Abstract
Purpose
In this study we compared the surface wettability of ocular prosthesis and depositions depending on different types of artificial tear eye drops.
Methods
The artificial tear eye drops contain sodium hyaluronate (HA) 0.1%, 0.18%, 0.3%, carboxylmethylcellulose sodium (CMC), hydroxymethylcelluose + dextran (HMC), propylene glycol + polyethylene glycol (PG), polysorbate 80 (PS) povidone (Pov) were evaluated. Flat rectangular parallelepiped blocks consisting of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) or silicone materials were made. One artificial tear eye drop was applied on the surface of two different blocks of artificial eyes using a 23-gauge needle. Then, the static method contact angle was measured by using a contact angle goniometer. To measure the deposits, a petri dish was covered with 3 mL of artificial tear eye drops and dried for 48 hours at room temperature. Then, the light transmittance at the center of the petri dish was measured to investigate the amount of the residue.
Results
The contact angles of HA 0.1%, 0.18%, 0.3%, CMC, HMC, PG, PS and Pov on PMMA were 78.69°, 84.29°, 75.46°, 80.93°, 66.29°, 71.26°, 58.40° and 70.24°, respectively. The contact angles on silicone were 53.68°, 60.87°, 64.46°, 62.78°, 38.89°, 63.58°, 30.68° and 51.41°, respectively. The largest decrease in transparency was observed in the artificial tear eye drops containing HMC.
Conclusions
The wettability and deposits on the surface of ocular prosthesis can vary based on the components and concentration of artificial tear eye drops. The results from this study should be considered when choosing the right artificial tear eye drops for improving dry eye symptoms in patients wearing ocular prostheses.
Go to : 
References
1. Lemp MA. Report of the National Eye Institute/Industry workshop on Clinical Trials in Dry Eyes. CLAO J. 1995; 21:221–32.
2. Kim SE, Yoon JS, Lee SY. Tear measurement in prosthetic eye users with fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:602–7.e1.

3. Aragona P, Papa V, Micali A, et al. Long term treatment with sodium hyaluronate-containing artificial tears reduces ocular surface damage in patients with dry eye. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:181–4.

4. Asbell PA. Increasing importance of dry eye syndrome and the ideal artificial tear: consensus views from a roundTable discussion. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006; 22:2149–57.

5. Carré A, Woehl P. Spreading of silicone oils on glass in two geometries. Langmuir. 2006; 22:134–9.

6. Churaev NV, Sobolev VD. Wetting of low-energy surfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2007; 134-5:15–23.

7. Molina R, Comelles F, Juliá MR, Erra P. Chemical Modifications on Human Hair Studied by Means of Contact Angle Determination. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2001; 237:40–6.

8. Tonge S, Jones L, Goodall S, Tighe B. The ex vivo wettability of soft contact lenses. Curr Eye Res. 2001; 23:51–9.

9. Cheng L, Muller SJ, Radke CJ. Wettability of silicone-hydrogel contact lenses in the presence of tear-film components. Curr Eye Res. 2004; 28:93–108.

10. Ketelson HA, Meadows DL, Stone RP. Dynamic wettability properties of a soft contact lens hydrogel. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2005; 40:1–9.

12. Adler M, Miller R, Weaire D. Advances in colloid and interface science. Foreword. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2008; 137:1.
13. Allen L, Kolder HE, Bulgarelli EM, Bulgarelli DM. Artificial eyes and tear measurements. Ophthalmology. 1980; 87:155–7.

14. Jang SY, Lee SY, Yoon JS. Meibomian gland dysfunction in longstanding prosthetic eye wearers. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:398–402.

15. Saedon H, Cheung D. Occult traumatic nasolacrimal duct obstruction causing anophthalmic socket contraction presenting 20 years later: a case report. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2008; 27:87–9.

16. Read ML, Morgan PB, Kelly JM, Maldonado-Codina C. Dynamic contact angle analysis of silicone hydrogel contact lenses. J Biomater Appl. 2011; 26:85–99.

17. Chau TT, Bruckard WJ, Koh PT, Nguyen AV. A review of factors that affect contact angle and implications for flotation practice. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2009; 150:106–15.

18. Yang J, Rose FR, Gadegaard N, Alexander MR. Effect of sessile drop volume on the wetting anisotropy observed on grooved surfaces. Langmuir. 2009; 25:2567–71.

19. Taylor M, Urquhart AJ, Zelzer M, et al. Picoliter water contact angle measurement on polymers. Langmuir. 2007; 23:6875–8.

