Ferrer-Blasco T, et al. Visual function after bilateral implantation of a new zonal refractive aspheric multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:2043–52.

7. Alfonso JF, Fernández-Vega L, Blázquez JI, Montés-Micó R. Visual function comparison of 2 aspheric multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:242–8.

8. Alió JL, Plaza-Puche AB, Montalban R, Javaloy J. Visual outcomes with a single-optic accommodating intraocular lens and a low-addition-power rotational asymmetric multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:978–85.

9. Kim SM, Kim CH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Visual outcome and patient satisfaction after implantation of multifocal IOLs: Three-month follow-up results. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:230–7.

10. Yoon SY, Song IS, Kim JY, et al. Bilateral mix-and-match versus unilateral multifocal intraocular lens implantation: long-term comparison. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1682–90.

11. Gwak JY, Choi JS, Pak KH, Baek NH. Visual and optical functions after diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:396–402.

12. Cheon MH, Lee JE, Kim JH, et al. One-year outcome of monocular implant of aspheric multifocal IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:822–8.

13. Rosa AM, Loureiro Silva MF, Lobo C, et al. Comparison of visual function after bilateral implantation of inferior sector-shaped near-addition and diffractive-refractive multifocal IOLs. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1653–9.

14. de Vries NE, Webers CA, Montés-Micó R, et al. Long-term follow-up of a multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1476–82.

15. Alio JL, Plaza-Puche AB, Javaloy J, et al. Comparison of a new refractive multifocal intraocular lens with an inferior segmental near add and a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:555–63.

16. Nanavaty MA, Spalton DJ, Marshall J. Effect of intraocular lens asphericity on vertical coma aberration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:215–21.

17. Nishi T, Nawa Y, Ueda T, et al. Effect of total higher-order aberrations on accommodation in pseudophakic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1643–9.

18. Nochez Y, Majzoub S, Pisella PJ. Effect of interaction of macro- aberrations and scattered light on objective quality of vision in pseudophakic eyes with aspheric monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:633–40.
19. Diaz-Valle D, Arriola-Villalobos P, García-Vidal SE, et al. Effect of lubricating eyedrops on ocular light scattering as a measure of vision quality in patients with dry eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:1192–7.

20. Cabot F, Saad A, McAlinden C, et al. Obj ective assessment of crystalline lens opacity level by measuring ocular light scattering with a double-pass system. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155:629–35.
21. Lee K, Ahn JM, Kim EK, Kim TI. Comparison of optical quality parameters and ocular aberrations after wavefront-guided laser in-situ keratomileusis versus wavefront-guided laser epithelial keratomileusis for myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:2163–9.

22. Saad A, Saab M, Gatinel D. Repeatability of measurements with a double-pass system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:28–33.

23. Castillo-Gómez A, Carmona-González D, Martínez-de-la-Casa JM, et al. Evaluation of image quality after implantation of 2 diffractive multifocal intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1244–50.

24. Yoon JU, Chung JL, Hong JP, et al. Comparison of wavefront analysis and visual function between monofocal and multifocal aspheric intraocular lenses. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2009; 50:195–201.

25. Ferreira TB, Marques EF, Rodrigues A, Montés-Micó R. Visual and optical outcomes of a diffractive multifocal toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1029–35.

26. Lee HS, Park SH, Kim MS. Clinical results and some problems of multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1235–41.

27. Kim JH, Lee JW, Chung JL, et al. Combined implantation of monofocal and multifocal intraocular lenses in senile cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1632–8.

28. Khoramnia R, Auffarth GU, Rabsilber TM, Holzer MP. Implantation of a multifocal toric intraocular lens with a surface-embedded near segment after repeated LASIK treatments. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2049–52.

29. Fernández-Vega L, Madrid-Costa D, Alfonso JF, et al. Optical and visual performance of diffractive intraocular lens implantation after myopic laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:825–32.

