Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical outcomes of patients with diffractive multifocal toric intraocular lens (IOL) implantation.
Methods
Thirty-four eyes of 26 patients underwent diffractive multifocal toric IOL. Uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA) at distant, intermediate and near and residual refractive astigmatism were measured on the first day, at 2 weeks, and 1, 3 and 6 months postoperatively. Optical quality obtained using the Optical Quality Analysis System II (OQAS II), high-order aberrations (HOA) and patient satisfaction questionnaire were evaluated 3 months postoperatively.
Results
At the 6 month postoperative visit, the mean UCVA at distant, intermediate (63 cm, 100 cm) and near were 0.06 ± 0.07, 0.18 ± 0.11, 0.16 ± 0.12 and 0.03 ± 0.06 (log MAR), respectively. The refractive astigmatism decreased significantly from −1.66 ± 1.04 D to-0.54 ± 0.32 D at 6 months postoperatively (p< 0.01). The means of objective scatter index, modulation transfer function (MTF) cut-off value, Strehl ratio and pseudo-accommodation range measured by OQAS II were 1.33 ± 0.67, 37.24 ± 9.67 cdp, 0.22 ± 0.09 and 3.08 ± 0.53 D, respectively. HOA scores for 5 mm and 6 mm were 0.30 ± 0.09 and 0.49 ± 0.15, respectively; 82.3% of the patients were satisfied with the postoperative results, 79.4% of the patients reported they would recommend the procedure to others, and 14.7% of patients reported moderate or severe visual disturbance at night.
Go to : 
References
1. Blaylock JF, Si Z, Vickers C. Visual and refractive status at different focal distances after implantation of the ReSTOR multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1464–73.

2. Kohnen T, Allen D, Boureau C, et al. European multicenter study of the AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:578–84.

3. Alfonso JF, Fernandez-Vega L, Baamonde MB, Montes-Mico R. Prospective visual evaluation of apodized diffractive intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1235–43.

4. Lee HS, Park SH, Kim MS. Clinical results and some problems of multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1235–41.

5. Cheon MH, Lee JE, Kim JH, et al. One-year outcome of monocular implant of aspheric multifocal IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:822–8.

6. Kang EC, Kim EK, Kim TI. Comparisons of visual acuity, spherical aberration and contrast sensitivity among spheric, aspheric ReSTOR(R), and Crystalens HD(R) lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:1275–80.
7. Kim SM, Kim CH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Visual outcome and patient satisfaction after implantation of multifocal IOLs: three- month follow-up results. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:230–7.
8. Kim S, Kim MS. The study on target refraction to improve visual quality in patients implanted with multifocal IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:223–9.

9. Gwak JY, Choi JS, Pak KH, Baek NH. Visual and optical functions after diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:396–402.
10. Hayashi K, Manabe S, Yoshida M, Hayashi H. Effect of astigmatism on visual acuity in eyes with a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1323–9.

11. Ferrer-Blasco T, Montes-Mico R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:70–5.

12. Budak K, Friedman NJ, Koch DD. Limbal relaxing incisions with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:503–8.

13. Kaufmann C, Peter J, Ooi K, et al. Limbal relaxing incisions versus on-axis incisions to reduce corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:2261–5.

14. Jendritza BB, Knorz MC, Morton S. Wavefront-guided excimer laser vision correction after multifocal IOL implantation. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:274–9.

15. Kim SI, Kim SJ, Oh JY, et al. The effects of laser refractive surgery for correcting residual refractive error after implantation of ReSTOR(R) multifocal IOL. J Koμ Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1742–8.
16. Kim MH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Long-term efficacy and rotational stability of AcrySof toric intraocular lens impalntation in cataract surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010; 24:207–12.
17. Visser N, Bauer NJ, Nuijts RM. Toric intraocular lenses: Historical overview, patient selection, IOL calculation, surgical techniques, clinical outcomes, and complications. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:624–37.

18. Ferreira TB, Marques EF, Rodrigues A, Montes-Mico R. Visual and optical outcomes of a diffractive multifocal toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1029–35.

19. Visser N, Nuijts RM, de Vries NE, Bauer NJ. Visual outcomes and patient satisfaction after cataract surgery with toric multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:2034–42.

20. Mojzis P, Pinero DP, Ctvrteckova V, Rydlova I. Analysis of internal astigmatism and higher order aberrations in eyes implanted with a new diffractive multifocal toric intraocular lens. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:341–8.

21. Koch DD, Ali SF, Weikert MP, et al. Contribution of posterior corneal astigmatism to total corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2080–7.

22. Ho JD, Tsai CY, Liou SW. Accuracy of corneal astigmatism estimation by neglecting the posterior corneal surface measurement. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:788–95.

23. Eom Y, Nam KT, Kang SY, et al. Axis Difference between corneal and internal astigmatism to consider for toric intraocular lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:1112–9.e2.

