Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the changes in each retinal layer thickness according to preoperative optical coherence tomography (OCT) patterns after idiopathic epiretinal membrane (ERM) removal and to investigate the correlation between retinal layer thickness and visual improvement.
Methods
The medical records of 63 patients (63 eyes) who underwent vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling for idiopathic ERM and followed for more than 6 months were retrospectively reviewed. The OCT images of preoperative idiopathic ERM were classified into 3 patterns being flat, convex, and concave. Then, the changes of each retinal layer thickness were compared among OCT patterns and the correlations between retinal layer thickness and visual improvement were analyzed.
Results
Improvement in visual acuity was measured in the following order: concave, flat, and convex patterns. The patients with the convex pattern only showed significant improvement of visual acuity. Ganglion cell layer plus inner plexiform layer (GCL + IPL), inner nuclear layer (INL), and outer plexiform layer (OPL) thicknesses were significantly larger in preoperative ERM patients than in normal controls in the following order: convex, concave, and flat patterns. Retinal layer thickness decreased significantly in GCL + IPL and INL after surgery in convex, flat, and concave patterns, in that order. Generally, preoperative retinal layer thickness and postoperative visual acuity were not correlated. However, improvement of visual acuity was significantly related to GCL + IPL and INL thicknesses in the convex pattern and IPL thickness in the flat pattern.
Conclusions
In patients with idiopathic ERM, preoperative difference in each retinal layer thickness according to preoperative OCT patterns was observed. After ERM removal, reduction of each retinal layer thickness and specific retinal layer related to visual improvement was different according to preoperative OCT patterns.
Go to : 
References
2. Ko TH, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS, et al. Comparison of ultrahigh- and standard-resolution optical coherence tomography for imaging macular pathology. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1922.e1–15.

3. Falkner-Radler CI, Glittenberg C, Hagen S, et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography for monitoring epiretinal membrane surgery. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:798–805.

4. Massin P, Allouch C, Haouchine B, et al. Optical coherence tomography of idiopathic macular epiretinal membranes before and after surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:732–9.

5. Michalewski J, Michalewska Z, Cisiecki S, Nawrocki J. Morphologically functional correlations of macular pathology connected with epiretinal membrane formation in spectral optical coherence tomography (SOCT). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007; 245:1623–31.

6. Inoue M, Morita S, Watanabe Y, et al. Inner segment/outer segment junction assessed by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in patients with idiopathic epiretinal membrane. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 150:834–9.

7. Oster SF, Mojana F, Brar M, et al. Disruption of the photoreceptor inner segment/outer segment layer on spectral domain-optical coherence tomography is a predictor of poor visual acuity in patients with epiretinal membranes. Retina. 2010; 30:713–8.

8. Arichika S, Hangai M, Yoshimura N. Correlation between thickening of the inner and outer retina and visual acuity in patients with epiretinal membrane. Retina. 2010; 30:503–8.

9. Watanabe A, Arimoto S, Nishi O. Correlation between meta-morphopsia and epiretinal membrane optical coherence tomography findings. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:1788–93.

10. Okamoto F, Sugiura Y, Okamoto Y, et al. Associations between metamorphopsia and foveal microstructure in patients with epiretinal membrane. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:6770–5.

11. Koo HC, Rhim WI, Lee EK. Morphologic and functional association of retinal layers beneath the epiretinal membrane with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in eyes without photoreceptor abnormality. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:491–8.

12. Wilkins JR, Puliafito CA, Hee MR, et al. Characterization of epiretinal membranes using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:2142–51.

13. Kim CH, Kim JI, Cho HY, Kang SW. Correlation between preoperative OCT pattern and visual improvement in macular epiretinal membrane. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:75–82.
14. Kinoshita T, Kovacs KD, Wagley S, Arroyo JG. Morphologic differences in epiretinal membranes on ocular coherence tomography as a predictive factor for surgical outcome. Retina. 2011; 31:1692–8.

15. Kim JH, Kang SW, Kong MG, Ha HS. Assessment of retinal layers and visual rehabilitation after epiretinal membrane removal. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:1055–64.

16. Seo SJ, Lee SJ, Park JM. Surgical outcome according to morphology in epiretinal membrane based on optical coherence tomography (OCT). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:736–44.

