Abstract
Case summary
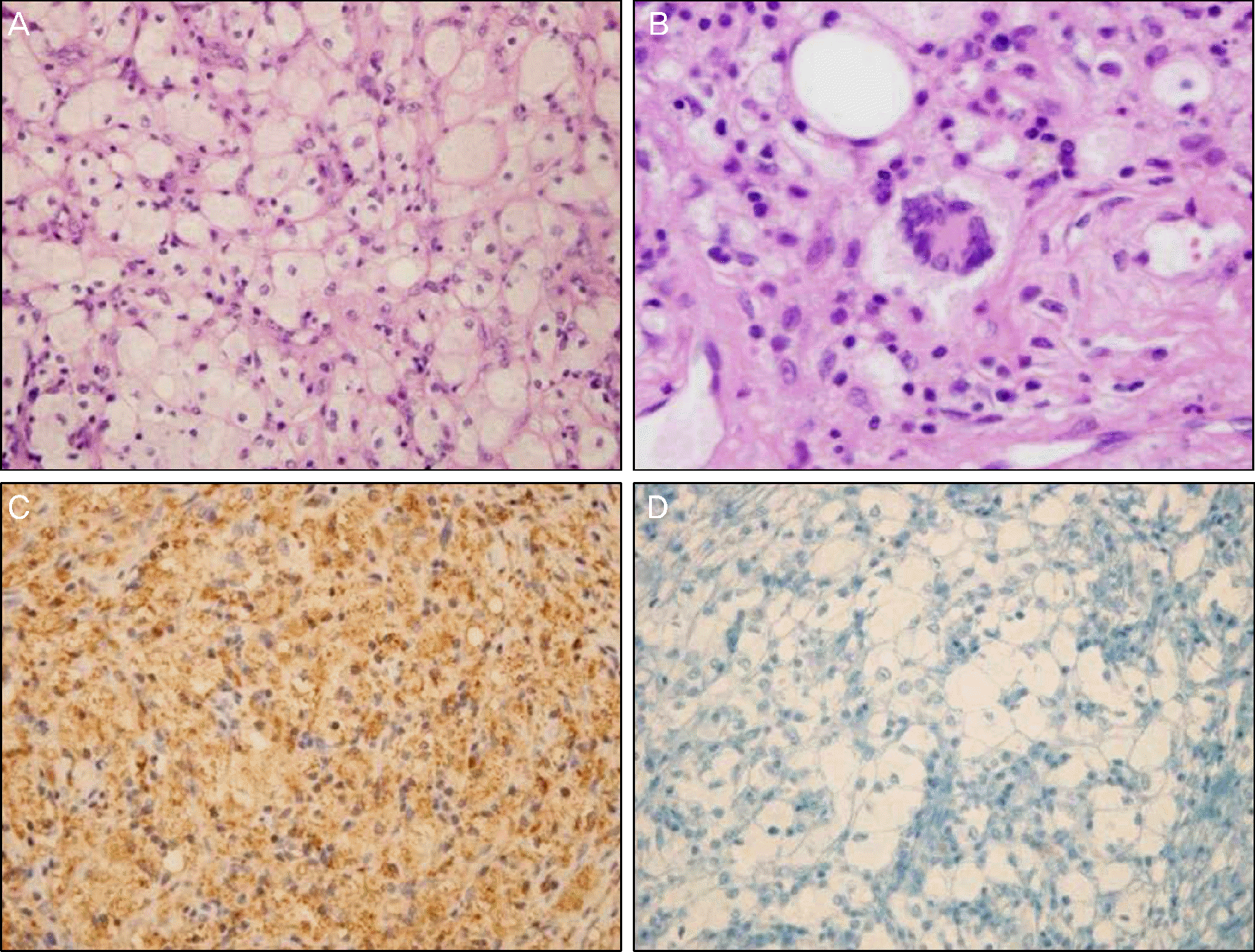
A 56-year-old woman came to the hospital with a 6-week history of diplopia on left lateral gaze. The right eye showed mildly limited adduction. Humphrey automated perimetry demonstrated inferior bitemporal quadrantanopia. Orbital and brain magnetic resonance imaging revealed well-defined orbital masses in both intraconal orbits with homogenous enhancement, as well as multiple masses of homogenous signal intensity in the brain. Systemic evaluation showed involvement of the long bones, and retroperitoneum, but no involvement of the heart, or lungs. Incisional biopsy of the right orbital mass was performed. Histopathological examination showed numerous lipid-laden histiocytes and few multinucleated Touton giant cells. Immunohistochemical staining showed positivity for CD68, but negativity for CD1a, and ECD was therefore diagnosed. The patient received treatment with radiation therapy and interferon-α, but died due to sepsis secondary to urinary tract infection after 2 months.