24. Lee JM, Seo KY, Kim EK. Comparison of optical aberrations and contrast sensitivity between monofocal and multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1882–6.
25. Montes-Mico R, Espana E, Bueno I, et al. Visual performance with multifocal intraocular lenses mesopic contrast sensitivity under distance and near conditions. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:85–96.
26. Vingolo EM, Grenga P, Iacobelli L, Grenga R. Visual acuity and contrast sensitivity: AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive versus AcrySof SA60AT monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1244–7.

27. Nochez Y, Majzoub S, Pisella PJ. Effect of interaction of macroaberrations and scattered light on objective quality of vision in pseudophakic eyes with aspheric monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:633–40.

28. Diaz-Valle D, Arriola-Villalobos P, Garcia-Vidal SE, et al. Effect of lubricating eyedrops on ocular light scattering as a measure of vision quality in patients with dry eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:1192–7.

29. Cabot F, Saad A, McAlinden C, et al. Objective assessment of crystalline lens opacity level by measuring ocular light scattering with a double-pass system. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155:629–35.

30. Lee K, Ahn JM, Kim EK, Kim TI. Comparison of optical quality parameters and ocular aberrations after wavefront-guided laser in-situ keratomileusis versus wavefront-guided laser epithelial keratomileusis for myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:2163–9.

31. Saad A, Saab M, Gatinel D. Repeatability of measurements with a double-pass system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:28–33.