20. Yuan Y, Lee TR. Contact angle and wetting properties. Surface Science Techniques. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2013; 51:3–34.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Two flat rectangular parallelepiped blocks. According to the conventional methods of manufacturing of ocular prosthesis, two blocks have been produced with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) or silicone. |
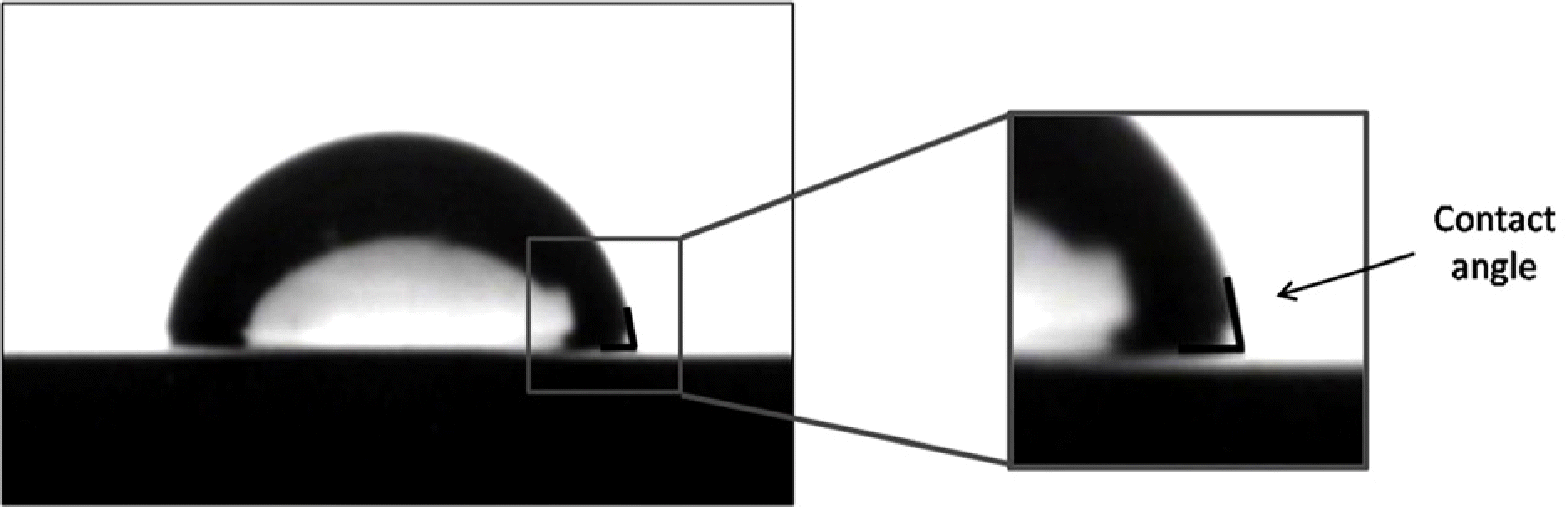 | Figure 2.Measurement of contact angle. The contact angle is an angle formed between the liquid/solid interface and the liquid/vapor interface. |
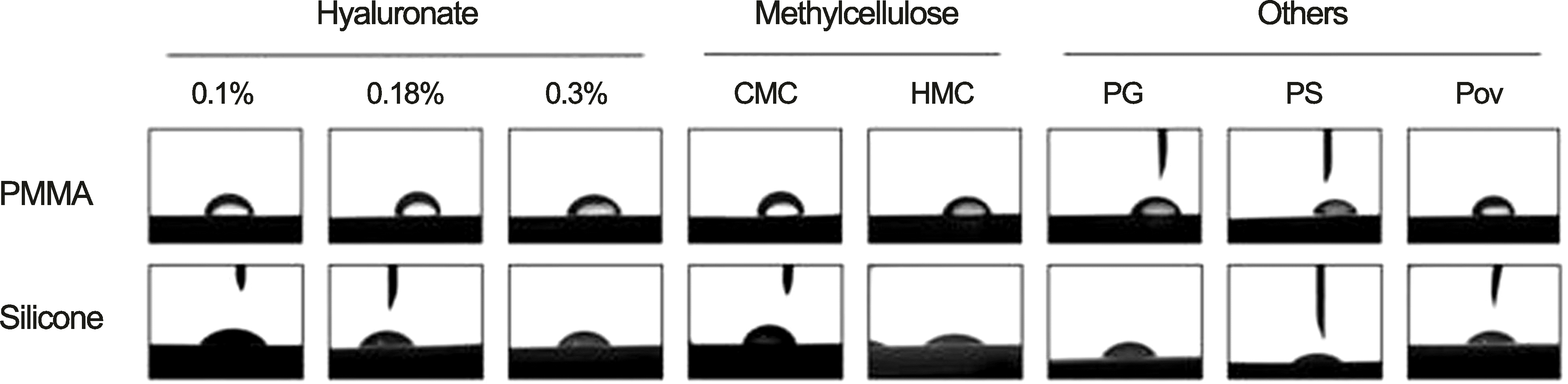 | Figure 3.Images obtained from a contact angle goniometer. One drop of each artificial tear eye drops was applied on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) or silicone block. CMC = carboxylmethylcellulose sodium; HMC = hydroxymethylcelluose + dextran; PG = propylene glycol + polyethylene glycol; PS = polysorbate 80; Pov = povidone. |