17. Kinoshita T, Kovacs KD, Wagley S, Arroyo JG. Morphologic differences in epiretinal membranes on ocular coherence tomography as a predictive factor for surgical outcome. Retina. 2011; 31:1692–8.

Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Three patterns of epiretinal membrane according to optical coherence tomography images. (A) The flat pattern (B) the convex pattern (C) the concave pattern. |
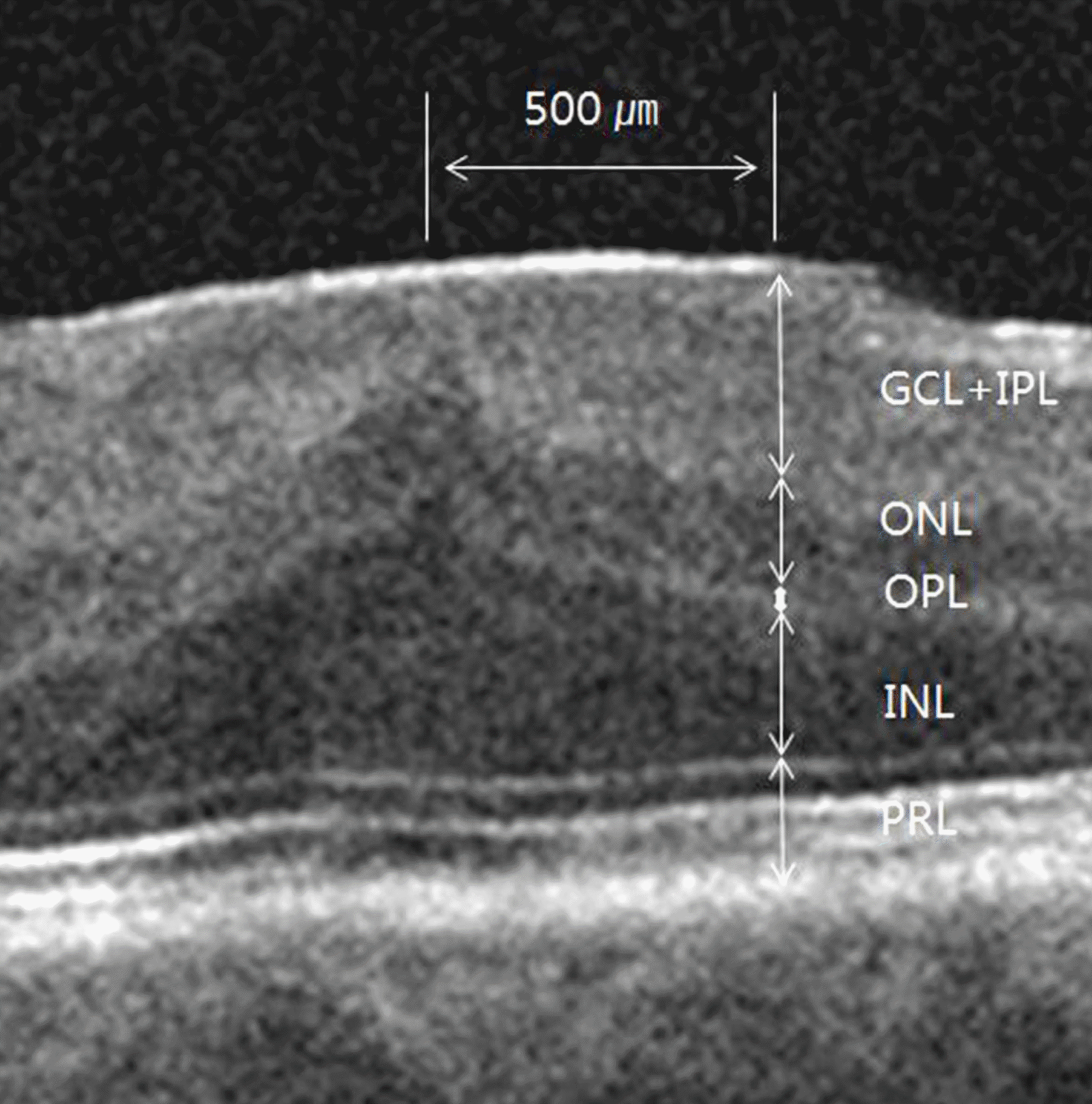 | Figure 2.Segmentation of inner and outer retina with epiretinal membrane. GCL + IPL = ganglion cell layer and inner plexiform layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; OPL = outer plexiform layer; ONL = outer nuclear layer; PRL = photoreceptor inner segment and outer segment. |
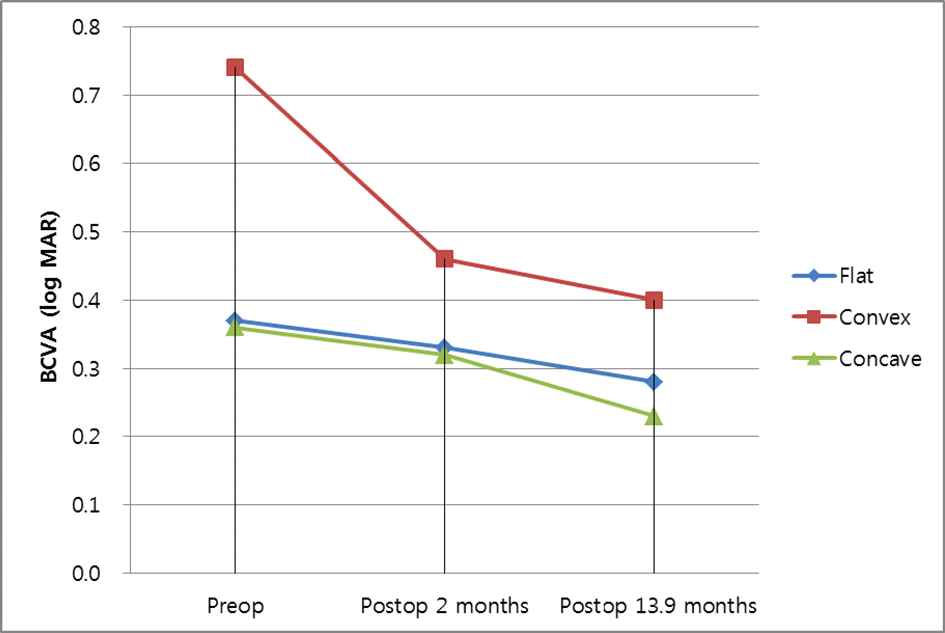 | Figure 3.Mean BCVA changes according to the pattern of epiretinal membrane. BCVA = best corrected visual acuity. |
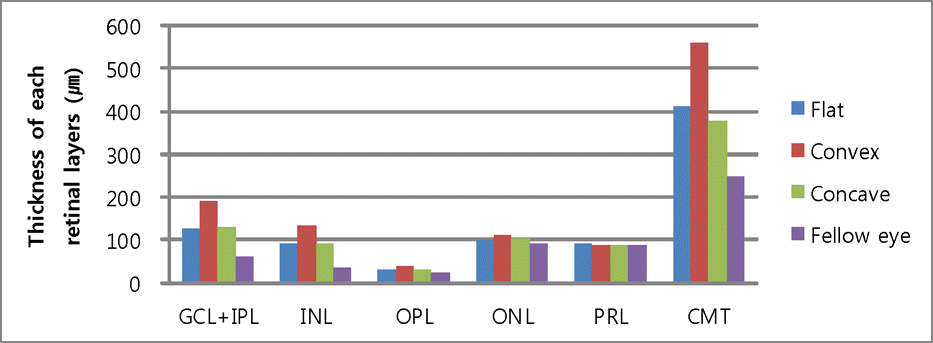 | Figure 4.A boxplot of each retinal layer thickness according to epiretinal membrane pattern before epiretinal membrane removal surgery. GCL + IPL = ganglion cell layer and inner plexiform layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; OPL = outer plexiform layer; ONL = outer nuclear layer; PRL = photoreceptor inner segment and outer segment; CMT = central macular thickness. |