References
1. Chester W. Über Lipoidgranulomatose Virchows Archiv. 1930; 279:561–602.
2. Jakobiec FA, Font RL., Orbit Spencer WH, Font RL, Green WR. Ophthalmic Pathology: An Atlas and Textbook. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;1986. p. 2716–29.
3. Kim YJ, Kim YD.Erdheim-chester disease: two cases of orbital involvement. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1323–9.
4. Hwang HS, Ji BS, Lee CK. . A case of Erdheim-Chester dis-ease that presented with chronic renal failure. Korean J Med. 2007; 73:216–22.
5. Lee W, Park NC.A case of erdheim-chester disease with bilateral hydronephrosis. Korean J Urol. 2001; 42:453–6.
6. Devouassoux G, Lantuejoul S, Chatelain P. . Erdheim-Chester disease: a primary macrophage cell disorder. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157:650–3.
7. Stoppacciaro A, Ferrarini M, Salmaggi C. . Immunohisto- chemical evidence of a cytokine and chemokine network in three patients with Erdheim-Chester disease: implications for pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:4018–22.
8. Arnaud L, Gorochov G, Charlotte F. . Systemic perturbation of cytokine and chemokine networks in Erdheim-Chester disease: a single-center series of 37 patients. Blood. 2011; 117:2783–90.

10. Veyssier-Belot C, Cacoub P, Caparros-Lefebvre D. . Erdheim- Chester disease. Clinical and radiologic characteristics of 59 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996; 75:157–69.
11. Park YK, Ryu KN, Huh B, Kim JD.Erdheim-Chester disease: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 1999; 14:323–6.

12. Evans S, Williams F.Case report: Erdheim-Chester disease: poly-ostotic sclerosing histiocytosis. Clin Radiol. 1986; 37:93–6.

13. Balink H, Hemmelder MH, de Graaf W, Grond J.Scintigraphic di-agnosis of Erdheim-Chester disease. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:e470–2.

14. Athanasou NA, Barbatis C.Erdheim-Chester disease with epi-physeal and systemic disease. J Clin Pathol. 1993; 46:481–2.

15. Ono K, Oshiro M, Uemura K. . Erdheim-Chester disease: a case report with immunohistochemical and biochemical examination. Hum Pathol. 1996; 27:91–5.

16. Broccoli A, Stefoni V, Faccioli L. . Bilateral orbital Erdheim- Chester disease treated with 12 weekly administrations of VNCOP-B chemotherapy: a case report and a review of literature. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:2209–13.
17. Braiteh F, Boxrud C, Esmaeli B, Kurzrock R.Successful treatment of Erdheim-Chester disease, a non-Langerhans-cell histiocytosis, with interferon-alpha. Blood. 2005; 106:2992–4.
Figure 1.
Nine cardinal photographs at the first visit showing mild limitation of adduction of the right eye and no definitive exophthalmos.
