Abstract
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of 27 patients (48 orbits) with thyroid-associated orbitopathy who underwent orbital decompression. Stereotactic navigation was performed on 28 orbits of 15 patients, and orbital decompression surgery without navigation was performed on 20 orbits of 12 patients. The changes in medial wall, lateral wall and inferior wall orbital volume in CT scans and horizontal and vertical eyeball deviation after surgery were analyzed in the 2 patient groups.
Results
The mean decompressed volume of orbits was significantly increased in the lateral wall decompression with stereotactic navigation patient group than without stereotactic navigation (p < 0.05, p = 0.025). However, in the inferior wall and the medial wall decompression, there was no significant difference between the 2 groups. The changes of horizontal and vertical deviation were not significant between the 2 groups and no patient experienced neural damage.
References
1. Bartalena L, Marocci C, Bogazzi F, et al. Glucocorticoid therapy of Graves' ophthalmopathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1991; 97(2-3):320–7.

2. Bartalena L, Pinchera A, Marcocci C. Management of Graves' ophthalmopathy: reality and perspectives. Endocr Rev. 2000; 21:168–99.

3. Lyons CJ, Rootman J. Orbital decompression for disfiguring exophthalmos in thyroid orbitopathy. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:223–30.

4. Fatourechi V, Garrity JA, Bartley GB, et al. Graves ophthalmopathy. Results of transantral orbital decompression performed primarily for cosmetic indications. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:938–42.
5. Garrity JA, Fatourechi V, Bergstralh EJ, et al. Results of transantral orbital decompression in 428 patients with severe Graves' ophthalmopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 116:533–47.

6. Maroon JC, Kennerdell JS. Radical orbital decompression for severe dysthyroid exophthalmos. J Neurosurg. 1982; 56:260–6.

7. Graham SM, Brown CL, Carter KD, et al. Medial and lateral orbital wall surgery for balanced decompression in thyroid eye disease. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113:1206–9.

8. Apuzzo ML, Sabshin JK. Computed tomographic guidance stereo-taxis in the management of intracranial mass lesions. Neurosurgery. 1983; 12:277–85.

9. Andrews BT, Surek CC, Tanna N, Bradley JP. Utilization of computed tomography image-guided navigation in orbit fracture repair. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:1389–93.

10. Cai EZ, Koh YP, Hing EC, et al. Computer-assisted navigational surgery improves outcomes in orbital reconstructive surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1567–73.

11. Lee KY, Ang BT, Ng I, Looi A. Stereotaxy for surgical navigation in orbital surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 25:300–2.

12. Patel BC. Stereotactic navigation for lateral orbital wall decompression. Eye (Lond). 2009; 23:1493–5.

13. Millar MJ, Maloof AJ. The application of stereotactic navigation surgery to orbital decompression for thyroid-associated orbitopathy. Eye (Lond). 2009; 23:1565–71.

14. Kennedy DW, Goodstein ML, Miller NR, Zinreich SJ. Endoscopic transnasal orbital decompression. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990; 116:275–82.

15. Metson R, Shore JW, Gliklich RE, Dallow RL. Endoscopic orbital decompression under local anesthesia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995; 113:661–7.

16. Dubin MR, Tabaee A, Scruggs JT, et al. Image-guided endoscopic orbital decompression for Graves' orbitopathy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008; 117:177–85.

17. Reardon EJ. Navigational risks associated with sinus surgery and the clinical effects of implementing a navigational system for sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 2002; 112(7 Pt 2 Suppl 99):1–19.

18. Kakizaki H, Nakano T, Asamoto K, Iwaki M. Posterior border of the deep lateral orbital wall--appearance, width, and distance from the orbital rim. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 24:262–5.

19. Oh DH, Lee JK. Surgical anatomy of deep lateral wall by adults ca-davers and computed tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:964–9.

