Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the stereoscopic acuity in patients with unilateral or bilateral visual field defects.
Methods
Stereoscopic acuity was measured using the Titmus stereo test for 36 subjects with visual field defects (VFD). VFD was assessed by sum of MD (mean deviation, MDsum) and PSD (pattern standard deviation, PSDsum) of both eyes in Humphrey visual field test and presence of central VFD (within 30° isopter) in Goldman visual field test. 25 glaucoma subjects and 11 optic neuritis subjects were included. Patients with strabismus or ocular motility disorders which could affect stereoscopic acuity were excluded.
Results
The mean of MDsum was −20.10 ± 12.31 dB (-45.13∼-10.64 dB) and PSDsum was 13.10 ± 8.76 dB (9.62-25.47 dB). The mean stereoscopic acuity was 710 ± 922 arc sec (40-3000 arc sec) with Titmus stereo test. The associations between stereoscopic acuity and PSDsum (r = 0.400, p = 0.016), presence of central VFD within 30 degrees (r = 0.428, p = 0.03) were statistically significant. There was positive trend between stereoscopic acuity and duration of VFD, but with no statistical significance.
Go to : 
References
1. Scott WE, Mash J. Stereoacuity in normal individuals. Annals of Ophthalmology. 1974; 6:99–101.
3. Lovasik JV, Szymkiw M. Effects of aniseikonia, anisometropia, accommodation, retinal illuminance, and pupil size on stereopsis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985; 26:741–50.
4. Bishop PO. Binocular vision. In : Moses RA, Hart WM, editors. Adler's Physiology of the Eye. 8th ed.St Louis: CV Mosby;1987. p. 619–89.
5. Romano PE, Romano JA, Puklin JE. Stereoacuity development in children with normal binocular single vision. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975; 79:966–71.

7. Cho YA, Cho SW, Roh GH. Evaluation of criteria of stereoacuity for Titumus Randot & TNO sterotests. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:532–7.
8. von Noorden GK. Binocular vision and ocular motilitiy: Theory and management of strabismus. 5th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;1996. p. 8–40.
9. Levy NS, Glick EB. Stereoscopic perception and Snellen visual acuity. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974; 78:722–4.

10. Larson WL. Does a small field of view degrade stereoacuity. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1987; 64:110–3.

11. Agarwal R, Gupta SK, Agarwal P, et al. Current concepts in the pathophysiology of glaucoma. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2009; 57:257–66.

12. Min BM, Park WC. The relationship between visual acuity and titmus stereoacuity. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1987; 28:1339–42.
13. Larson WL, Lachance A. Stereoscopic acuity with induced refractive errors. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1983; 60:509–13.

14. Yildirim C, Mutlu FM, Chen Y, Altinsoy HI. Assessment of central and peripheral fusion and near and distance stereoacuity in intermittent exotropic patients before and after strabismus surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 128:222–30.

15. Goodwin RT, Romano PE. Stereoacuity degradation by experimental and real monocular and binocular amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985; 26:917–23.
16. Lee DW, Nah YS, Lee MK, Lee JB. Effect of difference of binocular retinal illuminance on stereopsis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1828–32.
17. Seong MC, Choi JW, Lee JE, et al. The relationship between parameters measured by optical coherence tomography and visual field indices. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:771–7.

18. Heijl A, Lindgren G, Olsson J. Normal variability of static perimetric threshold values across the central visual field. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987; 105:1544–9.

19. Lakshmanan Y, George RJ. Stereoacuity in mild, moderate and severe glaucoma. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2013; 33:172–8.

20. Essock EA, Fechtner RD, Zimmerman TJ, et al. Binocular function in early glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 1996; 5:395–405.

