Abstract
Purpose
To assess the changes in mean corneal refractive power (ΔK) following pterygium surgery and to predict ΔK in cases of combined cataract and pterygium surgery.
Methods
Thirty-seven eyes of unilateral pterygium patients who underwent pterygium surgery were analyzed retrospectively with at least more than 1 month of follow-up. Preoperative and postoperative 1 month corneal refractive power was measured using auto-keratometer (RK-F1, Canon, Tokyo, Japan). Pterygium horizontal extension, width, and area were measured and correlation with ΔK before and after surgery analyzed. We also compared ΔK of the contralateral normal eye.
Results
The mean corneal refractive (Km) power measured before and 1 month after surgery was 43.30 ± 1.66 D and 44.07 ± 1.42 D, respectively. The Km significantly increased at 4 weeks after surgery (p < 0.001). However, postoperative Km was not significantly different when compared with the contralateral normal eye (43.86 ± 1.34 D; p = 0.59). All parameters of pterygium size including horizontal extension, width, and area were positively correlated with the mean ΔK. Among parameters, horizontal extension was best correlated with mean ΔK (p < 0.001). The mean ΔK with horizontal extension was predicted using linear regression (2.5 mm to 1 D, 4.0 mm to 1.8 D).
Go to : 
References
1. Bedrossian RH. The effects of pterygium surgery on refraction and corneal curvature. Arch Ophthalmol. 1960; 64:553–7.

2. Oldenburg JB, Garbus J, McDonnell JM, McDonnell PJ. Conjunctival pterygia. Mechanism of corneal topographic changes. Cornea. 1990; 9:200–4.
3. Starck T, Kenyon KR, Serrano F. Conjunctival autograft for primary and recurrent pterygia: surgical technique and problem management. Cornea. 1991; 10:196–202.

4. Hansen A, Norn M. Astigmatism and surface phenomena in pterygium. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1980; 58:174–81.

5. Lin A, Stern G. Correlation between pterygium size and induced corneal astigmatism. Cornea. 1998; 17:28–30.

6. Fong KS, Balakrishnan V, Chee SP, Tan DT. Refractive change following pterygium surgery. CLAO J. 1998; 24:115–7.
7. Tomidokoro A, Oshika T, Amano S, et al. Quantitative analysis of regular and irregular astigmatism induced by pterygium. Cornea. 1999; 18:412–5.

8. Tomidokoro A, Miyata K, Sakaguchi Y, et al. Effects of pterygium on corneal spherical power and astigmatism. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:1568–71.

9. Cinal A, Yasar T, Demirok A, Topuz H. The effect of pterygium surgery on corneal topography. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2001; 32:35–40.

10. Mohammad-Salih PA, Sharif AF. Analysis of pterygium size and induced corneal astigmatism. Cornea. 2008; 27:434–8.

11. Stern GA, Lin A. Effect of pterygium excision on induced corneal topographic abnormalities. Cornea. 1998; 17:23–7.

12. Lee DW, Kim JM, Choi CY, et al. Age-related changes of ocular parameters in Korean subjects. Clin Ophthalmol. 2010; 4:725–30.

13. Han HC, Kim JH, Lee DH. The changes of corneal higher-order aberrations after surgery according to pterygium size. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:32–9.

14. Kwon SM, Lee DJ, Jeung WJ, Park WC. Power vector and aberrations using corneal topographer and wavefront aberrometer before and after pterygium surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1737–45.

15. Moon HJ, Youn WS. Changes in the corneal curvature after pterygium surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1971; 12:167–9.
16. Budak K, Khater TT, Friedman NJ, Koch DD. Corneal topographic changes induced by excision of perilimbal lesions. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999; 30:458–64.

