Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the refractive outcomes of small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) in high myopia patients compared with mild to moderate myopia patients.
Methods
This study included 332 eyes of 166 myopic patients treated with SMILE using Visumax 500 kHz femtosecond laser. Treated eyes were divided into 2 groups according to preoperative spherical equivalent (SE): mild to moderate myopia (A group, <-6.0 D) and high myopia (B group, >-6.0 D). Follow-up visits were at 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. The out-come measures included uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA), best corrected distance visual acuity (BDVA), post-operative SE, efficacy index, safety index and predictability.
Results
Preoperative SE was −4.85 ± 0.86 D in the A group and −7.70 ± 1.0 D in the B group. No differences were observed between −0.04 ± 0.29 D in the A group and −0.30 ± 0.37 D in the B group at 6 months postoperatively (p = 0.062). At 6 months post-operatively, 98.3% and 97.3% had UDVA of 20/25 or better in the A group and B group, respectively. In the A group, 97.3% and 100% were within ±0.5 D and ±1.0 D of intended correction and in the B group, 91.7% and 96.9% were within ±0.5 D and ±1.0 D, respectively. Efficacy indices were 1.02 ± 0.19 in the A group and 0.99 ± 0.18 in the B group. Safety indices were 1.16 ± 0.16 in the A group and 1.14 ± 0.16 in the B group. The efficacy and safety indices were not significantly different between the A and B groups at 6 months postoperatively (p = 0.09, p = 0.695, respectively).
Go to : 
References
1. Sandoval HP, de Castro LE, Vroman DT, Solomon KD. Refractive Surgery Survey 2004. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:221–33.

3. Mohammadpour M, Jabbarvand M. Risk factors for ectasia after LASIK. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1056.

4. Kim HJ, Cho SH, Kim JH, Joo CK. Risk factors and clinical evalu-ation for corneal ectasia after LASIK. J Korean Ophthalmol. 2005; 46:589–96.
5. Khoueir Z, Haddad NM, Saad A, et al. Traumatic flap dislocation 10 years after LASIK. Case report and literature review. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2013; 36:82–6.

6. Reinstein DZ, Archer TJ, Randleman JB. Mathematical model to compare the relative tensile strength of the cornea after PRK, LASIK, and small incision lenticule extraction. J Refract Surg. 2013; 29:454–60.

7. Li M, Zhao J, Shen Y, et al. Comparison of dry eye and corneal sensitivity between small incision lenticule extraction and femtosecond LASIK for myopia. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e77797.

8. Shah R, Shah S, Sengupta S. Results of small incision lenticule extraction: All-in-one femtosecond laser refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:127–37.

9. Hjortdal JO, Vestergaard AH, Ivarsen A, et al. Predictors for the outcome of small-incision lenticule extraction for Myopia. J Refract Surg. 2012; 28:865–71.

10. Sekundo W, Kunert KS, Blum M. Small incision corneal refractive surgery using the small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) procedure for the correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism: results of a 6 month prospective study. Br J of Ophthalmol. 2011; 95:335–9.

11. Kamiya K, Shimizu K, Igarashi A, Kobashi H. Visual and refractive outcomes of femtosecond lenticule extraction and small-incision lenticule extraction for myopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014; 157:128–34.e2.
12. Vestergaard A, Ivarsen AR, Asp S, Hjortdal JO. Small-incision lenticule extraction for moderate to high myopia: Predictability, safety, and patient satisfaction. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2003–10.

13. Li M, Niu L, Qin B, et al. Confocal comparison of corneal reinnervation after small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) and femtosecond laser in situ keratomileusis (FS-LASIK). PLoS One. 2013; 8:e81435.

14. Ang M, Chaurasia SS, Angunawela RI, et al. Femtosecond lenticule extraction (FLEx): clinical results, interface evaluation, and intraocular pressure variation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:1414–21.