Go to : 
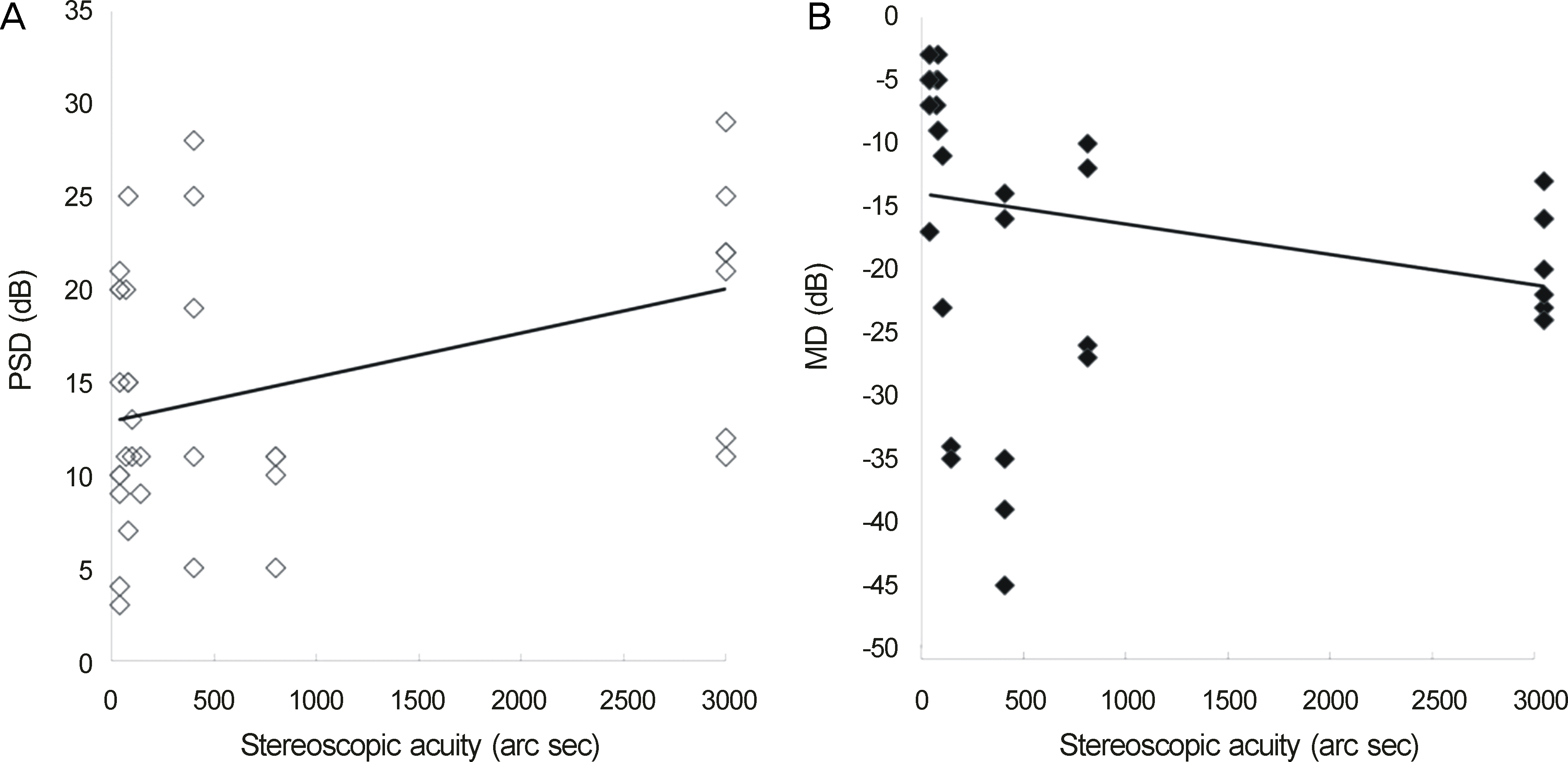 | Figure 1.Correlation between visual field defects and stereoscopic acuity. (A) There is significant positive correlation between the mean value of sum of pattern standard deviation (PSDsum) (dB) and stereoscopic acuity (arc sec) (r = 0.400, p = 0.016). (B) There is no significant correlation between the mean value of sum of mean deviation (MDsum) (dB) and stereoscopic acuity (arc sec) (r = −0.245, p = 0.078). |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients
Table 2.
Variables in interpretation of visual field (VF) defect
Table 3.
Levels of significance of various clinical factors on the stereoscopic acuity
| Parameter | Significance (p-value†) |
|---|---|
| MDsum* | r = −0.245 (0.078) |
| PSDsum | r = 0.400 (0.016) |
| Mean duration of VFD | r = 0.170 (0.42) |
| Presence of VFD within 30° isopter | r = 0.428 (0.03) |
| Unilateral vs. bilateral VFD | r = 0.331 (0.11) |
Table 4.
Distribution of stereoscopic acuity and visual field defects
| Stereoscopic acuity (arc sec) | MDsum | PSDsum | VFD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >-25 (n = 19) | ≤-25 (n = 17) | >12.5 (n = 18) | <12.5 (n = 18) | None (n = 6) | Present (n = 25) | |
| Normal (40″) (%) | 4 (21)* | 2 (11)* | 0 (0)* | 5 (28)* | 4 (33)* | 2 (8)* |
| Reduced (50-800″) (%) | 9 (47) | 10 (59) | 9 (50) | 11 (61) | 2 (67) | 15 (60) |
| Absence (>3000″) (%) | 6 (32) | 5 (30) | 9 (50)* | 2 (11)* | 0 (0)* | 8 (32)* |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download