Abstract
Purpose
To investigate and compare the clinical courses and surgical success rates of secondary operations in recurrent exotropia according to the type of first operation for correction of exotropia.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed for all patients with recurrent exotropia of the basic or pseudodivergence excess types. In group A (36 patients), bilateral lateral rectus (LR) recession was performed as the first operation and uni- or bilateral medial rectus (MR) resection was performed as the second operation. In group B (19 patients), unilateral LR recession- MR resection (R&R) was performed as the first operation and LR recession or R&R in contralateral eye as the second operation.
Results
There were no significant differences between the 2 groups when considering age at each operation, frequency of the amblyopia, prescription of prism, time interval for recurrence and reoperation and the final and cumulative success rates. No postoperative complications were observed in either group. The mean number of used muscles for the first and second operation was 3.9 ± 0.4 in group A, and 3.4 ± 0.5 in group B (p = 0.001). Mean time interval for occurrence of postoperative orthophoria was 3.7 ± 6.2 months in group A and 6.5 ± 16.2 in group B (p = 0.047). In group B, the incidence of esodeviation tended to increase after postoperative 1 month.
Conclusions
The final success rates of reoperation between the 2 types of the first operation in recurrent exotropia were similar. Mean time between postoperative overcorrection of orthophoria was shorter in the group with bilateral LR recession followed by secondary MR resection than in the other group. Unilateral R&R followed by LR recession or R&R in contralateral eye may be more helpful to decrease the number of used muscles than in the bilateral LR recession followed by secondary MR resection.
Go to : 
References
1. Shin HH, Nam SH, Kim CH, Park SH. A vision screening in the preschool children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1089–95.
2. Yu YS, Kim SM, Kwon JY, et al. Preschool vision screening in Korea: Preliminary study. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:1092–6.
4. Friedman Z, Neumann E, Hyams SW, Peleg B. Ophthalmic screening of 38,000 children, age 1 to 2 1/2 years, in child welfare clinics. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1980; 17:261–7.

5. Burian HM, Spivey BE. The surgical management of exodeviations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965; 59:603–20.
6. Burian HM. Exodeviations: their classification, diagnosis and treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966; 62:1161–6.

7. Kushner BJ. Selective surgery for intermittent exotropia based on distance/near differences. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:324–8.

8. Kim SJ. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992; 33:733–8.
9. Hur J, Won IG. Surgical results of 79 cases of intermittent exo-tropia in children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1594–9.
10. Mun HJ, Kim MM. Comparison of surgical results between bi-lateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in 25 PD inter-mittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2202–7.
11. Scott AB, Mash AJ, Jampolsky A. Quantitative guidelines for exo-tropia surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1975; 14:428–36.
13. Lew HL, Lee JB, Kim TK. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral rectus muscle recessions and lateral rectus muscle re-cession and medial rectus muscle resection in exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:115–9.
14. Lee SY, Lee YC. Comparison of surgical results by initial post-operative alignment following bilateral lateral rectus recession and unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection in inter-mittent exotropes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2604–10.
15. Choi MY. Surgical results in basic exotropia of moderate degree. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:764–70.
16. Park HG, Paik HJ. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral recession and unilateral resection-recession in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:911–6.
17. Kim YH, Choi MY. Clinical analysis of reoperation for strabismus after strabismus surgery in childhood. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:954–9.
18. Kim SJ, Choi DG. The clinical analysis after reoperation for re-current intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:321–7.
19. Kim WJ, Kim MM. Unilateral recession-resection versus re-re-section of medial rectus in recurrent intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1088–92.

20. Kim WJ, Kim MM. The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia after previous unilateral recess-resection surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1386–91.

21. Cho WK, Lee SY, Lee YC. The effect of medial rectus resection in recurrent exotropia after lateral rectus recession. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1093–7.
22. Park HY, Yoo MH, Choi DG. Comparison of surgical results be-tween unilateral recession-resection and bilateral resections in re-current exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:148–53.
23. Olitsky SE, Kelly C, Lee H, Nelson LB. Unilateral rectus resection in the treatment of undercorrected or recurrent strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2001; 38:349–53.

24. Kim SC, Kim MM. The efficacy of unilateral rectus resection in the reoperation of strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:904–10.
25. Hardesty HH, Boynton JR, Keenan JP. Treatment of intermittent exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978; 96:268–74.