Figure 1.
(A) Operating setup. A patient reference is placed under the patient’s zygoma (white arrow head). The AxiEM ™ Localizing emmiter generating an electromagnetic field is positioned right beside the patient’s head (white arrow) by the fixation accessary (black arrow). We register patient information by AxiEM ™ system pointer probes (black arrow head). (B) Intraoperative screen shot of a surgical field. We could know operating location on CT (axial, coronal, sagittal plane) by AxiEM ™ system pointer probes.
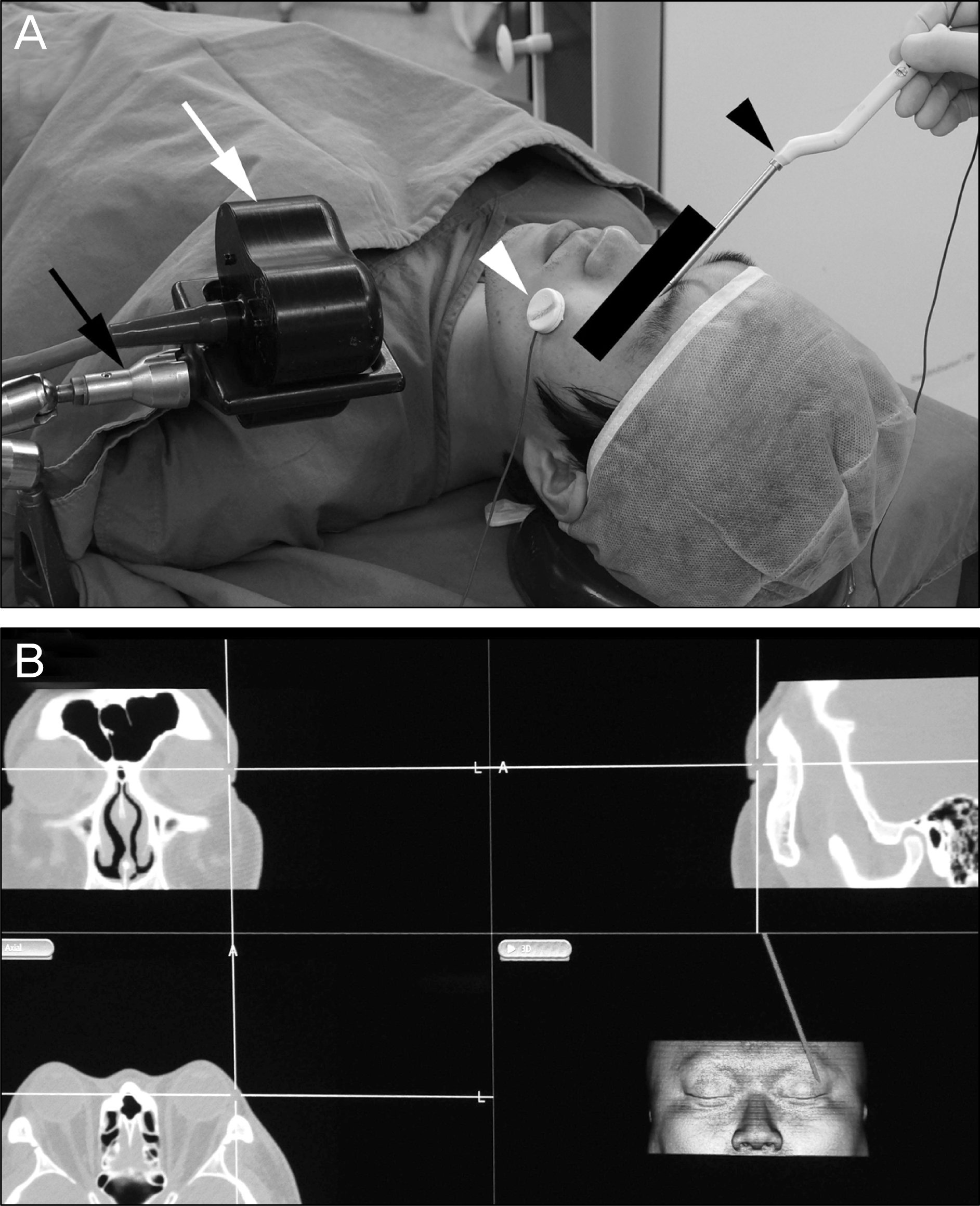
Figure 2.
The expanded area at each orbital slice was marked from the imaginary preoperative wall border to the decompressed bony edge, and the marked areas were calculated with Image J software. The deep lateral wall was analyzed on axial CT planes, as well as medial and inferior walls on coronal planes. The summation of all surface areas (cm2) multiplied by 0.25 cm (2.5 mm) was considered as an expanded orbital volume (cm3) in each orbital wall. (A) Axial CT plane. (B) Coronal plane.
