Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the difference in astigmatism and the mean change in total astigmatism between inferior clear corneal incision and superior clear corneal incision following cataract surgery in surgically-induced astigmatism (SIA). Methods: Fifty-five eyes of 55 patients with with-the-rule astigmatism >0.5 diopters were evaluated. Patients were divided into two groups according to incision location (Group 1, 26 eyes with an inferior incision; Group 2, 29 eyes with a superior incision). Patients were evaluatied one month postoperatively. Uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA, log MAR), best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA, log MAR), SIA and mean change in corneal astigmatism were measured in both groups.
Results
One month postoperatively, mean UCVA was 0.15 ± 0.17 log MAR in Group 1 and 0.23 ± 0.24 log MAR in Group 2 (p = 0.253). Mean BCVA was 0.08 ± 0.13 and 0.08 ± 0.12 log MAR in Groups 1 and 2, respectively (p = 0.926). The SIA was 0.50 ± 0.17 diopter and 0.57 ± 0.34 diopter (p = 0.253) and mean change in total astigmatism was 0.50 ± 0.96 diopter and 0.38 ± 0.86 diopter in Groups 1 and 2, respectively (p = 0.426).
Go to : 
References
1. Tejedor J, Murube J. Choosing the location of corneal incision based on preexisting astigmatism in phacoemulsification. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:767–76.

2. Khokhar S, Lohiya P, Murugiesan V, Panda A. Corneal astigmatism correction with opposite clear corneal incisions or single clear corneal incision: comparative analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1432–7.

3. Bayramlar H, Hü Dağlioğlu MC, Borazan M. Limbal relaxing incisions for primary mixed astigmatism and mixed astigmatism after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:723–8.

4. Barequet IS, Yu E, Vitale S, et al. Astigmatism outcomes of horizontal temporal versus nasal clear corneal incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:418–23.

5. Kaufmann C, Peter J, Ooi K, et al. Limbal relaxing incisions versus on-axis incisions to reduce corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:2261–5.

6. Wang Li, Misra M, Koch DD. Peripheral corneal relaxing incisions combined with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:712–22.

7. Seo JB, Joo CK. Long-term course of induced astigmatism after temporal clear corneal incision in cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3038–43.
8. Shepherd JR. Induced astigmatism in small incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989; 15:85–8.

9. Cravy TV. Routine use of a lateral approach to cataract extraction to achieve rapid and sustained stabilization of postoperative astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:415–23.

10. Vasavada A, Singh R. Relationship between lens and capsular bag size. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:547–51.

11. Axt JC, McCaffery JM. Reduction of postoperative against-the-rule astigmatism by lateral incision technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:380–6.

13. Koch PS. Mastering phacoemulsification: A simplified manual of strategies for the spring, crack, and stop & chop technique. 4th ed.Thorofare, NJ: Slack;1994; 7–44.
15. Axt JC, McCaffery JM. Reduction of postoperative against-the-rule astigmatism by lateral incision technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:380–6.

16. Mendívil A. Comparative study of astigmatism through superior and lateral small incisions. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1996; 6:389–92.

17. Roman S, Ullern M. [Astigmatism caused by superior and temporal corneal incisions in cataract surgery]. J Fr Ophtalmol. 1997; 20:277–83.
18. Joo CK, Han HK, Kim JH. Computer-assisted videokeratography to measure changes in astigmatism induced by sutureless cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:555–61.

