Abstract
Case summary
A 42-year-old female presented with decreased visual acuity for one month in duration in the left eye. Her best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 20/20 in the right eye and 20/250 in the left eye. There was no sign of inflammation in the anterior segment. Fundus examination showed no distinct abnormal findings including vitreous cell or haziness except mild diabetic retinopathy and subtle opacity of the macula. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed a marked distortion of the inner segment-outer segment (IS-OS) junction in the photoreceptor layer without macular edema. Fluorescent angiography revealed diffuse subtle hyperfluorescence with microvasculitis in late phase. Full-field electroretinography (ERG) and multifocal ERG showed decreased amplitude; thus, acute zonal occult outer retinopathy (AZOOR) was considered as the diagnosis. Laboratory work-ups before steroid therapy revealed positive serology for active syphilis. One month after treatment with penicillin G (6 million international units per day for 14 days), best-corrected VA improved to 20/30, and restoration of the IS-OS junction was observed on OCT.
Go to : 
References
1. Kiss S, Damico FM, Young LH. Ocular manifestations and treat-ment of syphilis. Semin Ophthalmol. 2005; 20:161–7.

2. Puech C, Gennai S, Pavese P, et al. Ocular manifestations of syph-ilis: recent cases over a 2.5-year period. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010; 248:1623–9.

4. Eandi CM, Neri P, Adelman RA, et al. Acute syphylitic posterior placoid chorioretinitis: report of a case series and comprehensive review of the literature. Retina. 2012; 32:1915–41.
5. Yoo C, Kim SK, Huh K, Oh J. Atypical acute syphilitic posterior placoid chorioretinitis. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2009; 23:108–11.

6. Brito P, Penas S, Carneiro A, et al. Spectral-domain optical coher-ence tomography features of acute syphilitic posterior placoid cho-rioretinitis: The role of autoimmune response in pathogenesis. Case Report Ophthalmol. 2011; 2:39–44.

Go to : 
