Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the diagnostic ability of the modified ISNT rule (disc rim thickness of the smaller of inferior and superior > the larger of nasal and temporal) for normal and glaucomatous eyes compared to the classic ISNT rule (disc rim thickness of inferior > superior > nasal > temporal).
Methods
Color stereo optic disc photographs of 113 normal subjects and 108 open angle glaucoma patients with early and moderate stage were morphometrically evaluated. The classic ISNT rule and the modified ISNT rule were assessed by masked evaluation of disc photographs at the 3, 6, 9 and 12 o’clock positions.
Results
Among normal subjects, 58 of 113 eyes (51.3%) were normal and in open angle glaucoma patients, 104 of 108 eyes (96.3%) were abnormal with the classic ISNT rule. Among normal subjects, 98 of 113 eyes (94.2%) were normal and in open angle glaucoma patients, 102 of 108 eyes (94.4%) were abnormal with the modified ISNT rule. The modified ISNT rule was more accurate than the classic ISNT rule in terms of Cohen’s Kappa analysis used for discriminating between normal and glaucomatous eyes.
References
1. Bowd C, Weinreb RN, Zangwill LM.Evaluating the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer in glaucoma. I: Clinical examination and photographic methods. Semin Ophthalmol. 2000; 15:194–205.

2. Caprioli J.Clinical evaluation of the optic nerve in glaucoma. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 92:589–641.
3. Jonas JB, Gusek GC, Naumann GO.Optic disc, cup and neuro-retinal rim size, configuration and correlations in normal eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988; 29:1151–8.
4. Morgan JE, Bourtsoukli I, Rajkumar KN. . The accuracy of the inferior>superior>nasal>temporal neuroretinal rim area rule for diagnosing glaucomatous optic disc damage. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:723–30.
5. Per OL, Goran BS, Paal AN. . Use of the ISNT rule for optic disc evaluation in 40 to 79 year old. SJOVS. 2010; 3:16–22.
6. Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ.Population prevalence of tilted optic disks and the relationship of this sign to refractive error. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 133:679–85.

7. Foster PJ, Buhrmann R, Quigley HA, Johnson GJ.The definition and classification of glaucoma in prevalence surveys. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:238–42.

8. Vijaya L, George R, Baskaran M. . Prevalence of primary open-angle glaucoma in an urban south Indian population and comparison with a rural population. The Chennai Glaucoma Study. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:648–54.e1.
9. Anderson DR, Patella VM.Automated static perimetry. 2nd ed.Mosby: St. Louis;1999. p. 152–3.
10. Budde WM, Jonas JB, Martus P, Gründler AE.Influence of optic disc size on neuroretinal rim shape in healthy eyes. J Glaucoma. 2000; 9:357–62.

11. Harizman N, Oliveira C, Chiang A. . The ISNT rule and differ-entiation of normal from glaucomatous eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:1579–83.

12. Arvind H, George R, Raju P. . Neural rim characteristics of healthy South Indians: the Chennai Glaucoma Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:3457–64.

13. Sihota R, Srinivasan G, Dada T. . Is the ISNT rule violated in early primary open-angle glaucoma–a scanning laser tomography study. Eye (Lond). 2008; 22:819–24.

14. Jonas JB, Mardin CY, Gründler AE.Comparison of measurements of neuroretinal rim area between confocal laser scanning tomog-raphy and planimetry of photographs. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:362–6.

15. Pogrebniak AE, Wehrung B, Pogrebniak KL. . Violation of the ISNT rule in Nonglaucomatous pediatric optic disc cupping. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:890–5.

16. Quigley HA, Brown AE, Morrison JD, Drance SM.The size and shape of the optic disc in normal human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:51–7.