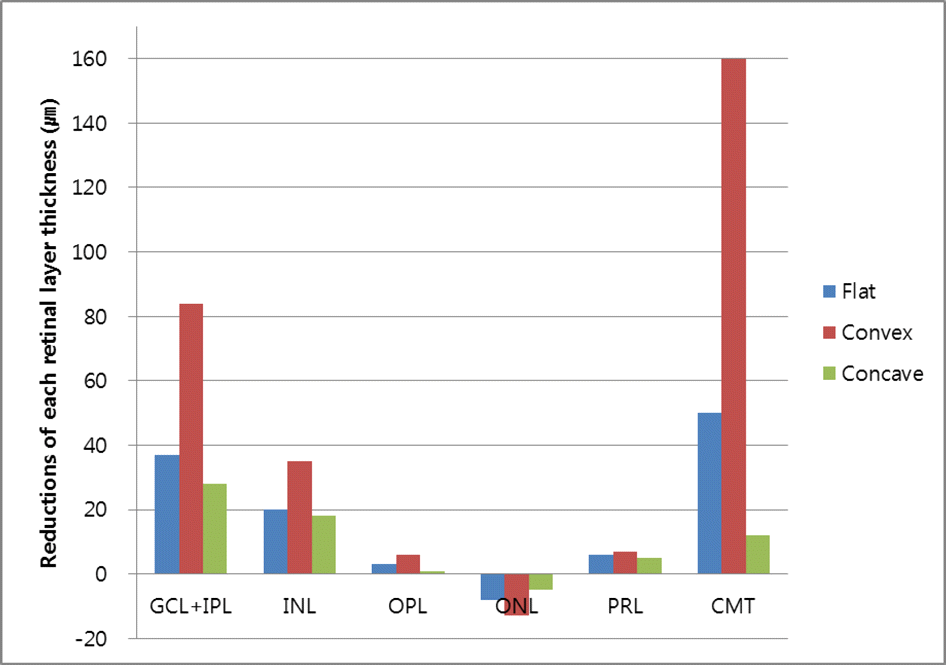 | Figure 5.A boxplot of reductions of each retinal layer thickness according to epiretinal membrane pattern after epiretinal membrane removal surgery. GCL + IPL = ganglion cell layer and inner plexiform layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; OPL = outer plexiform layer; ONL = outer nuclear layer; PRL = photoreceptor inner segment and outer segment; CMT = central macular thickness. |
Table 1.
Preoperative demographics and clinical characteristics of the patients
Table 2.
Preoperative and postoperative log MAR visual acuity according to the pattern of epiretinal membrane
| Flat | Convex | Concave | Total | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative BCVA (log MAR) | 0.37 ± 0.23 | 0.74 ± 0.41 | 0.36 ± 0.18 | 0.53 ± 0.36 | <0.001‡ |
| Postoperative 2 months BCVA (log MAR) | 0.33 ± 0.2 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 0.32 ± 0.19 | 0.38 ± 0.19 | 0.046‡ |
| Postoperative 13.9 months BCVA (log MAR) | 0.28 ± 0.24 | 0.4 ± 0.24 | 0.23 ± 0.13 | 0.32 ± 0.23 | 0.022‡ |
| Mean BCVA change (log MAR) | 0.09 ± 0.29 | 0.34 ± 0.39 | 0.13 ± 0.23 | 0.21 ± 0.35 | 0.045‡ |
| p-value† | 0.184 | <0.001‡ | 0.062 |
Table 3.
Thickness of each retinal layers according to epiretinal membrane patterns before epiretinal membrane removal surgery
| Flat | Convex | Concave | p-value* | Fellow eye | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCL + IPL | 125.76 ± 36.59 | 189.2 ± 67.64 | 131.16 ± 40.55 | 0.001† | 63.33 ± 10.97 | <0.001† |
