Abstract
Case summary
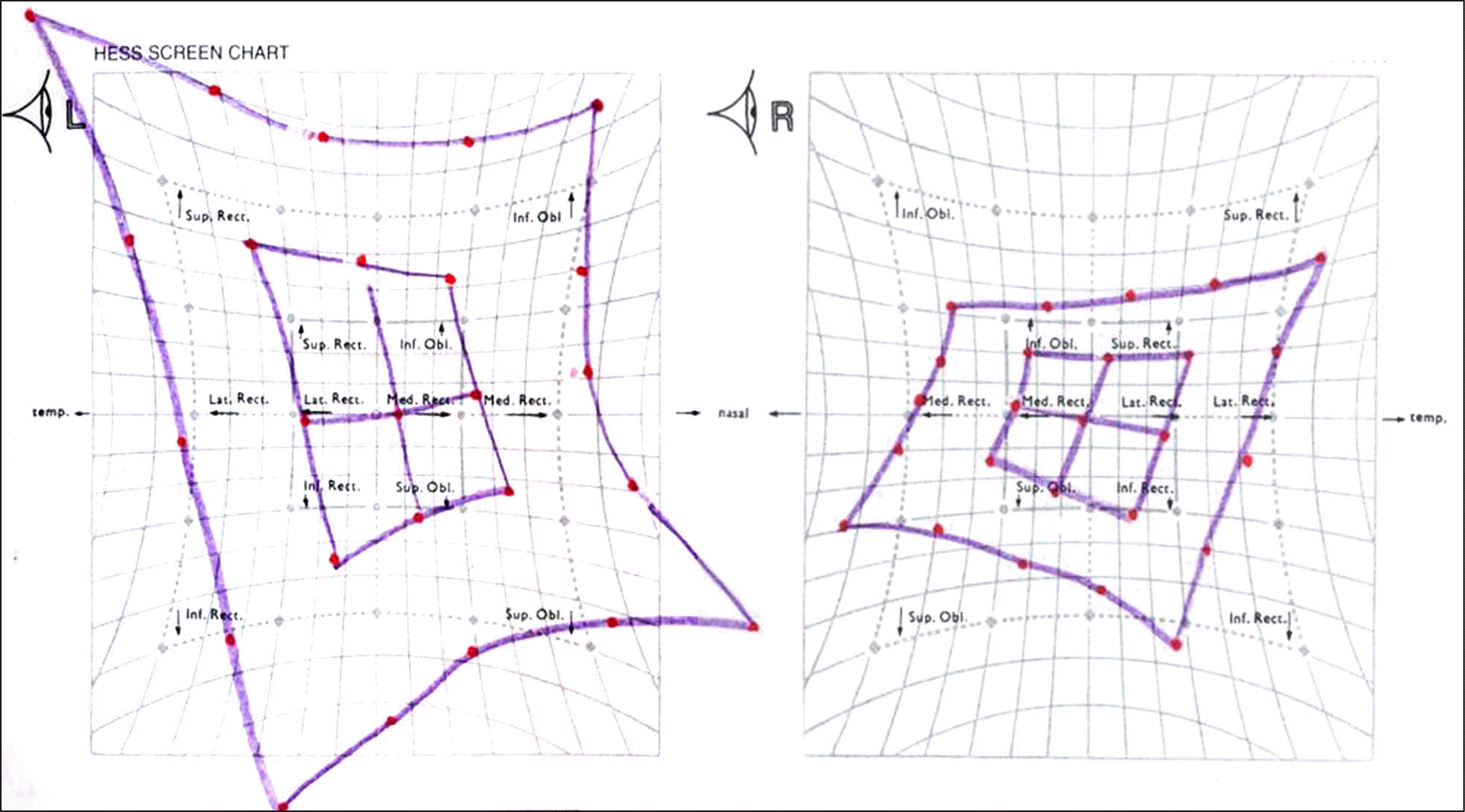
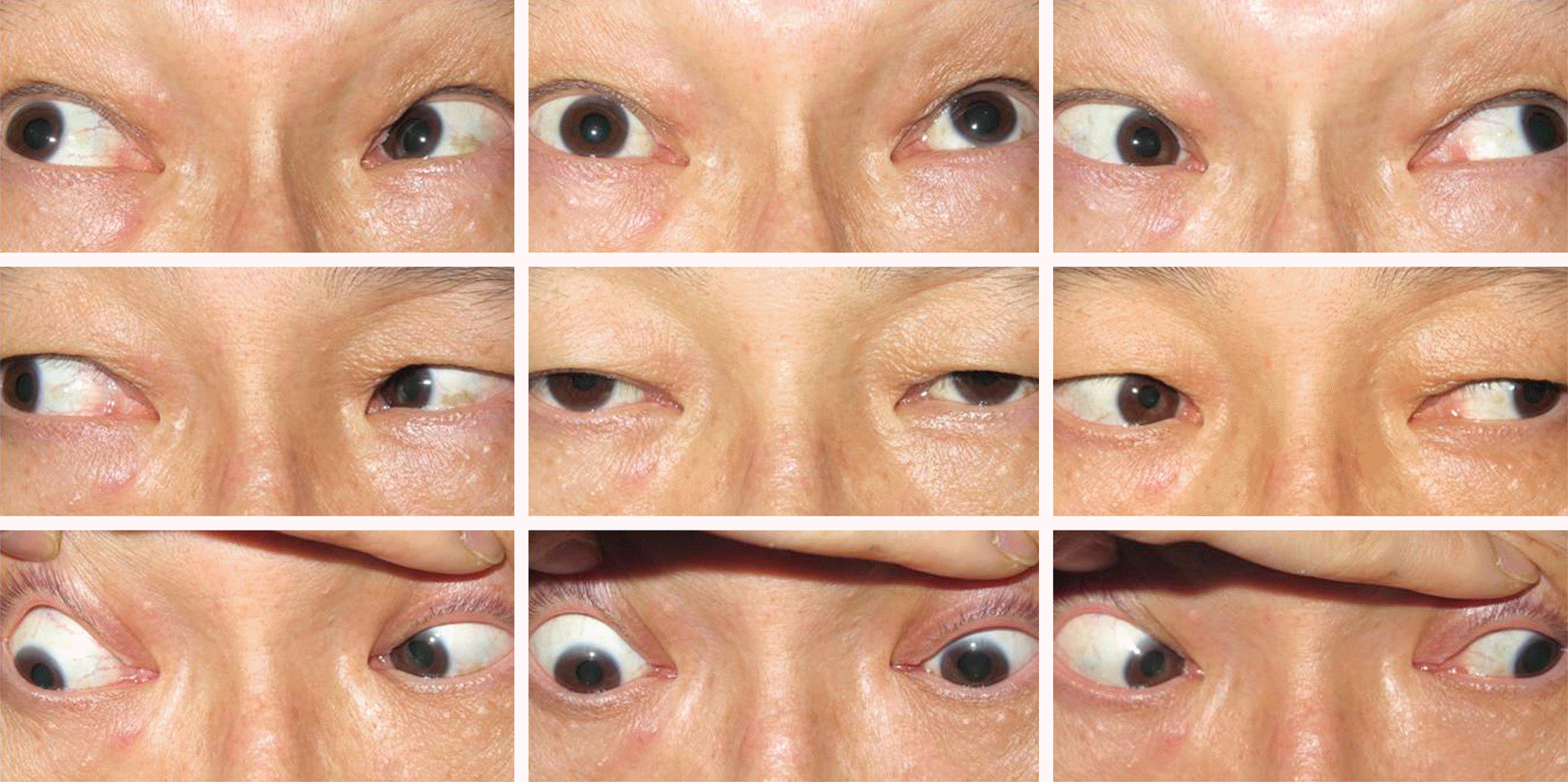
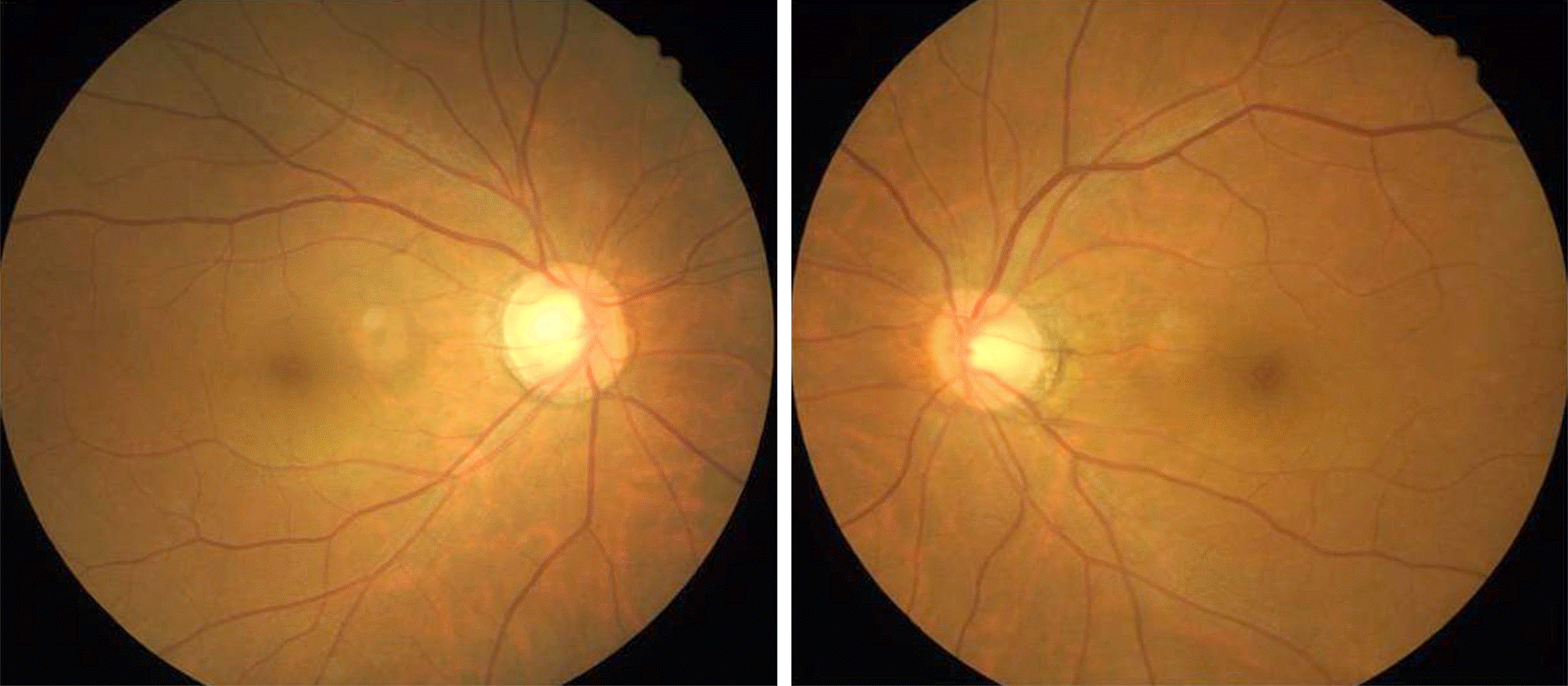
A 43-year-old male with intermittent watery rhinorrhea persisting for 3 months visited the neurosurgery department of our institute. His past medical history included removal of a pituitary adenoma 22 years prior to presentation. Cerebrospinal fluid leakage was suspected and cisternography was performed. The patient was referred to our ophthalmology department for diplopia 3 days after the cisternography. An alternate prism cover test showed 5 prism diopter (PD) right hypertrophia in the primary position, and underaction of bilateral superior oblique muscles and overaction of the left inferior oblique muscle. A positive Bielschowsky test with the head tilted to either side was observed and excyclotorsion was 9° on the double Maddox rod test. The patient was diagnosed with bilateral trochlear nerve palsy. After 2 years of fol-low-up, diplopia persisted and recession of the bilateral inferior oblique muscles was performed. After the surgery, diplopia dis-appeared, the fundus photography showed no excyclotorsion, and the double Maddox rod test indicated 3° of excyclotorsion.
Go to : 
References
1. King RA, Calhoun JH.Fourth cranial nerve palsy following spinal anesthesia. A case report. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1987; 7:20–2.
