Abstract
Purpose
To report peripheral vascular retinal leakage findings of asymptomatic eyes based on fluorescein angiography, and investigate the associated factors.
Methods
Data were collected retrospectively from 47 subjects (94 eyes) and the peripheral leakage results based on fluorescein angiography were analyzed. The relationship between peripheral leakage findings and other factors including- arm-retinal circulation time (ARCT) and venous filling time (VFT), refractive error, age, hypertension, and diabetes- was evaluated.
Results
Ten eyes had peripheral leakage (21.3%). The mean age was 34.7 ± 7.86 years in the non-leakage group and 44.3 ± 9.63 years in the leakage group; the difference between the groups was statistically significant (p = 0.001). The mean spherical equivalent was −2.85 ± 2.71 diopter in the non-leakage group and −3.46 ± 3.62 diopter in the leakage group; the difference between the groups were not significant (p = 0.471). The mean ARCT was 10.50 ± 2.06 seconds in the non-leakage group and 11.76 ± 2.47 seconds in the leakage group; the difference between the groups was statistically significant (p = 0.041). The mean VFT was 9.70 ± 1.91 seconds in the non-leakage group and 10.75 ± 1.40 seconds in the leakage group; the difference between the groups was statistically significant (p = 0.048).
References
1. Novotny HR, Alvis DL. A method of photographing fluorescencein circulating blood in the human retina. Circulation. 1961; 24:82–6.
2. Blair NP, Feke GT, Morales-Stoppello J, et al. Prolongation of the retinal mean circulation time in diabetes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:764–8.

3. Soeldner JS, Christacopoulos PS, Gleason RE. Mean retinal circulation time as determined by fluorescein angiography in normal, prediabetic, and chemical-diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1976; 25:903–8.
4. Yang YS, Kang P, Hwang JY, Kim JD. A study on microcirculation time including retinal periphery in diabetic retinopathy using the fluorescein angiography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:931–7.
5. Sinclair SH. Macular retinal capillary hemodynamics in diabetic patients. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:1580–6.

6. Wolf S, Arend O, Toonen H, et al. Retinal capillary blood flow measurement with a scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Preliminary results. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:996–1000.

7. Asdourian GK, Goldberg MF. The angiographic pattern of the peripheral retinal vasculature. Arch ophthalmol. 1979; 97:2316–8.

8. Spitznas M, Bornfeld N. The architecture of the most peripheral retinal vessels. Albrecht von Graefes Arch kiln Exp Ophthalmol. 1977; 203:217–29.

9. Kang HR, Yang YS. Comparison of venous filling times and SLO findings at each quadrant region in diabetic retinopathy. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2003; 17:133–9.

10. Azad RV, Baishya B, Pal N, et al. Comparative evaluation of oral fluorescein angiography using the confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope and digital fundus camera with intravenous fluorescein angiography using the digital fundus camera. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006; 34:425–9.

11. Tsui I, Bajwa A, Franco-Cardenas V, et al. Peripheral fluorescein angiographic findings in fellow eyes of patients with branch retinal vein occlusion. Int J Inflam. 2013; 2013:464127.

12. Rutnin U, Schepens CL. Fundus appearance in normal eyes. II. The standard peripheral fundus and developmental variations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967; 64:840–52.
13. Rutnin U, Schepens CL. Fundus appearance in normal eyes. 3. Peripheral degenerations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967; 64:1040–62.
Figure 1.
Peripheral leakage patterns in fluorescein angiography. (A) Temporal localized leakage. (B) Leakage in multiple directions (3 quadrants). (C) Leakage in two directions (temporal, inferonasal).