32. Castillo-Gomez A, Carmona-Gonzalez D, Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, et al. Evaluation of image quality after implantation of 2 diffractive multifocal intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1244–50.
Go to : 
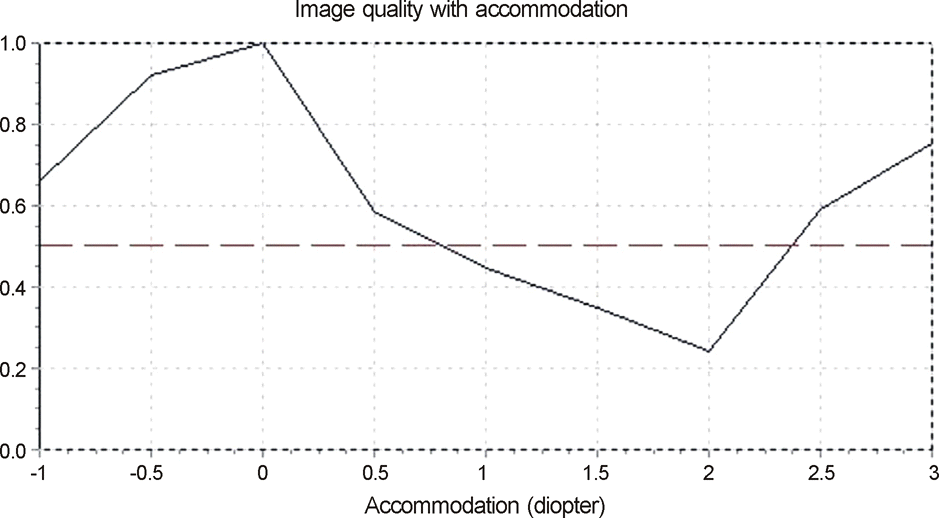 | Figure 2.An example of a patient's image quality with accommodation measured by optical quality analysis system II at post-op 3 months. The graph shows good optical quality at distant (0.0 D) and near (3.0 D). At the 3-month postoperative visit, the mean pseudo-accommodation range of total enrolled patients was 3.08 ± 0.53 D. |
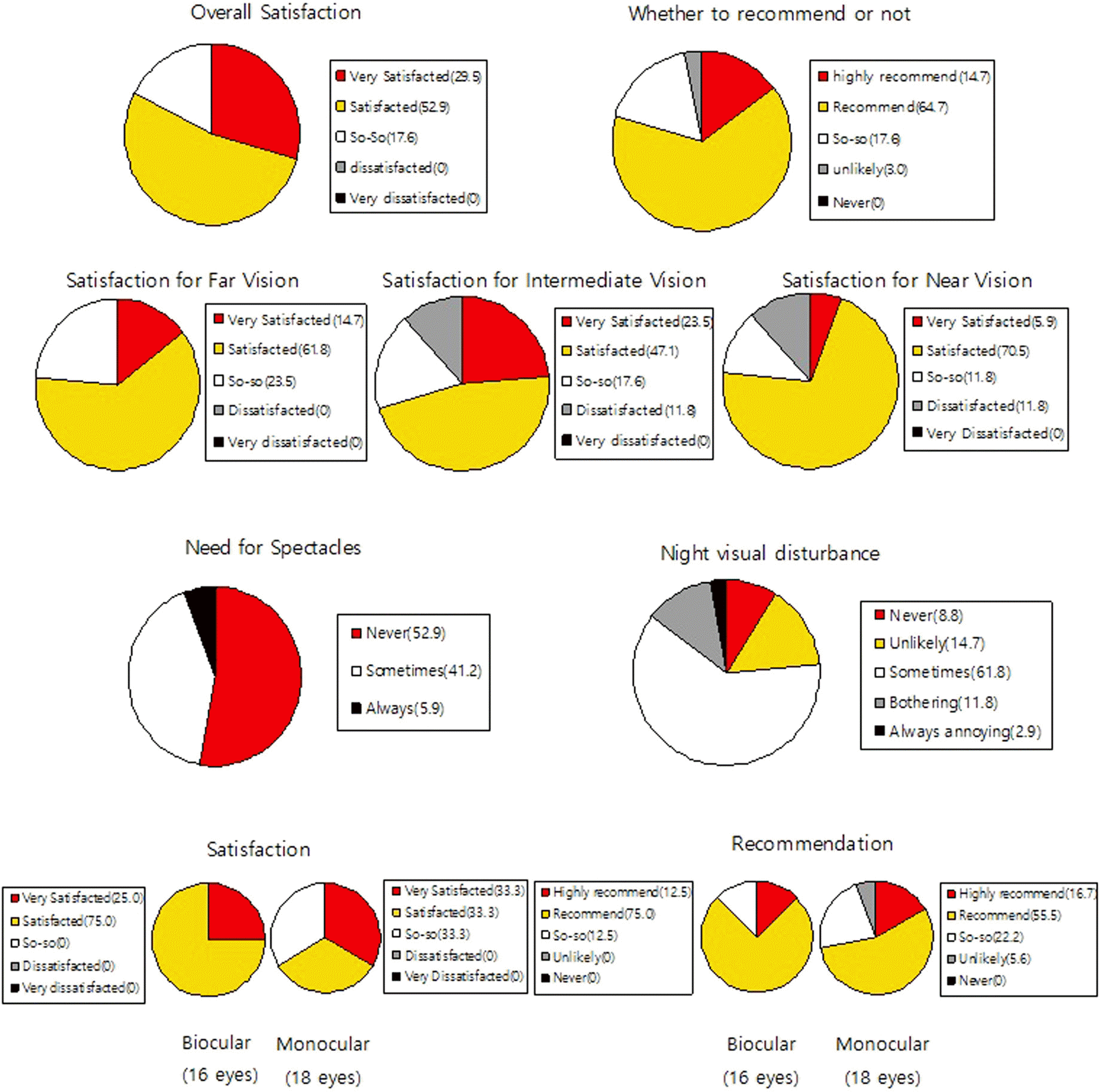 | Figure 3.Satisfaction of the patients with the diffractive multifocal toric intraocular lens (IOL) (%). |
Table 1.
Patient demographics and clinical information
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Eyes (n) | 34 |
| Patients (n) | 26 |
| Sex (M:F) | 12:14 |
| Age (years) (range) | 51.8 ± 5.5 (43-66) |
| UCDVA (log MAR) | 0.77 ± 0.48 |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) (range) | -3.57 ± 4.41 (2.00∼-11.75) |
| Mean astigmatism magnitude (diopter) | |
| Refractive* (range) | -1.66 ± 1.04 (-0.50∼-4.00) |
| Corneal† (range) | 1.21 ± 0.95 (0.50-3.50) |
| Mean D power (diopter) (range) | 17.24 ± 4.42 (7.50-22.5) |
| IOL model (n) | |
| SND1T2 | 2 |
| SND1T3 | 16 |
| SND1T4 | 9 |
| SND1T5 | 7 |
Table 2.
Postoperative visual acuity over time after implantation of the Acrysof® IQ Restor® toric IOL
IOL = intraocular lens; UCDVA = uncorrected distance visual acuity; BCDVA = best corrected distance visual acuity; UNVA = uncorrected near visual acuity at 40 cm distance; UIVA63 = uncorrected intermediate visual acuity at 63 cm distance; UIVA100 = uncorrected intermediate visual acuity at 100 cm distance.
Table 3.
Cylinder refraction (Cyl) and spherical equivalent (SE) at pre op, post op 1 day, 2 weeks, 1, 3 and 6 months
| Pre op | 1 day | 2 weeks | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyl (D) | -1.66 ± 1.04 | -0.58 ± 0.40 | -0.59 ± 0.41 | -0.55 ± 0.40 | -0.59 ± 0.22 | -0.54 ± 0.32 | <0.01 |
| SE (D) | -3.5 ± 4.41 | -0.23 ± 0.45 | -0.27 ± 0.37 | -0.31 ± 0.32 | -0.29 ± 0.37 | -0.34 ± 0.35 | <0.01 |
Table 4.
Postoperative astigmatism analysis according to preoperative corneal astigmatism
Table 5.
Optical quality parameters measured by optical quality analysis system (OQAS) II at post-op 3 months
| Parameters | OQAS values |
|---|---|
| OSI | 1.33 ± 0.67 |
| MTF cut-off value (cpd) | 37.24 ± 9.67 |
| Strehl ratio | 0.22 ± 0.09 |
Table 6.
Ocular aberrometry analysis measured by Zywave II® at post-op 3 months




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download