2. Thorsén G.Neurological complications after spinal anaesthesia: and results from 2493 follow-up cases. Acta Chirg Scand. 1947; 95:75–94.
3. Follens I, Godts D, Evens PA, Tassignon MJ.Combined fourth and sixth cranial nerve palsy after lumbar puncture: a rare complication. A case report. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2001(281):29–33.
5. Sakurai K, Nishio M, Yamada K. . Comparison of the radio-isotope cisternography findings of spontaneous intracranial hypo-tension and iatrogenic cerebrospinal fluid leakage focusing on chronological changes. Cephalalgia. 2012; 32:1131–9.

7. Guy G, Comoy J, Chevet D. . [Aseptic meningitis after isotope cisternography. 2 Cases]. Neurochirurgie. 1976; 22:631–8.
8. Ponto JA.Special safety considerations in preparation of techne-tium Tc-99m DTPA for cerebrospinal fluid-related imaging procedures. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2008; 48:413–6.

9. Park BS, Park J, Koh SH. . Conus medullaris syndrome as a complication of radioisotope cisternography. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012; 39:347–51.

Go to : 
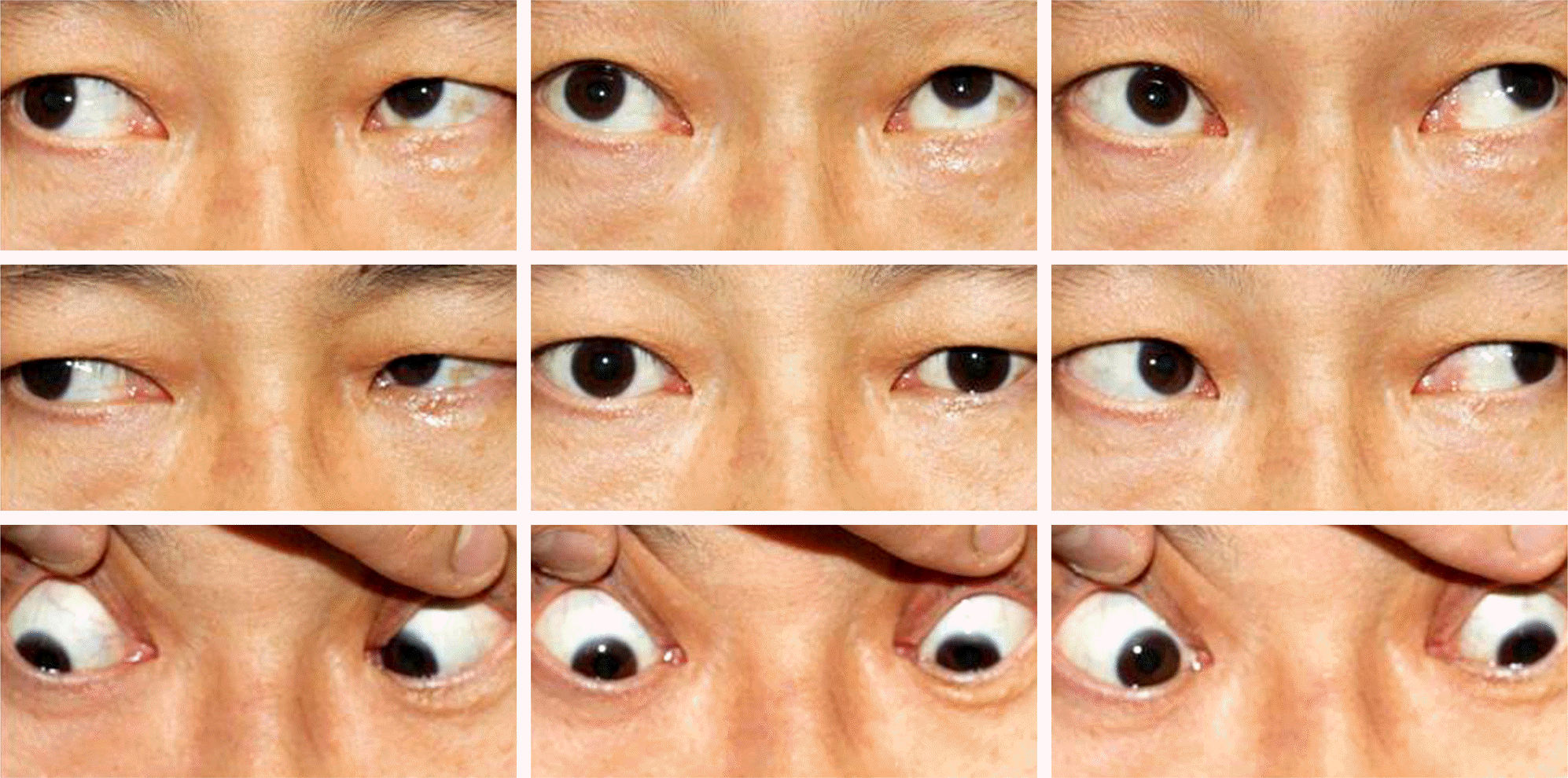 | Figure 1.Nine cardinal photographs at the first visit showing underaction of bilateral superior oblique muscles and overaction of the left inferior oblique muscle. |
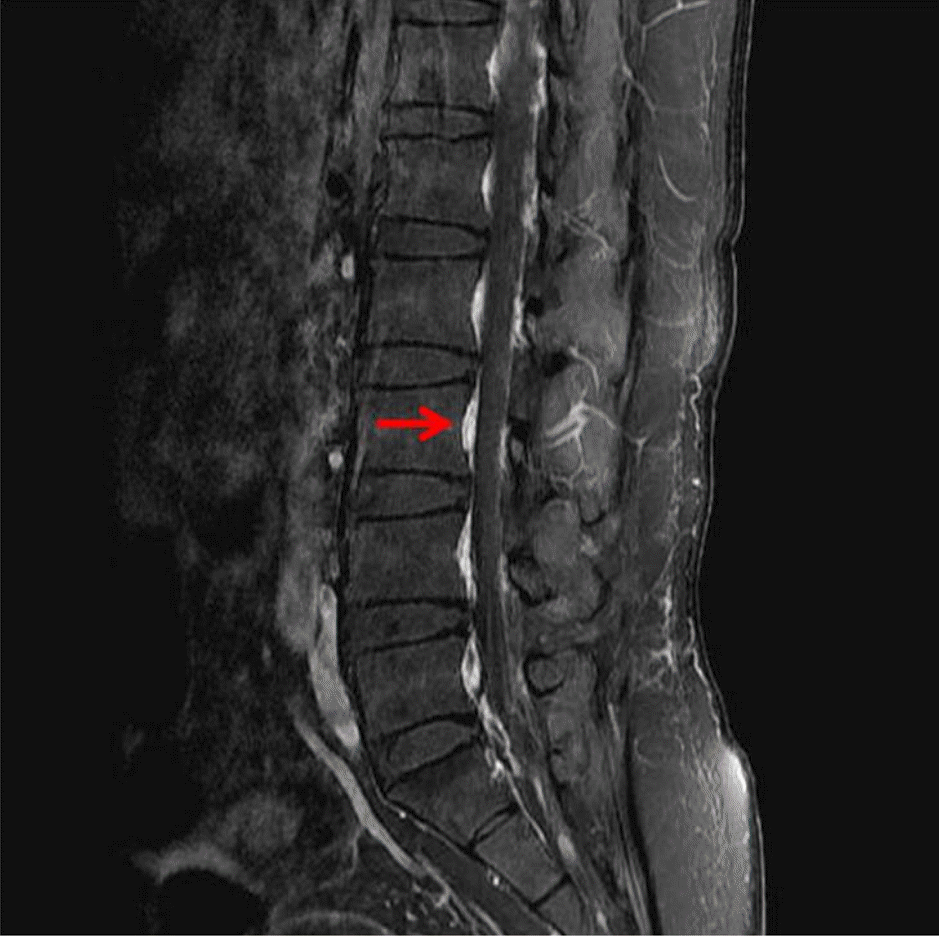 | Figure 3.Lumbar spine MRI with postcontrast fat-suppressed T1-weighted sagittal image showing increased epidural enhancement (arrow). |
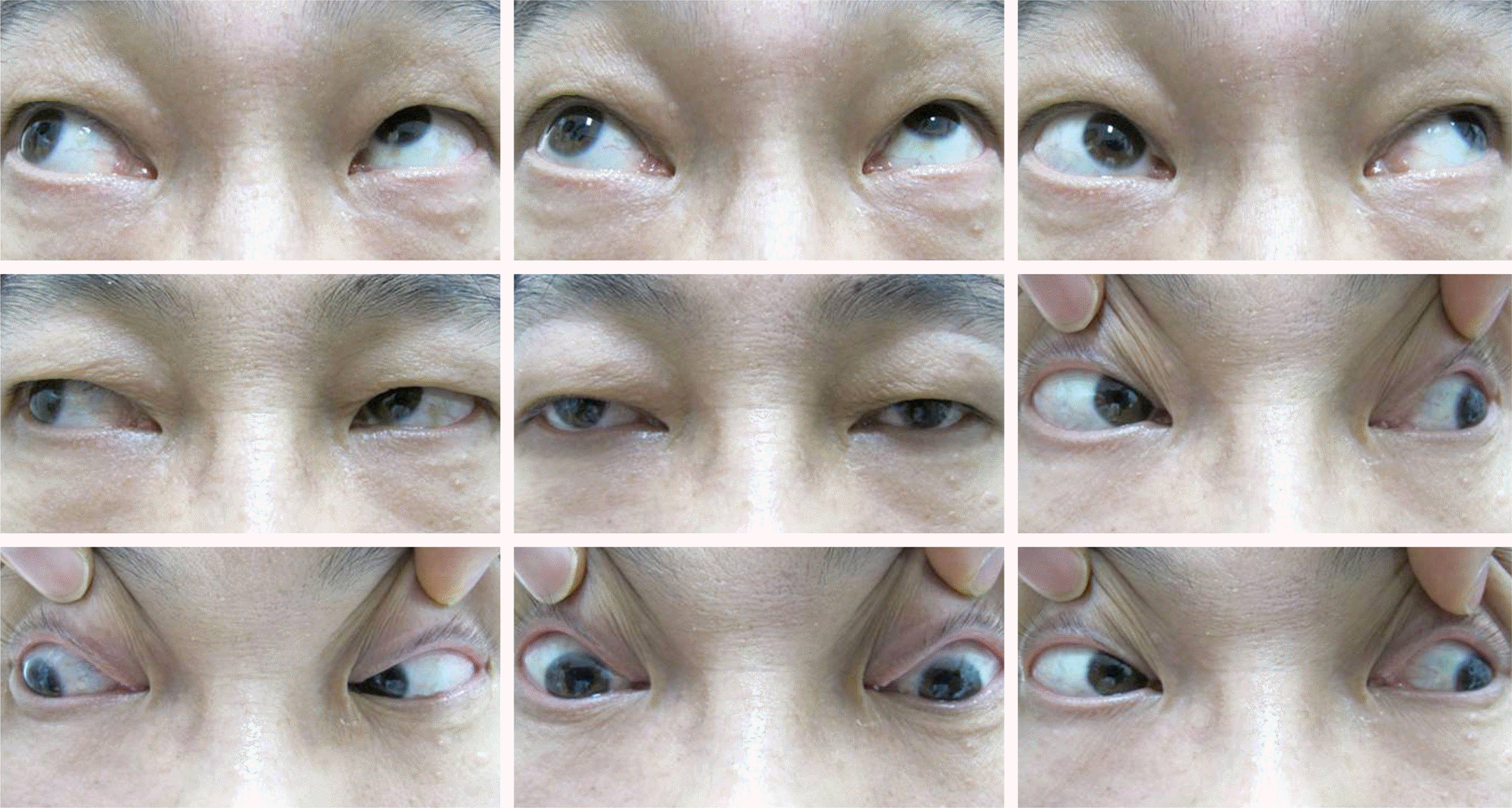 | Figure 4.Preoperative nine cardinal photographs showing underaction of bilateral superior oblique muscles and marked overaction of the left inferior oblique muscle. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download