| INL | 90.95 ± 29.31 | 131.9 ± 39.18 | 91.16 ± 36.54 | 0.001† | 36.75 ± 7.01 | <0.001† |
| OPL | 30.95 ± 7.43 | 38.4 ± 5.18 | 31.2 ± 8.2 | 0.002† | 22.75 ± 5.38 | <0.001† |
| ONL | 99.42 ± 22.1 | 109.8 ± 24.22 | 102.83 ± 23.59 | 0.266 | 91.25 ± 19.63 | 0.163 |
| PRL | 90.9 ± 7.61 | 89.15 ± 10.12 | 88.11 ± 7.93 | 0.604 | 88.96 ± 9.14 | 0.173 |
| CMT | 413.09 ± 66.31 | 560.7 ± 77.64 | 378.66 ± 102.6 | <0.001† | 249.75 ± 15.77 | <0.001† |
Table 4.
Reductions of each retinal layer thickness according to epiretinal membrane patterns after epiretinal membrane removal surgery
|
Flat |
p-value* |
Convex |
p-value* |
Concave |
p-value* | p-value† | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (μm) | Reductions (%‡) | Thickness (μm) | Reductions (%‡) | Thickness (μm) | Reductions (%‡) | |||||
| GCL + IPL | 88.09 ± 22.07 | 37.66 ± 28.35 (29.9) | <0.001 | 105.4 ± 22.05 | 83.8 ± 76.24 (44.2) | <0.001 | 102.91 ± 28.13 | 28.25 ± 40.81 (21.5) | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| INL | 70.66 ± 16.04 | 20.29 ± 22.83 (22.3) | 0.003 | 96.05 ± 19.43 | 35.85 ± 35.72 (27.1) | 0.001 | 71.75 ± 9.56 | 18.41 ± 35.74 (20.4) | 0.05 | <0.001 |
| OPL | 27.85 ± 8.47 | 3.09 ± 10.55 (10.1) | 0.213 | 32.05 ± 6.5 | 6.35 ± 7.95 (16.5) | 0.003 | 31 ± 10.29 | 0.25 ± 8.99 (0.6) | 0.755 | 0. 212 |
| ONL | 107.14 ± 19.39 | −7.71 ± 28.8 (-7.7) | 0.192 | 122.75 ± 19.41 | −12.95 ± 28.26 (-11.7) | 0.070 | 108.41 ± 27.04 | −5.58 ± 18.36 (-5.4) | 0.343 | 0. 022 |