26. Richard JM, Parks MM. Intermmitent exotropia. Surgical results in different age groups. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:1172–7.
27. Scott WE, Keech R, Mash AJ. The postoperative results and stabil-ity of exodeviations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:1814–8.

28. Rabb EL, Parks MM. Recession of the lateral recti. Early and late postoperative alignments. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969; 82:203–8.
29. Kim MM, Cho ST. Long-term surgical results of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1321–6.
30. You IC, Yoon KC, Park YG. Assessment of esotropia more than 10PD after surgery of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:2278–84.
Go to : 
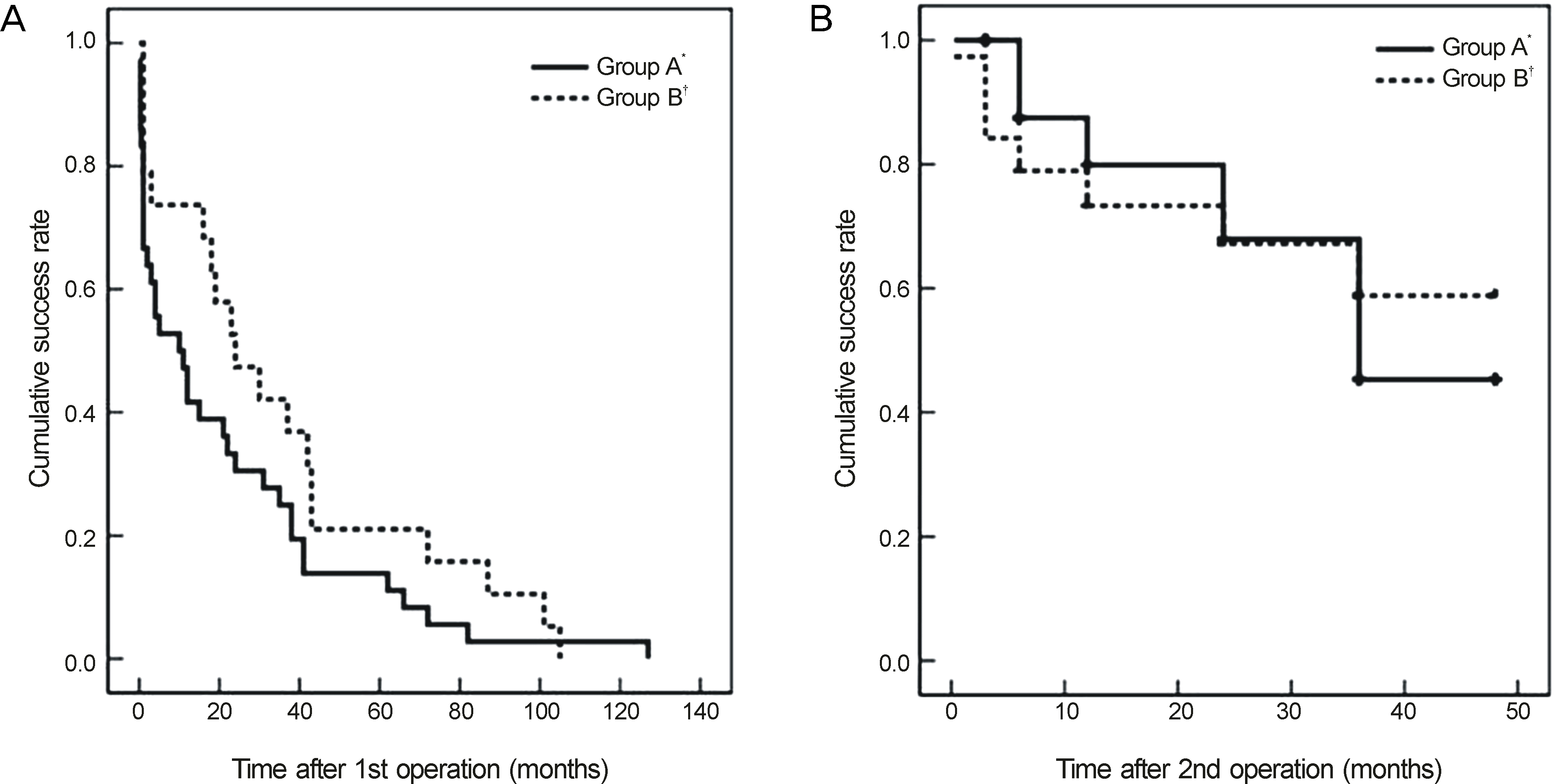 | Figure 1.Kaplan-Meier survival curve. (A) The cumulative probability of surgical success after 1st operation between Group A and B (p = 0.130, log rank test). (B) The cumulative probability of surgical success after 2nd operation between Group A and B (p = 0.877, log rank test). *Bilateral Lateral rectus muscles (LR) recession at first operation, and unilateral Medial rectus muscles (MR) or bilateral MR resection at second operation. †Unilateral Lateral rectus muscle recession and medial rectus muscle resection (R&R) at first operation, and contralateral unilateral LR recession or R&R at second operation. |
Table 1.
Demographic data of patients
| Group A* | Group B† | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients (n) | 36 | 19 | |
| Sex (M/F) (n) | 13/23 | 7/12 | |
| Mean age at 1st op. (years) | 6.4 ± 5.5 | 6.4 ± 4.2 | 0.337 |
| Time at recurrence after 1st op. (months) | 21.8 ± 29.2 | 35.1 ± 33.6 | 0.060 |
| Time interval between 1st and 2nd op. (months) | 49.1 ± 27.1 | 62.7 ± 40.9 | 0.284 |
| Mean age at 2nd operation (years) | 10.3 ± 5.7 | 11.7 ± 5.1 | 0.100 |
| Angle of exodeviation at 1st op. (PD) | 32.2 ± 10.0 | 31.1 ± 12.5 | 0.467 |
| Angle of exodeviation at 2nd op. (PD) | 23.1 ± 5.0 | 23.3 ± 7.9 | 0.649 |