17. Sekhar GC, Prasad K, Dandona R. . Planimetric optic disc pa-rameters in normal eyes: a population-based study in South India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2001; 49:19–23.
Figure 1.
Clinical assessment of the ISNT rule for a normal optic nerve. The classic ISNT rule is that the neuroretinal rim width is greatest in the order, inferior > superior > nasal > temporal. The modified ISNT rule is that the neuroretinal rim width shows the smaller of inferior and superior is greater than the larger of nasal and temporal.
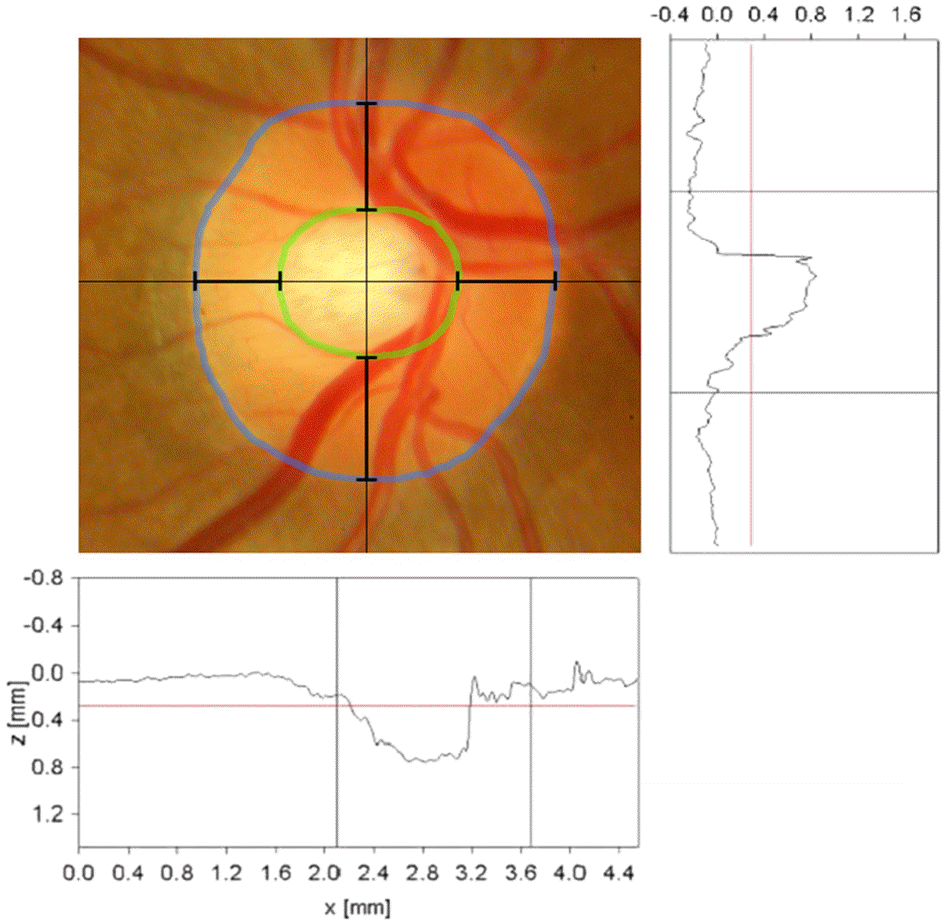
Figure 2.
(A) Optic disc having a cup with temporal flat slope, (B) Optic nerve head with steep, punched-out optic cup.