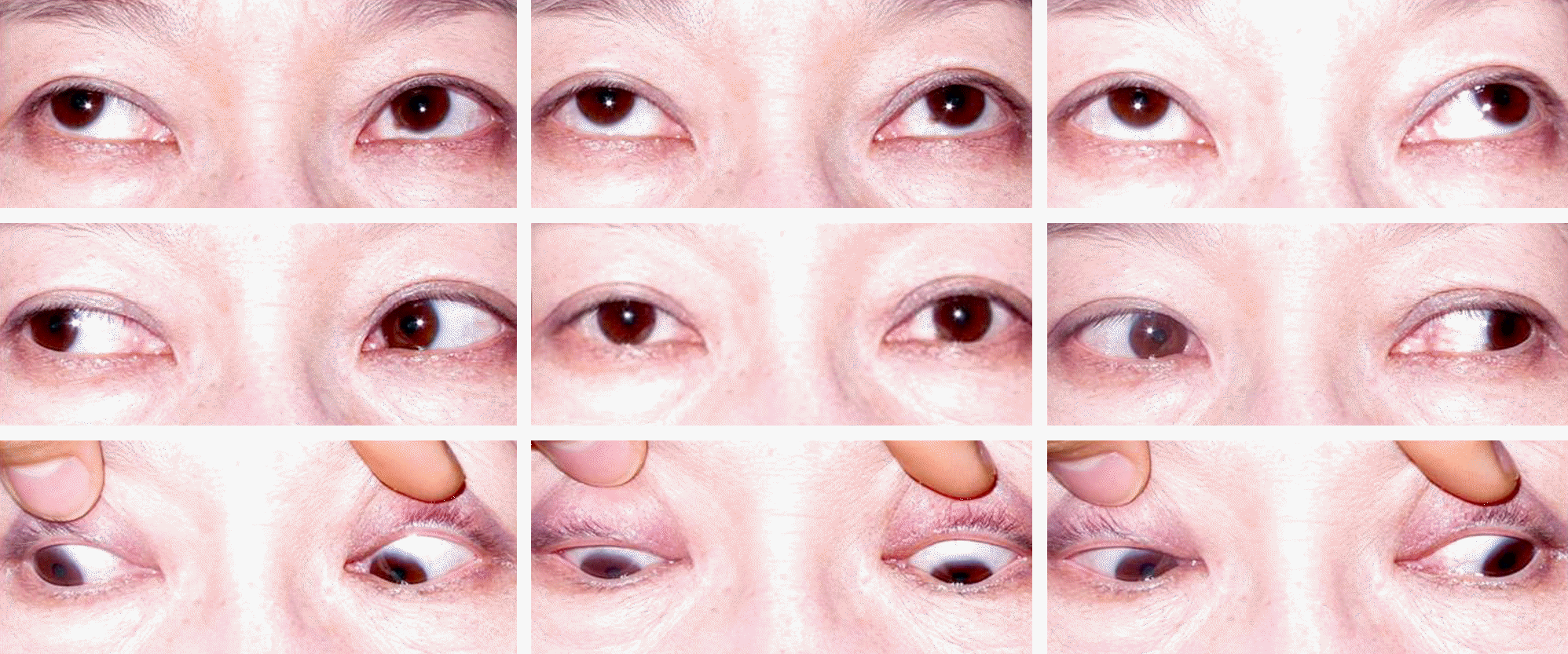
Figure 2.
Humphrey automated perimetry at first visit demonstrated inferior bitemporal quadrantanopia.