17. Kampitak K. The effect of pterygium on corneal astigmatism. J Med Assoc Thai. 2003; 86:16–23.
Go to : 
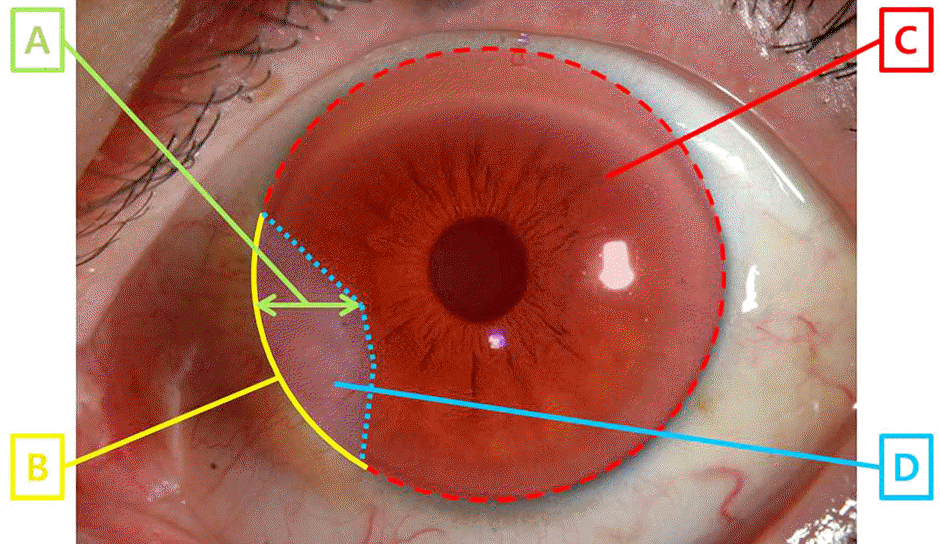 | Figure 1.The parameter of pterygium size by graphic program. The horizontal extension of pterygium on cornea (A) was measured between the nasal limbus and the point farthest away from the limbus and the width (B) was the base arc between 2 limbal points where the pterygium intersected with the limbus. Each area of entire cornea (C) and pterygium on cornea (D) was measured and then the area ratio of pterygium (D/C × 100) was calculated with proportion of pterygium invaded onto the cornea. |
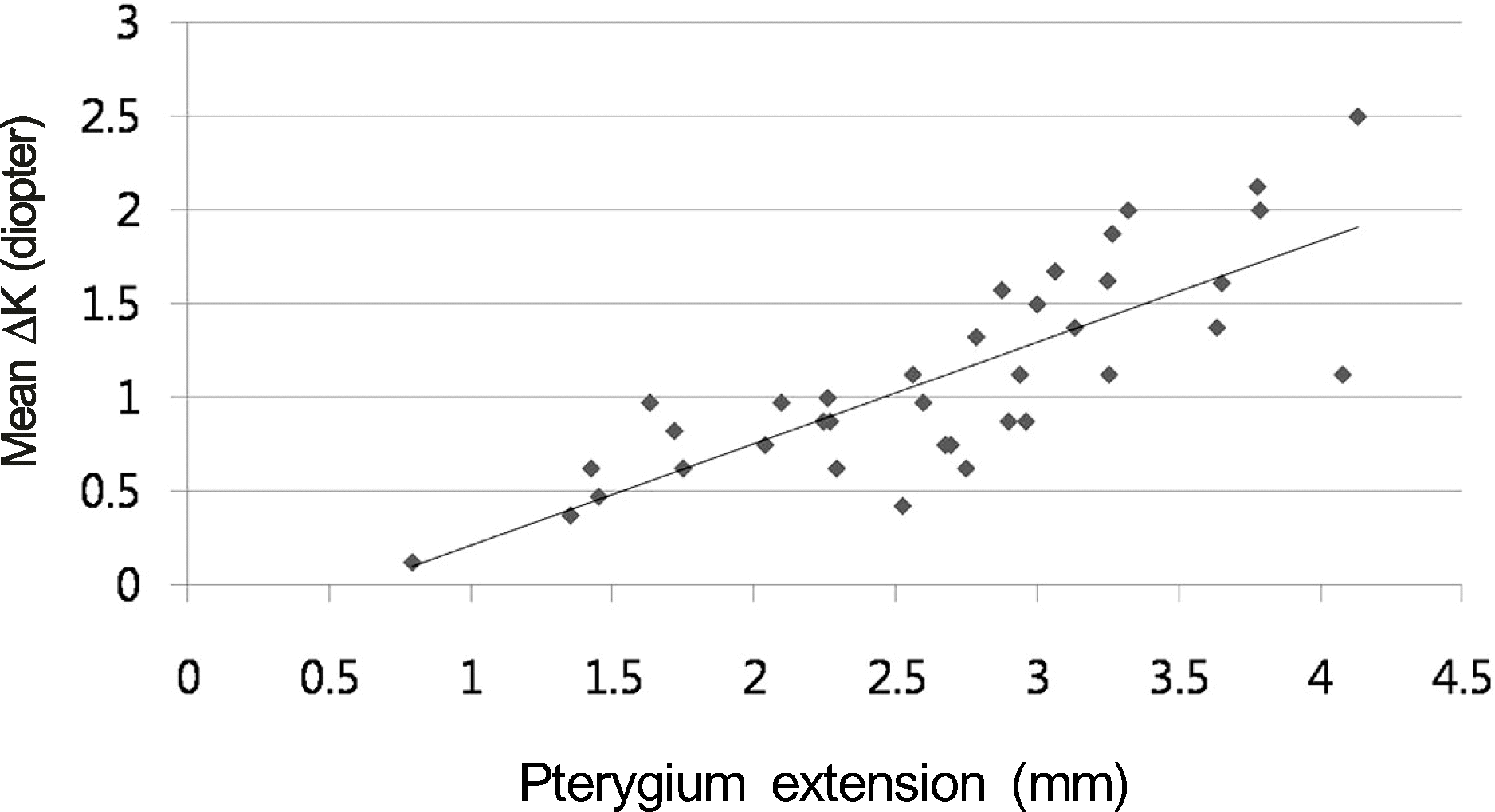 | Figure 2.Scatterplot of mean ΔK and pterygium extension. Mean ΔK: postoperative mean corneal refractive power minus preoperative mean corneal refractive power. Pterygium extension: distance between the nasal limbus and the point of pterygium farthest away from the limbus. |
Table 1.
The patient characteristics
| Subjects (n = 40) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56.86 ± 8.10 |
| Sex (M:F) | 21:16 |
| Recurred (eye) | 0 |