Table 1.
Agreement of the modified ISNT rule and the classic ISNT rule in normal group and glaucoma group
|
Classic ISNT rule |
Modified ISNT rule |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Glaucoma | Normal | Glaucoma | ||
| Diagnosis | Normal | 58 (51.3%) | 55 (48.7%) | 98 (86.7%) | 15 (13.3%) |
| Glaucoma | 4 (3.7%) | 104 (96.3%) | 6 (5.6%) | 102 (94.4%) | |
Table 2.
Comparison of the modified ISNT rule with the classic ISNT rule
| Classic ISNT rule | Modified ISNT rule | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.963 | 0.944 | 0.68* |
| Specificity | 0.513 | 0.867 | 0.00* |
| Positive predictive value | 0.654 | 0.872 | 0.00† |
| Negative predictive value | 0.935 | 0.942 | 0.82† |
| Kappa | 0.471 | 0.887 | 0.00‡ |
Table 3.
Patient demographics and ocular findings by diagnosis using the modified ISNT rule and results of univariate analysis (normal group, n = 113)
| Characteristic |
Modified ISNT rule |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (n = 98) | Glaucoma (n = 15) | ||
| Age (years) | 51.0 ± 13.2 | 49.3 ± 11.6 | 1.00* |
| Range | 19 to 77 | 29 to 66 | |
| Sex (no, %) | 0.11† | ||
| Female | 46 (47) | 11 (73) | |
| Male | 52 (53) | 4 (27) | |
| Refractive error (spherical equivalent) (diopters) | -1.65 ± 2.20 | -1.48 ± 2.20 | 1.00* |
| Range | -8.00 to 3.00 | -5.75 to 1.50 | |
| Intraocular pressure (mm Hg) | 14.9 ± 3.0 | 14.0 ± 2.6 | 0.50* |
| Range | 9 to 23 | 10 to 18 | |
| Average visual field measures | |||
| Mean deviation (dB) | -0.11 | -0.41 | 0.73* |
| Range | -6.88 to 3.22 | -3.02 to 2.55 | |
| Central corneal thickness (mm) | 532.2 ± 36.7 | 522.8 ± 38.4 | 0.98* |
| Range | 454 to 623 | 427 to 576 | |
| Diameter | |||
| Horizontal (mm) | 1.77 ± 0.26 | 1.80 ± 0.21 | 1.00* |
| Range | 0.96 to 2.55 | 1.43 to 2.23 | |
| Vertical (mm) | 1.82 ± 0.20 | 1.82 ± 0.19 | 1.00* |
| Range | 1.25 to 2.28 | 1.48 to 2.12 | |
| CD ratio | |||
| Horizontal | 0.69 ± 0.10 | 0.66 ± 0.10 | 0.23* |
| Range | 0.39 to 0.88 | 0.51 to 0.77 | |
| Vertical | 0.54 ± 0.11 | 0.60 ± 0.10 | 0.16* |
| Range | 0.27 to 0.71 | 0.44 to 0.74 | |
| Cup shape (no, %) | 1.00† | ||
| Punched-out cup | 68 (69) | 10 (67) | |
| Cup with temporal flat slopes | 30 (31) | 5 (33) | |
| Rim thickness | |||
| Inferior (mm) | 0.43 ± 0.09 | 0.38 ± 0.10 | 0.26* |
| Range | 0.26 to 0.67 | 0.23 to 0.55 | |
| Superior (mm) | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 0.01* |
| Range | 0.26 to 0.59 | 0.24 to 0.46 | |
| Nasal (mm) | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.01* |
| Range | 0.17 to 0.52 | 0.27 to 0.47 | |
| Temporal (mm) | 0.22 ± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 1.00* |
| Range | 0 to 0.41 | 0.15 to 0.37 | |
| Diameter vertical / diameter horizontal | 1.04 ± 0.09 | 1.01 ± 0.09 | 0.78* |
| Range | 0.83 to 1.30 | 0.89 to 1.21 | |
Table 4.
Patient demographics and ocular findings by diagnosis using the modified ISNT rule and results of univariate analysis (glaucoma group, n = 108)
| Characteristic |
Modified ISNT rule |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (n = 6) | Glaucoma (n = 102) | ||
| Age (years) | 54.5 ± 6.4 | 58.2 ± 13.6 | 0.87* |
| Range | 44 to 63 | 29 to 88 | |
| Sex (no, %) | 0.40† | ||
| Female | 4 (67) | 37 (36) | |
| Male | 2 (33) | 65 (64) | |
| Refractive error (spherical equivalent), diopters | -0.25 ± 0.50 | -1.79 ± 2.90 | 0.64* |
| Range | -0.75 to 0.50 | -13.25 to 2.00 | |
| Intraocular pressure (mm Hg) | 16.2 ± 2.6 | 17.9 ± 4.4 | 0.65* |
| Range | 14 to 21 | 10 to 37 | |