 | Figure 4.The residues of each artificial tear eye drops in petri dishes. After evaporation, the HMC containing artificial tear eye drops showed the most residues on the petri dish. HA = hyaluronate; HMC = hydroxymethylcelluose + dextran; CMC = carboxylmethylcellulose sodium; PG = propylene glycol + polyethylene glycol; PS = polysorbate 80; Pov = povidone. |
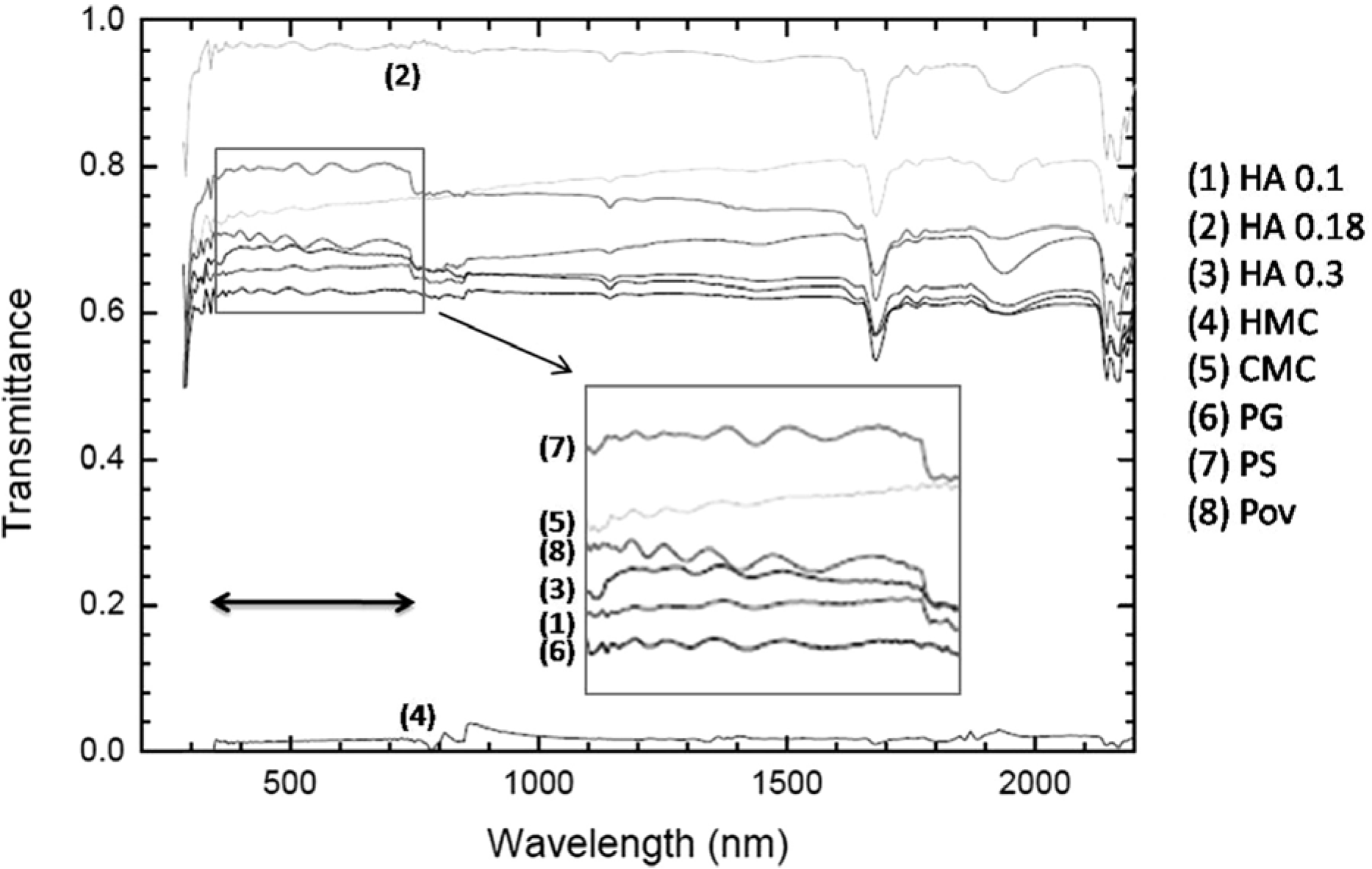 | Figure 5.Transmittance through the residue of artificial tear eye drops. After drying of each eye drop on petri dishes, the transmittance was measured by spectrometer. A double head arrow indicates the visible light wavelength range (330-770 nm). HA = hyaluronate; HMC = hydroxymethylcelluose + dextran; CMC = carboxylmethylcellulose sodium; PG = propylene glycol + polyethylene glycol; PS = polysorbate 80; Pov = povidone. |
Table 1.
Selected artificial tear eye drops
Table 2.
Contact angles of artificial tear eye drops on PMMA or silicone block (°)
|
Hyaluronate |
Methylcellulose |
Others |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1% | 0.18% | 0.3% | CMC | HMC | PG | PS | Pov | |
| PMMA | 78.69 | 84.29 | 75.46 | 80.93 | 66.29 | 71.26 | 58.40 | 70.24 |
| Silicone | 53.68 | 60.87 | 64.46 | 62.78 | 38.89 | 63.58 | 30.68 | 51.41 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download