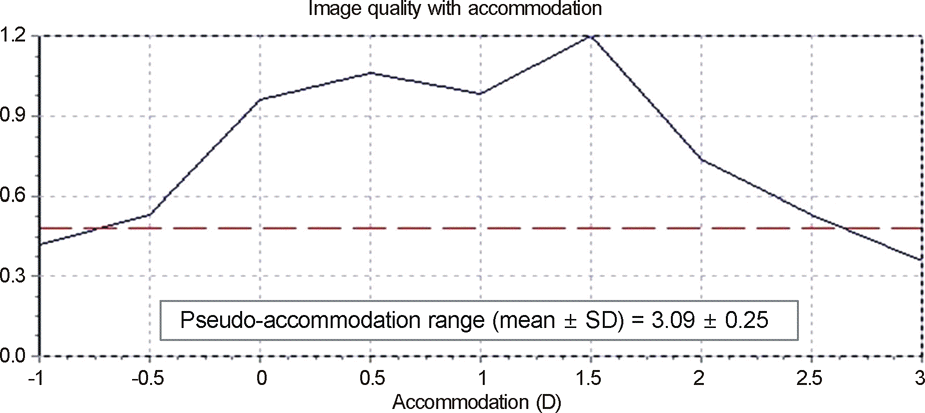




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



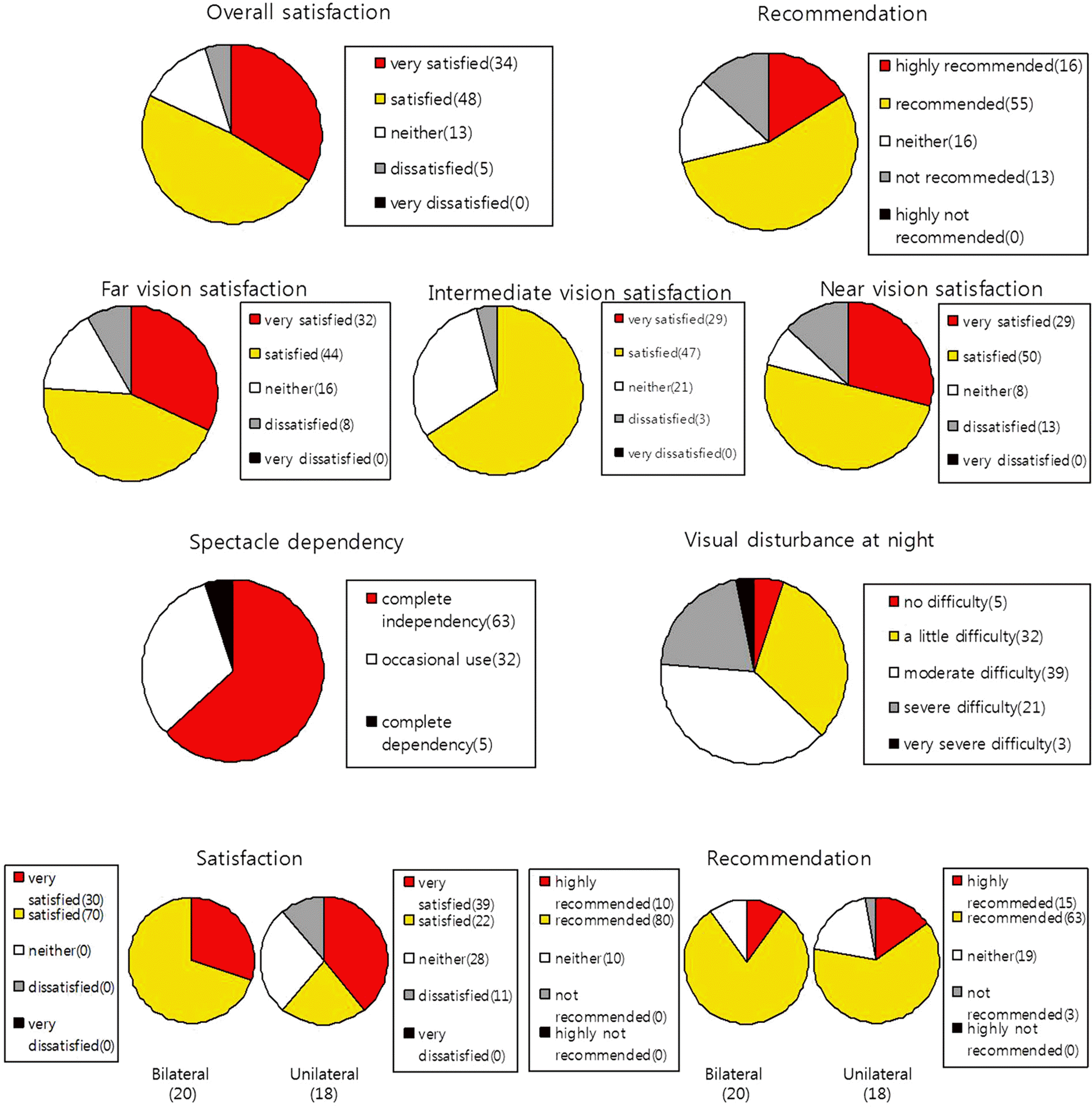
 XML Download
XML Download