15. Ivarsen A, Asp S, Hjortdal J. Safety and complications of more than 1500 small-incision lenticule extraction procedures. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:822–8.
Go to : 
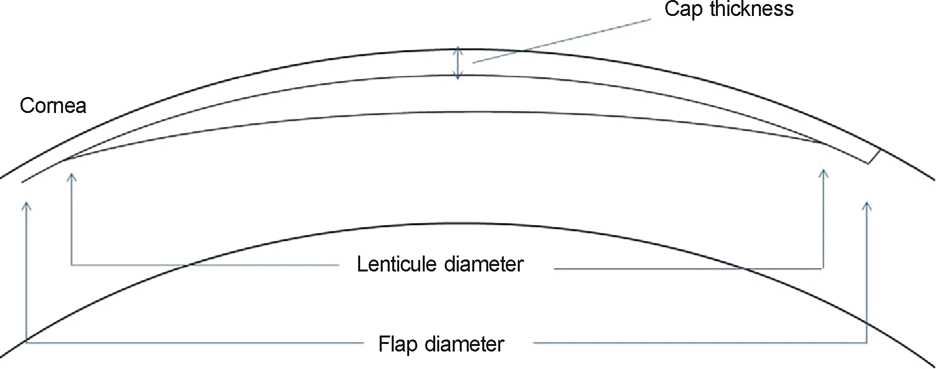 | Figure 1.A schematic drawing of cornea in small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) procedure. |
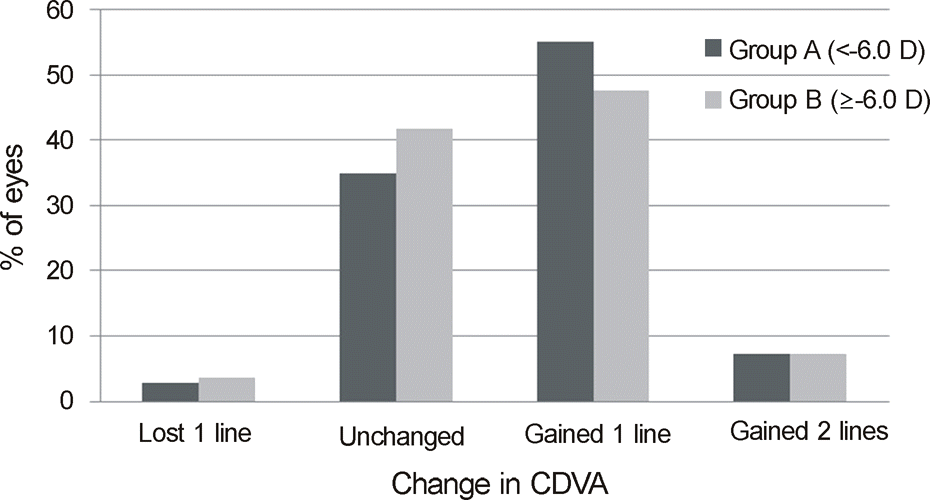 | Figure 2.Safety. Gain and loss of CDVA of 2 groups 6 months postoperatively. CDVA = corrected distance visual acuity; D = diopters. |
 | Figure 3.Predictability. (A) Bar graph represents the percentage of eyes within ±0.5 D of intended correction at 3 and 6 months postoperatively. (B) The percentage of eyes within ±1.0 D of intended correction. D = diopters; POD = post-operative day. |
Table 1.
Demographics of patients
| Characteristics | Total | Group A | Group B | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes (n) | 332 | 109 | 223 | |
| Sex (M/F) | 102/230 | 27/82 | 75/148 | |
| Age (years) | 27 ± 6 (18-48) | 28 ± 7 (18-48) | 26 ± 6 (18-48) | 0.231 |
| Mean corneal power (diopter) | 44.2 ± 1.49 (39.4-48.3) | 44.3 ± 1.47 (40.4-47) | 44.2 ± 1.51 (39.4-48.3) | 0.934 |
| UDVA (log MAR) | 1.63 ± 0.25 (0.5-2.0) | 1.53 ± 0.31 (0.5-2.0) | 1.68 ± 0.19 (0.7-2.0) | 0.000* |
| CDVA (log MAR) | -0.054 ± 0.05 (-0.2∼0.2) | -0.07 ± 0.05 (-0.2 ∼ 0.1) | -0.05 ± 0.06 (-2∼0.2) | 0.003* |
| IOP (mm Hg) | 15.1 ± 2.62 (8-24) | 14.6 ± 2.75 (8-20) | 15.4 ± 2.51 (9-24) | 0.166 |
| Sphere (diopter) | -6.17 ± 1.68 (-10∼-2.25) | -4.24 ± 0.89 (-5.75∼-2.25) | -7. 07 ± 1.15 (-10 ∼ −4.5) | 0.001* |
| Cylinder (diopter) | -1.18 ± 0.80 (-4∼0) | -1.03 ± 0.83 (-4∼ 0) | -1.25 ± 0.77 (-4∼0) | 0.313 |
| Spherical equivalence (diopter) | -6.76 ± 1.66 (-10.5∼-2.25) | -4.85 ± 0.86 (-5.88∼-2.25) | -7.70 ± 1.04 (-10.50 ∼ −6) | 0.004* |
| CCT (μm) | 525 ± 31 (450∼625) | 517 ± 34 (450 ∼ 596) | 529 ± 29 (462∼625) | 0.007* |
| Expected residual corneal bed (μm) | 298 ± 28 (450∼625) | 311 ± 30 (253∼389) | 293 ± 24 (252 ∼389) | 0.014* |
Table 2.
Comparison of uncorrected and corrected distance visual acuity of 2 groups
Table 3.
Comparison of error in spherical equivalent refraction of 2 groups
Table 4.
Comparison of efficacy index and safety index of 2 groups




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download