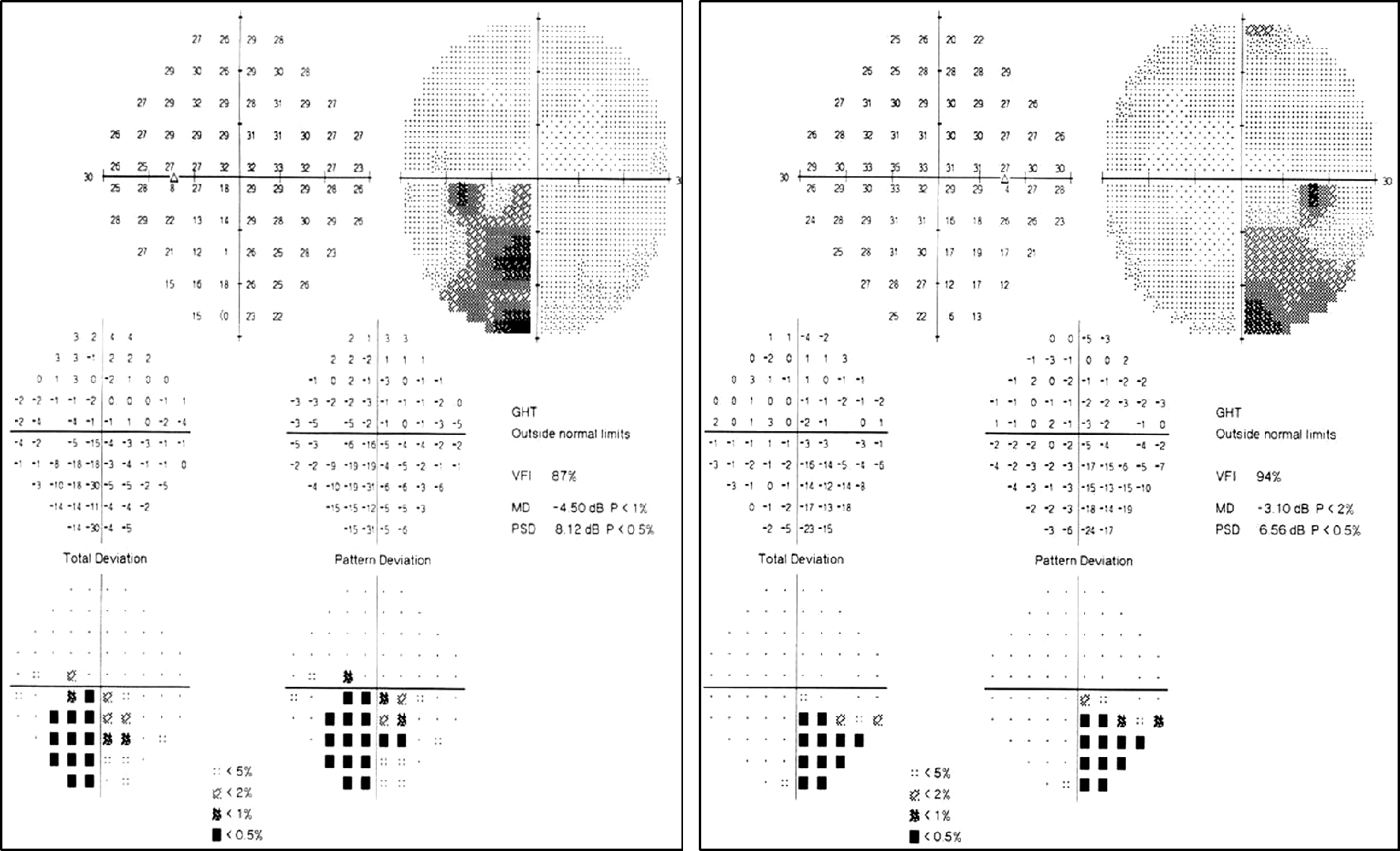
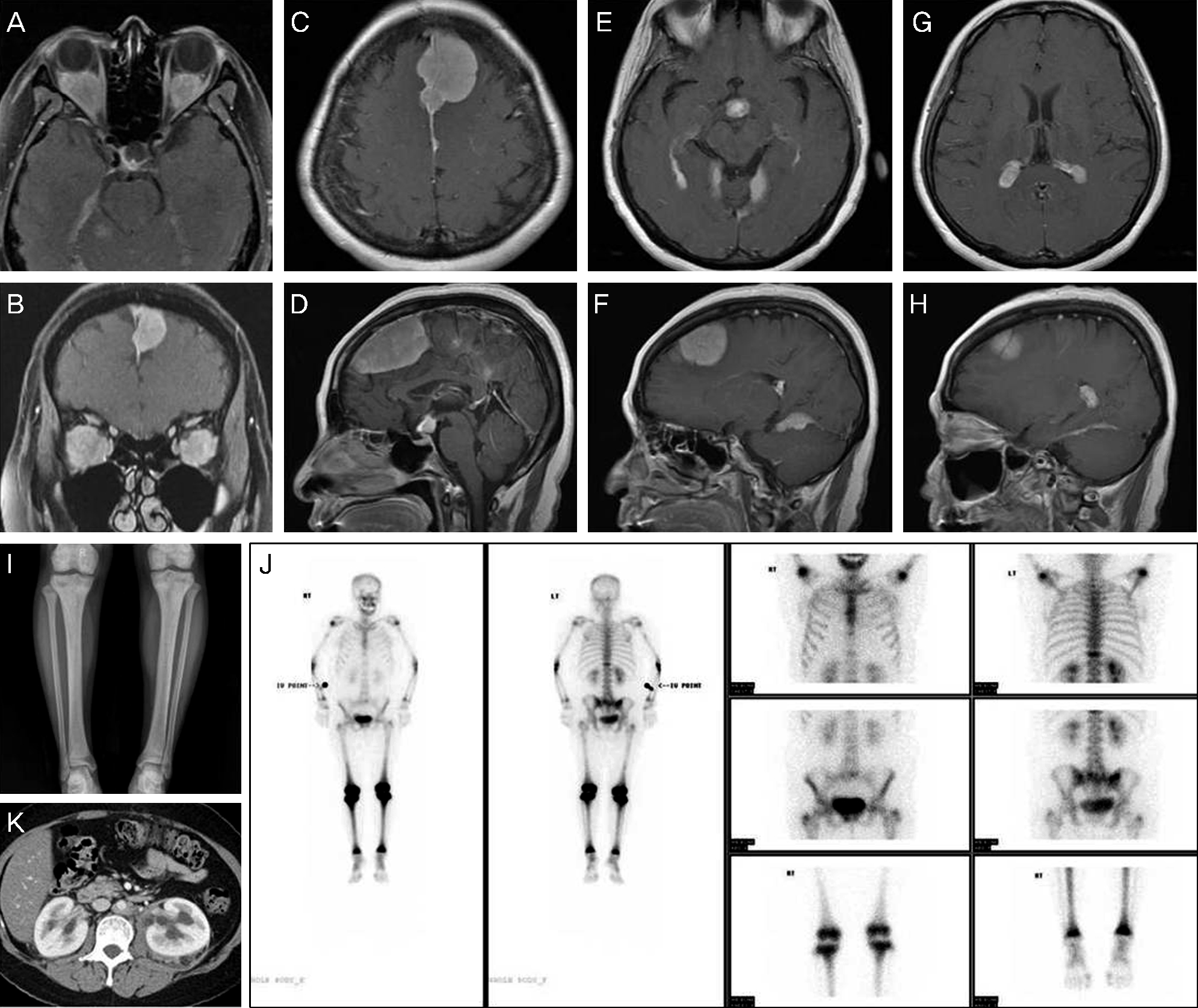
Figure 3.
Postcontrast T1-weighted axial (A) and coronal (B) orbital MRI showed homogenous enhancement of both round retrobulbar masses. T1-weighted axial and sagittal Brain MRI demonstrated multiple masses of homogenous signal intensity in the falx cerebrum, pituitary stalk, lower aspect of tentorium cerebelli and choroid plexus (C-H). (I) Anteroposterior radiograph of the both tibiae showed diffuse increased density and trabecular pattern at the metaphyseal regions of both proximal tibiae. (J) Technetium-99m HDP bone scintigraphy showed increased symmetric uptake in the both proximal and distal humerus, both proximal radii and ulnae, both distal femurs, both proximal and distal tibiae, and T11 vertebra. (K) Dynamic abdominal CT demonstrated retroperitoneal fibrosis and bilateral hydronephrosis secondary to bilateral ureteral obstruction, circumferential periaortic sheathing of the abdominal aorta and symmetrical infiltration of the perirenal fat and of the perirenal fascia taking the appearance of ‘hairy kidneys’.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download