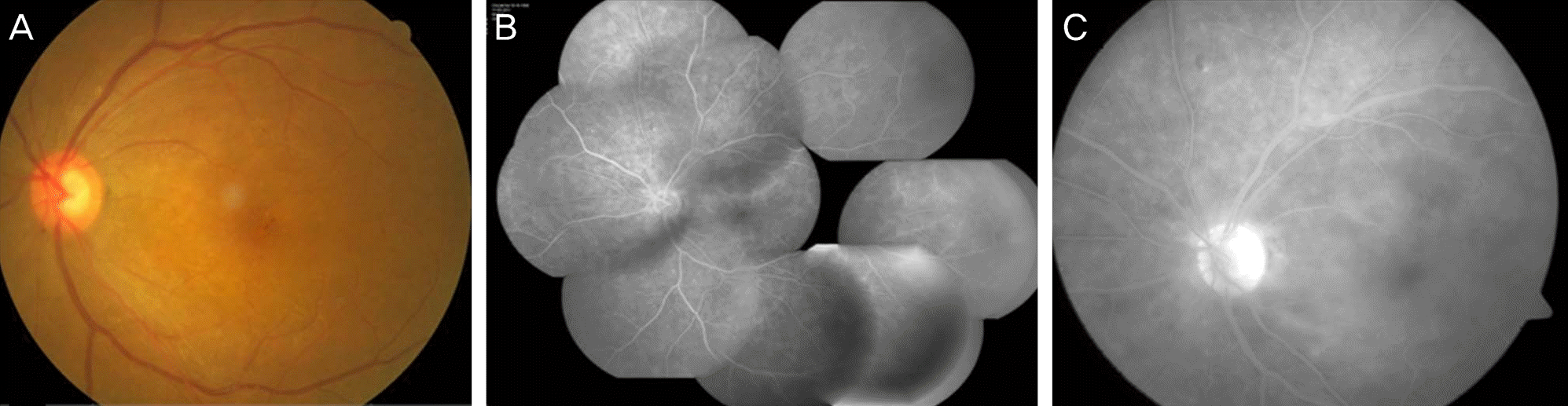 | Figure 1.(A) Fundus phograph at presentation shows microaneurysms and subtle opaque of the macula at the initial visit. (B) Fluorescent angiography shows multiple microaneurysms associated with diabetic retinopathy. (C) Mild leakage is seen suspecting diffuse microvasculitis in the late phase. |
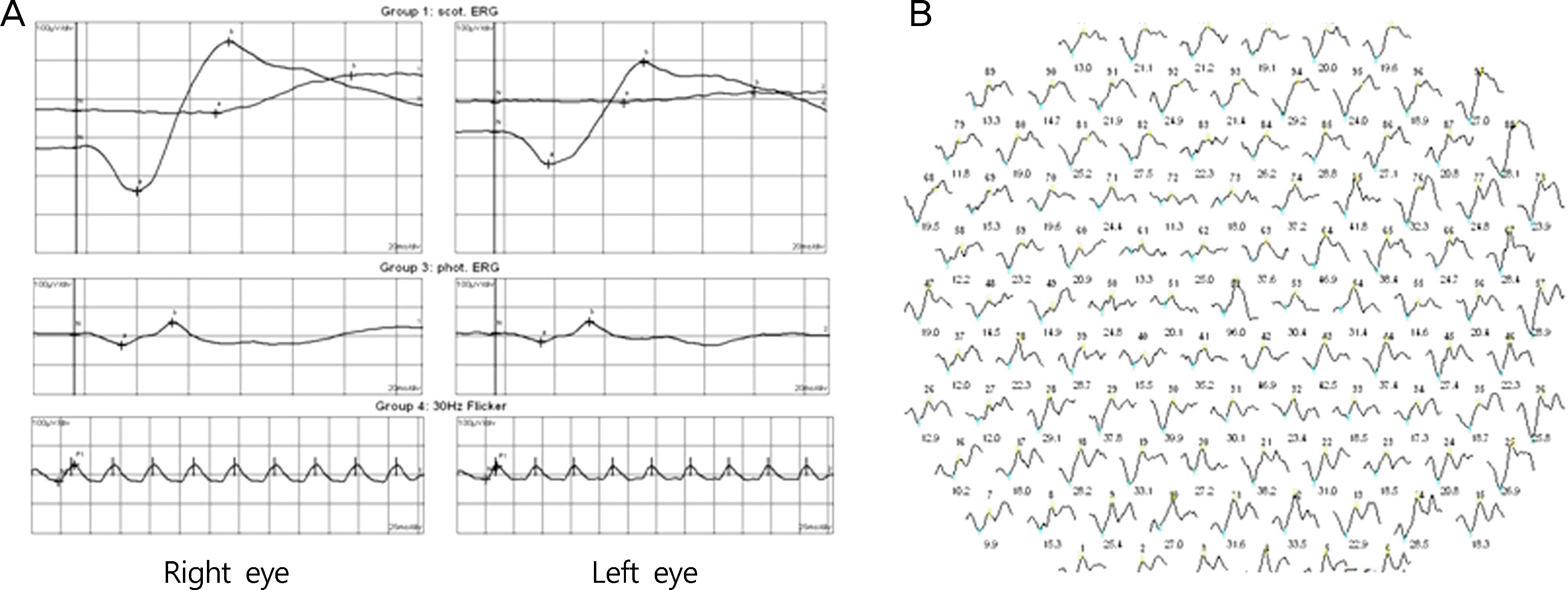 | Figure 2.(A) Full field electroretinography (ERG) and (B) multifocal ERG showed decreased amplitude in the left eye. |
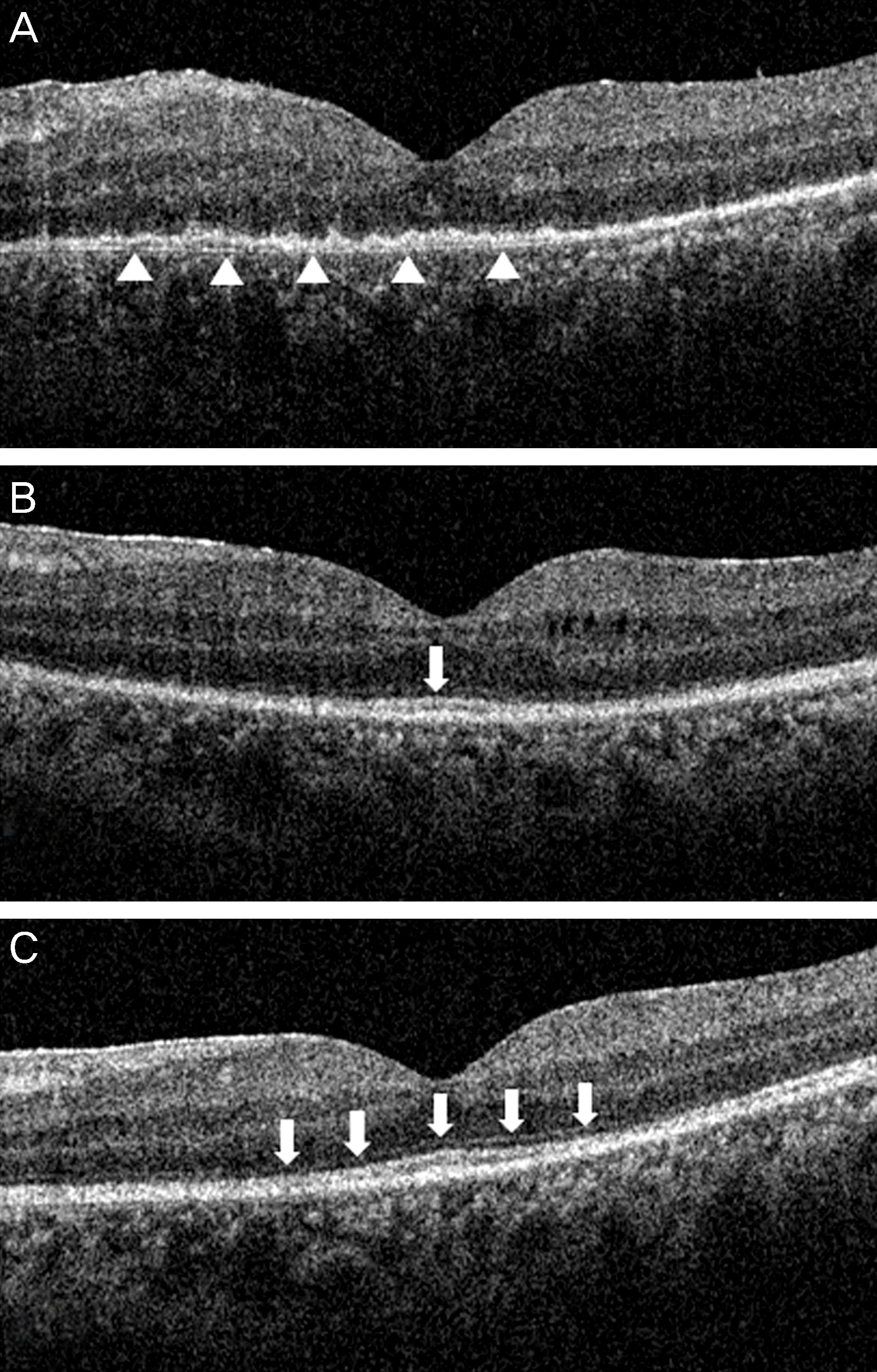 | Figure 3.(A) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) shows diffuse loss of signal from the photoreceptor inner/outer segment (IS-OS) junction and the external limiting membrane (ELM), and presumed inflammation signs including indistinct retinal layers and the undulated signal of the pigment epithelium (arrowheads). (B) One months after treatment, IS-OS junction (arrow) was recovered partly. (C) At 3 months, IS-OS junction and ELM (arrows) became distinct as well as the retinal layers. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download