| Involved eye (right:left) | 37 (25:12) |
| Pterygium size | |
| Extension (mm)∗ | 2.74 ± 0.86 |
| Width (mm)† | 6.00 ± 1.53 |
| Area ratio (%)‡ | 12.22 ± 7.85 |
| UCVA (Scale) | |
| Preoperative | 0.78 ± 0.27 |
| Postoperative 1 month | 0.85 ± 0.23 |
Table 2.
The mean corneal refractive power measured by autokeratometry before and after pterygium surgery
| Keratometry | Preoperative (range) | Postoperative 1 month (range) |
|---|---|---|
| Kh (diopter) | 42.30 ± 1.97 (36.75-46.0) | 43.74 ± 1.30 (40.5-46.25)∗ |
| Kv (diopter) | 44.29 ± 1.70 (40.25-47.5) | 44.41 ± 1.61 (39.75-47.0) |
| Km (diopter) | 43.30 ± 1.66 (38.5-46.13) | 44.07 ± 1.42 (40.125-46.38)∗ |
Table 3.
The correlation between parameters of pterygium size and changes of mean corneal refractive power (mean ΔK) between preoperative and postoperative 1 month
| Mean ΔK | |
|---|---|
| Extension∗ | |
| Pearson's coefficient r | 0.80 |
| p-value | <0.001 |
| Width† | |
| Pearson's coefficient r | 0.29 |
| p-value | 0.14 |
| Area ratio‡ | |
| Pearson's coefficient r | 0.19 |
| p-value | 0.35 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download