| Average visual field measures | |||
| Mean deviation (dB) | -3.91 | -6.32 | 0.88* |
| Range | -9.92 to -1.59 | -29.19 to 1.94 | |
| Central corneal thickness (mm) | 516.2 ± 31.9 | 521.2 ± 35.2 | 1.00* |
| Range | 455 to 535 | 418 to 616 | |
| Diameter | |||
| Horizontal (mm) | 1.88 ± 0.23 | 1.77 ± 0.25 | 0.49* |
| Range | 1.63 to 2.17 | 1.19 to 2.72 | |
| Vertical (mm) | 1.97 ± 0.18 | 1.85 ± 0.20 | 0.22* |
| Range | 1.70 to 2.21 | 1.43 to 2.58 | |
| CD ratio | |||
| Horizontal | 0.81 ± 0.10 | 0.74 ± 0.07 | 0.03* |
| Range | 0.65 to 0.87 | 0.56 to 0.88 | |
| Vertical | 0.75 ± 0.08 | 0.76 ± 0.06 | 1.00* |
| Range | 0.60 to 0.82 | 0.57 to 0.90 | |
| Cup shape (no, %) | 1.00† | ||
| Punched-out cup | 3 (50) | 73 (72) | |
| Cup with temporal flat slopes | 3 (50) | 29 (28) | |
| Rim thickness | |||
| Inferior (mm) | 0.25 ± 0.11 | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 0.30* |
| Range | 0.17 to 0.44 | 0.08 to 0.45 | |
| Superior (mm) | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 1.00* |
| Range | 0.14 to 0.34 | 0.05 to 0.40 | |
| Nasal (mm) | 0.18 ± 0.07 | 0.25 ± 0.07 | 0.04* |
| Range | 0.12 to 0.29 | 0.11 to 0.48 | |
| Temporal (mm) | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.26* |
| Range | 0.10 to 0.32 | 0.07 to 0.38 | |
| Diameter vertical / diameter horizontal | 1.05 ± 0.05 | 1.06 ± 0.13 | 1.00* |
| Range | 1.00 to 1.12 | 0.79 to 1.48 | |
Table 5.
Results of multivariate analysis using logistic regression analysis (normal group)
| Odds ratio | 97.5% Confidence limits | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.99 | 0.92-1.08 | 1.00 |
| Male (ref: female) | 0.66 | 0.11-3.94 | 1.00 |
| Refractive error (spherical equivalent) | 0.94 | 0.58-1.53 | 1.00 |
| IOP > 18 mm Hg (ref: IOP ≤ 18 mm Hg) | 0.67 | 0.07-6.78 | 1.00 |
| Mean deviation | 1.00 | 0.64-1.58 | 1.00 |
| Central corneal thickness | 1.01 | 0.98-1.03 | 1.00 |
| Cup shape | 2.89 | 0.37-22.37 | 0.49 |
| Punched-out cups (ref: Cups with temporal flat slopes) | |||
| Horizontal diameter (ref: ≤1.7 mm) | |||
| 1.7-1.8 mm | 0.44 | 0.03-5.76 | 0.95 |
| >1.8 mm | 0.19 | 0.01-3.45 | 0.39 |
| Vertical diameter (ref: ≤1.7 mm) | |||
| 1.7-1.8 mm | 0.79 | 0.04-15.50 | 1.00 |
| >1.8 mm | 1.73 | 0.08-36.17 | 1.00 |
| Vertical diameter / horizontal diameter | 0.40 | 0.09-1.73 | 0.32 |
| Horizontal CD ratio | 0.06† | 0.01-0.42 | 0.00 |
| Vertical CD ratio | 15.55† | 2.24-108.01 | 0.00 |
Table 6.
Results of multivariate analysis using logistic regression analysis (glaucoma group)
| Odds Ratio | 97.5% Confidence Limits | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.04 | 0.97-1.11 | 0.44 |
| Male (ref: female) | 1.72 | 0.39-7.69 | 0.83 |
| Refractive error (spherical equivalent) | 0.86 | 0.62-1.18 | 0.56 |
| IOP > 18 mm Hg (ref: IOP ≤ 18 mm Hg) | 1.62 | 0.32-8.15 | 1.00 |
| Mean deviation | 0.99 | 0.84-1.17 | 1.00 |
| Central corneal thickness | 1.00 | 0.98-1.02 | 1.00 |
| Cup shape | 0.78 | 0.14-4.32 | 1.00 |
| Punched-out cups (ref: Cups with temporal flat slopes) | |||
| Horizontal diameter (ref: ≤1.7 mm) | |||
| 1.7-1.8 mm | 1.63 | 0.19-14.03 | 1.00 |
| >1.8 mm | 1.13 | 0.1-12.73 | 1.00 |
| Vertical diameter (ref: ≤1.7 mm) | |||
| 1.7-1.8 mm | 1.14 | 0.06-20.32 | 1.00 |
| >1.8 mm | 0.68 | 0.04-11.58 | 1.00 |
| Vertical diameter / horizontal diameter | 0.88 | 0.33-2.39 | 1.00 |
| Horizontal CD ratio | 0.25† | 0.05-1.27 | 0.19 |
| Vertical CD ratio | 3.48† | 0.66-18.28 | 0.11 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download