| Follow-up after 2nd op. (months) | 20.8 ± 14.4 | 30.3 ± 12.1 | 0.111 |
| Number of operated muscles at total op. (n) | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 0.001 |
Table 2.
Time interval between each operations and postoperative orthophoria
| 1st operation (months) | 2nd operation (months) | p-value§ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A* | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 6.2 | 0.000 |
| Group B† | 2.1 ± 6.0 | 6.5 ± 16.2 | 0.238 |
| p-value‡ | 0.019 | 0.047 |
* Bilateral Lateral rectus muscles (LR) recession at first operation, and unilateral Medial rectus muscles (MR) or bilateral MR resection at second operation;
Table 3.
Incidence of esodeviation after 1st and 2nd operation in Group A and B
| Follow-up after surgery | Group A* (%) | p-value‡ | Group B† (%) | p-value§ | p-valueπ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | |||||
| 1st operation | 37.9 | 0.011 | 68.8 | 0.176 | 0.065 |
| 2nd operation | 69.4 | 42.1 | 0.049 | ||
| 1 week | |||||
| 1st operation | 17.2 | 0.000 | 43.8 | 0.311 | 0.080 |
| 2nd operation | 69.4 | 26.3 | 0.004 | ||
| 1 month | |||||
| 1st operation | 0.0 | 0.000 | 7.1 | 0.602 | 0.326 |
| 2nd operation | 52.8 | 18.8 | 0.033 | ||
| 3 months | |||||
| 1st operation | 4.2 | 0.123 | 21.4 | 0.455 | 0.132 |
| 2nd operation | 20.6 | 36.8 | 0.198 | ||
| 6 months | |||||
| 1st operation | 0.0 | 0.051 | 7.7 | 0.092 | 0.325 |
| 2nd operation | 18.5 | 41.2 | 0.164 | ||
* Bilateral Lateral rectus muscles (LR) recession at first operation, and unilateral Medial rectus muscles (MR) or bilateral MR resection at second operation;
Table 4.
Final success rates after second operation
| Group A* (%) | Group B† (%) | p-value‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Success | 63.9 | 63.2 | 0.750 |
| Undercorrection | 30.1 | 26.3 | |
| Overcorrection | 6 | 10.5 |
* Bilateral Lateral rectus muscles (LR) recession at first operation, and unilateral Medial rectus muscles (MR) or bilateral MR resection at second operation;




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download