| PRL | 84.61 ± 5.66 | 6.28 ± 8.94 (6.9) | 0.004 | 82.15 ± 12.61 | 7.1 ± 16.65 (7.8) | 0.059 | 82.91 ± 15.93 | 5.08 ± 14.41 (5.9) | 0.326 | 0. 653 |
| CMT | 363 ± 42.88 | 50.09 ± 62.95 (12.1) | 0.003 | 400.15 ± 35.75 | 160.55 ± 76.79 (28.6) | <0.001 | 366.16 ± 58.04 | 12.5 ± 102.11 (3.3) | 0.969 | 0. 023 |
Table 5.
Correlation between visual acuity and each retinal layer thickness according to epiretinal membrane patterns before and after epiretinal membrane
| Preop retinal layer |
Flat |
Convex |
Concave |
Total |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop VA | Postop VA | Change of VA | Preop VA | Postop VA | Change of VA | Preop VA | Postop VA | Change of VA | Preop VA | Postop VA | Change of VA | |
| GCL + IPL | −0.121 | −0.296 | 0.082 | 0.600* | 0.164 | 0.562* | −0.132 | 0.109 | −0.137 | 0.552† | 0.242 | 0.383† |
| INL | −0.09 | −0.272 | 0.165 | 0.605* | 0.074 | 0.633* | −0.206 | −0.044 | −0.158 | 0.49† | 0.124 | 0.414† |
| OPL | −0.044 | −0.497‡ | 0.585* | −0.153 | 0.124 | −0.295 | −0.132 | 0.046 | −0.053 | 0.197 | −0.076 | 0.268 |
| ONL | −0.065 | 0.12 | −0.291 | 0.105 | −0.145 | 0.066 | 0.406 | −0.455 | 0.54 | 0.127 | 0.048 | 0.094 |
| PRL | 0.015 | 0.071 | −0.103 | 0.296 | 0.513* | −0.126 | 0.14 | −0.197 | 0.137 | 0.006 | 0.114 | −0.086 |
| CMT | −0.121 | −0.301 | 0.156 | 0.661* | 0.374 | 0.445‡ | 0.089 | −0.08 | 0.095 | 0.527† | 0.234 | 0.363† |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download