19. Simşek S, Yaşar T, Demirok A, et al. Effect of superior and temporal clear corneal incisions on astigmatism after sutureless phacoe-mulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:515–8.
Go to : 
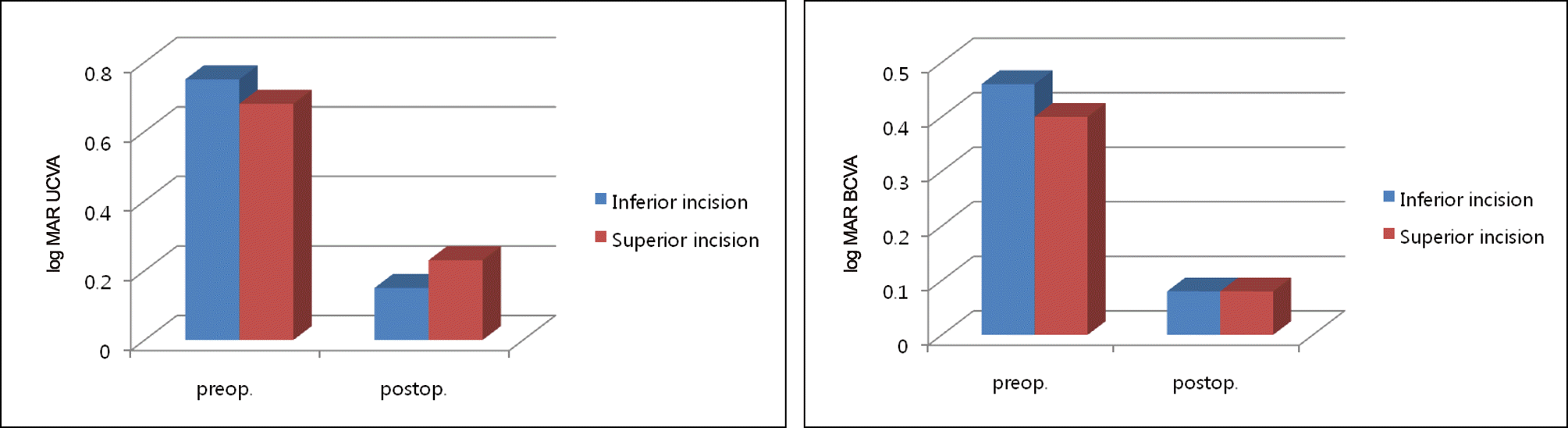 | Figure 1.Uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA) and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) in the 2 groups. |
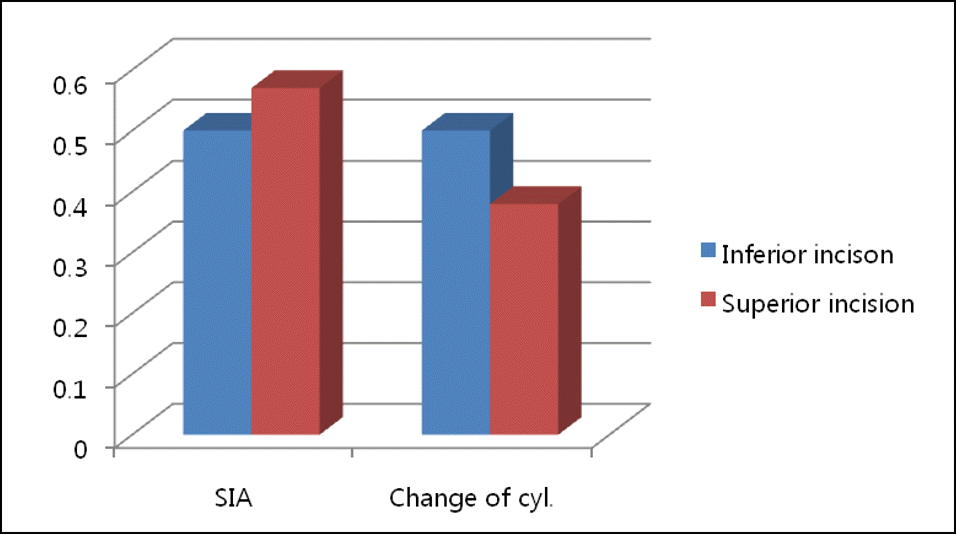 | Figure 2.Surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) and change in cylinder (absolute value of preoperative cylinder - absolute value of postoperative cylinder) doesn't show statistically significant difference between 2 groups. |
Table 1.
Demographics and preoperative data in each group
| Inferior incision | Superior incision | *p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of eyes | 26 | 29 | |
| Sex (M/F) | 10/16 | 16/13 | |
| Age (years) | 55.31 ± 11.60 | 53.38 ± 11.48 | 0.224 |
| UCVA (log MAR) | 0.75 ± 0.50 | 0.68 ± 0.36 | 0.933 |
| BCVA (log MAR) | 0.46 ± 0.37 | 0.40 ± 0.28 | 0.664 |
| Autorefraction cylinder (diopter) | 1.18 ± 0.59 | 1.14 ± 0.54 | 0.687 |
| Topographic cylinder (diopter) | 1.12 ± 0.65 | 1.09 ± 0.52 | 0.906 |
Table 2.
Postoperative UCVA (log MAR) and BCVA (log MAR) in both inferior incision group and superior incision group
| Inferior incision | Superior incision | *p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| UCVA (log MAR) | 0.15 ± 0.17 | 0.23 ± 0.24 | 0.253 |
| BCVA (log MAR) | 0.08 ± 0.13 | 0.08 ± 0.12 | 0.926 |
Table 3.
Surgically induced astigmatism and change in cylinder according to preoperative astigmatism in both inferior incision group and superior incision group
| Inferior incision | Superior incision | *p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgically induced astigmatism (diopter) | 0.50 ± 0.33 | 0.57 ± 0.34 | 0.324 |
| Change in autorefraction cylinder (diopter) | 0.50 ± 0.96 | 0.38 ± 0.86 | 0.426 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download