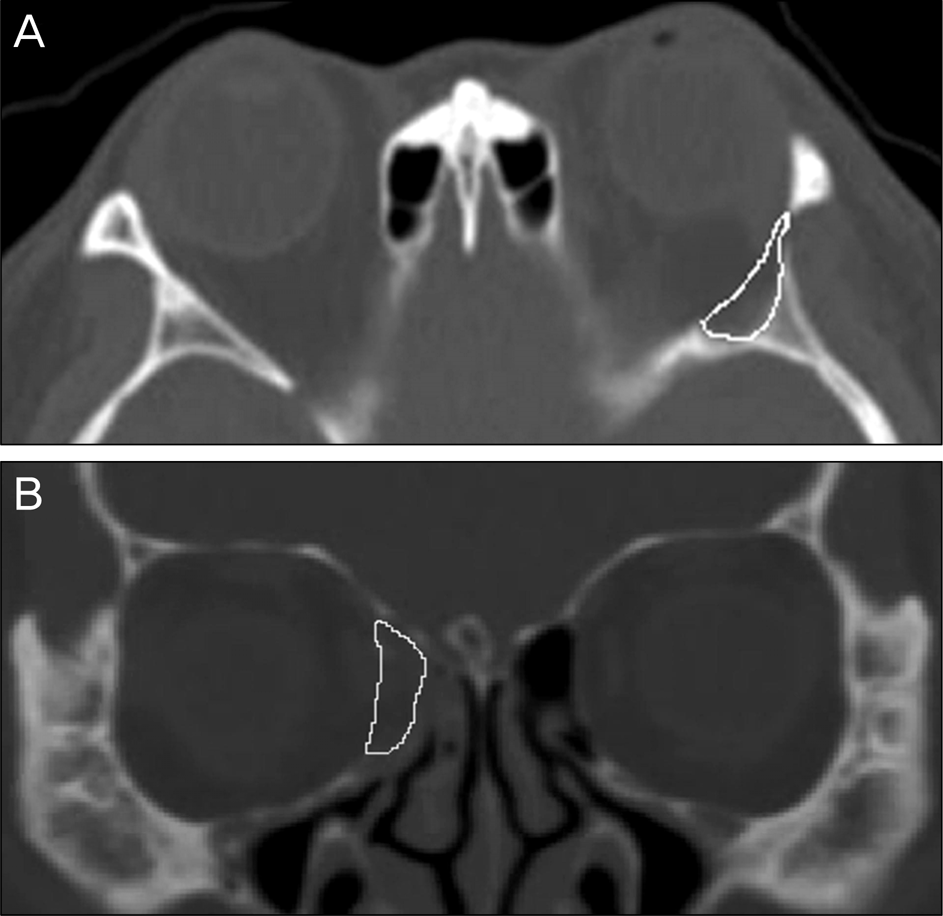
Figure 3.
The decompression surgery induce esotropia (3.48 ± 1.214 prism diopter) (A) and reduce vertical strabismus (-0.67 ± 0.671 prism diopter) (B). However, between using the navigation or not, there was no significant difference in horizontal or vertical strabismal change (Mann-Whitney test).
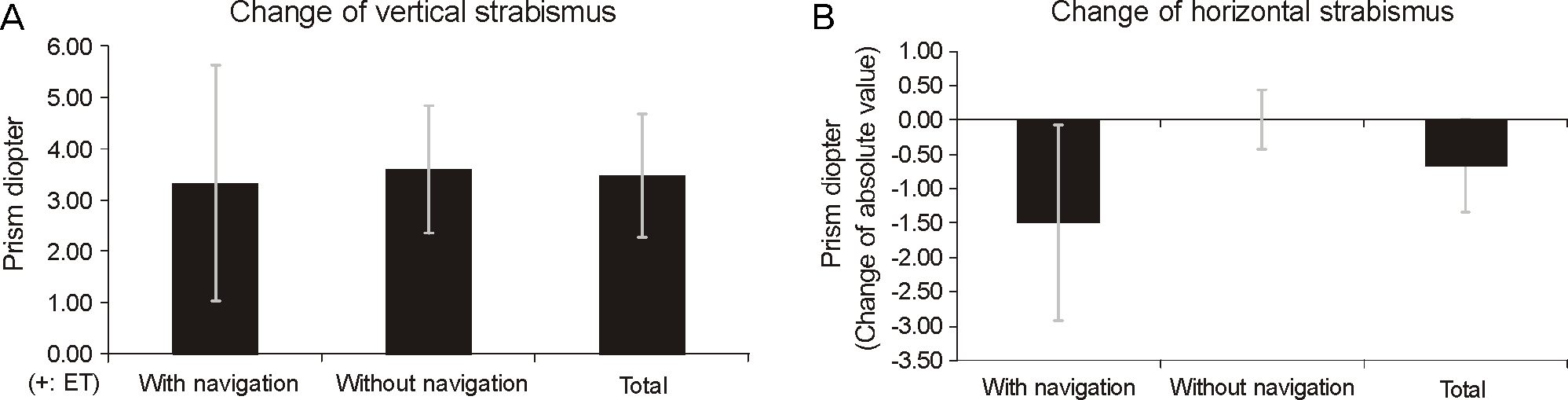
Table 1.
Demographics of study population
| Demographic | Using Navigation | Not Using Navigation | Total | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. of orbits (patients) | 28 (15) | 20 (12) | 48(27) | |
| Sex (Male / Female) | 7 / 21 | 3 / 17 | 10 / 38 | 0.488† |
| Age (years) | 37.2 ± 14.4 | 41.7 ± 15.2 | 39.3 ± 14.7 | 0.286* |
| Duration of dysthyroidism (years) | 5.9 ± 2.2 | 5.3 ± 1.8 | 5.6 ± 2.0 | 0.545* |
| Preoperative exophthalmometry | 19.4 ± 2.5 | 20.1 ± 2.2 | 19.9 ± 2.4 | 0.332* |
| Steroid therapy (%) | 7 (25.0) | 4 (20.0) | 11 (22.9) | 0.741† |
| Radiotherapy (%) | 4 (14.3) | 2 (10.0) | 6 (12.5) | 1.000† |
| Thyroidectomy (%) | 9 (32.10 | 4 (20.0) | 13 (27.1) | 0.512† |
| Smoking (%) | 6 (21.4) | 3 (15.0) | 9 (18.8) | 0.716† |
| Bony decompression of orbital wall | ||||
| 1-wall : DLW (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (10.0) | 2 (4.2) | |
| 2-wall : Balancing DLW and med. wall (% | %) 11 (39) | 5 (25.0) | 16 (33.3) | |
| 2-wall : Med. and inf. wall (%) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (15.0) | 3 (6.3) | |
| 3-wall : DLW, med. and inf. wall (%) | 17 (60.7) | 10 (50.0) | 27 (56.3) |
Table 2.
Decompression volume at different areas
| Area of Decompression |
Volume (cm3) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navigation | No Navigation | p-value | Total | |
| Deep lateral orbital wall | 0.503 ± 0.140† (28 cases) | 0.412 ± 0.118† (17 cases) | 0.025* | 0.470 ± 0.138† (45 cases) |
| Medial orbital wall | 0.824 ± 0.355† (28 cases) | 0.712 ± 0.335† (18 cases) | 0.287* | 0.780 ± 0.348† (46 cases) |
| Inferior orbital wall | 0.239 ± 0.262† (17 cases) | 0.224 ± 0.196† (13 cases) | 0.853* | 0.230 ± 0.232† (30 cases) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download