Figure 2.
Distribution of associative factors classified according to leakage. (A) Distribution of age, (B) distribution of arm-retinal circulation time (ARCT), (C) distribution of venous filling time (VFT).
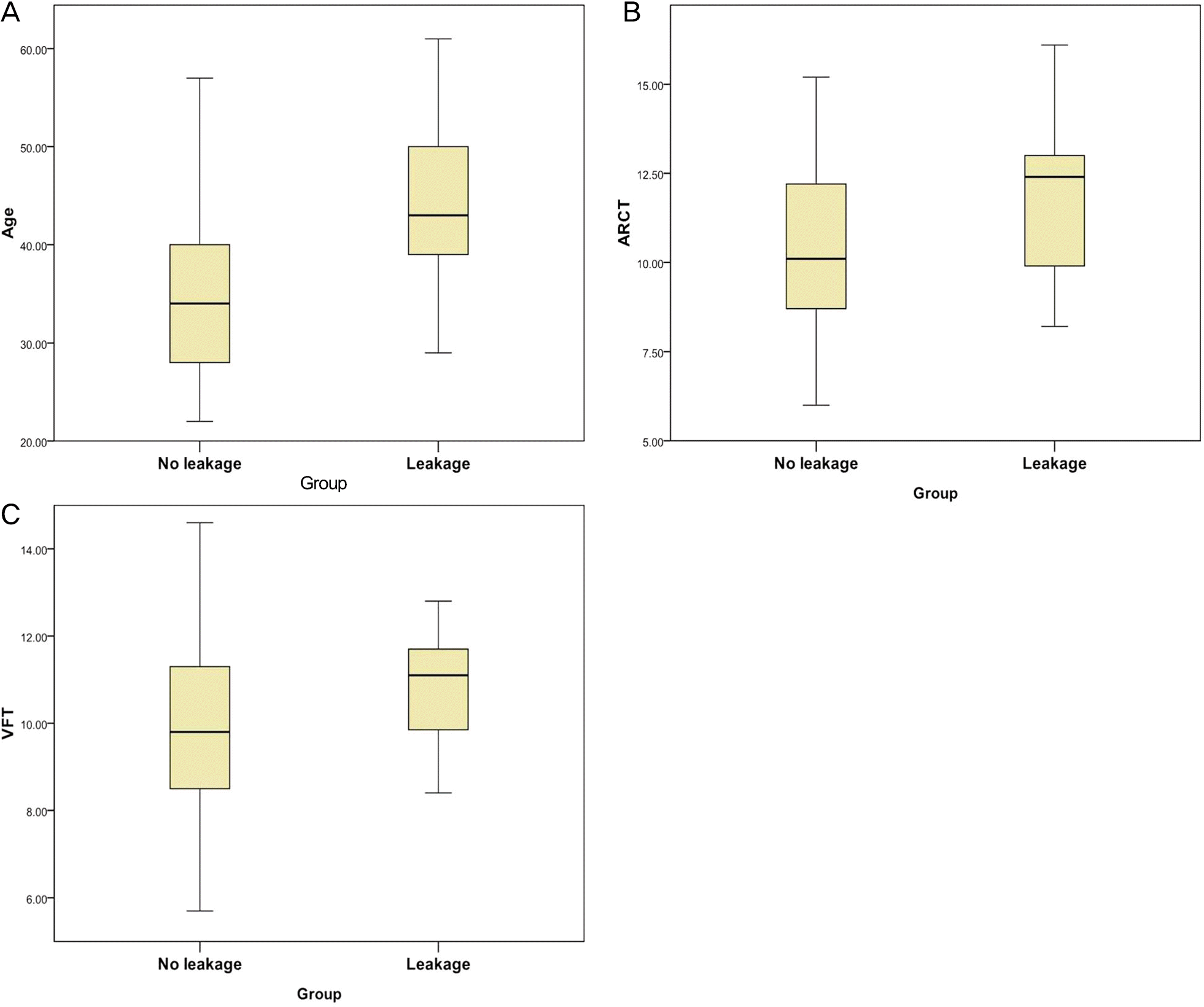
Figure 3.
Graph of Spearman correlation analysis. (A) Age versus venous filling time (VFT), (B) age versus arm-retinal circulation time (ARCT), (C) arm-retinal circulation time (ARCT) versus venous filling time (VFT).
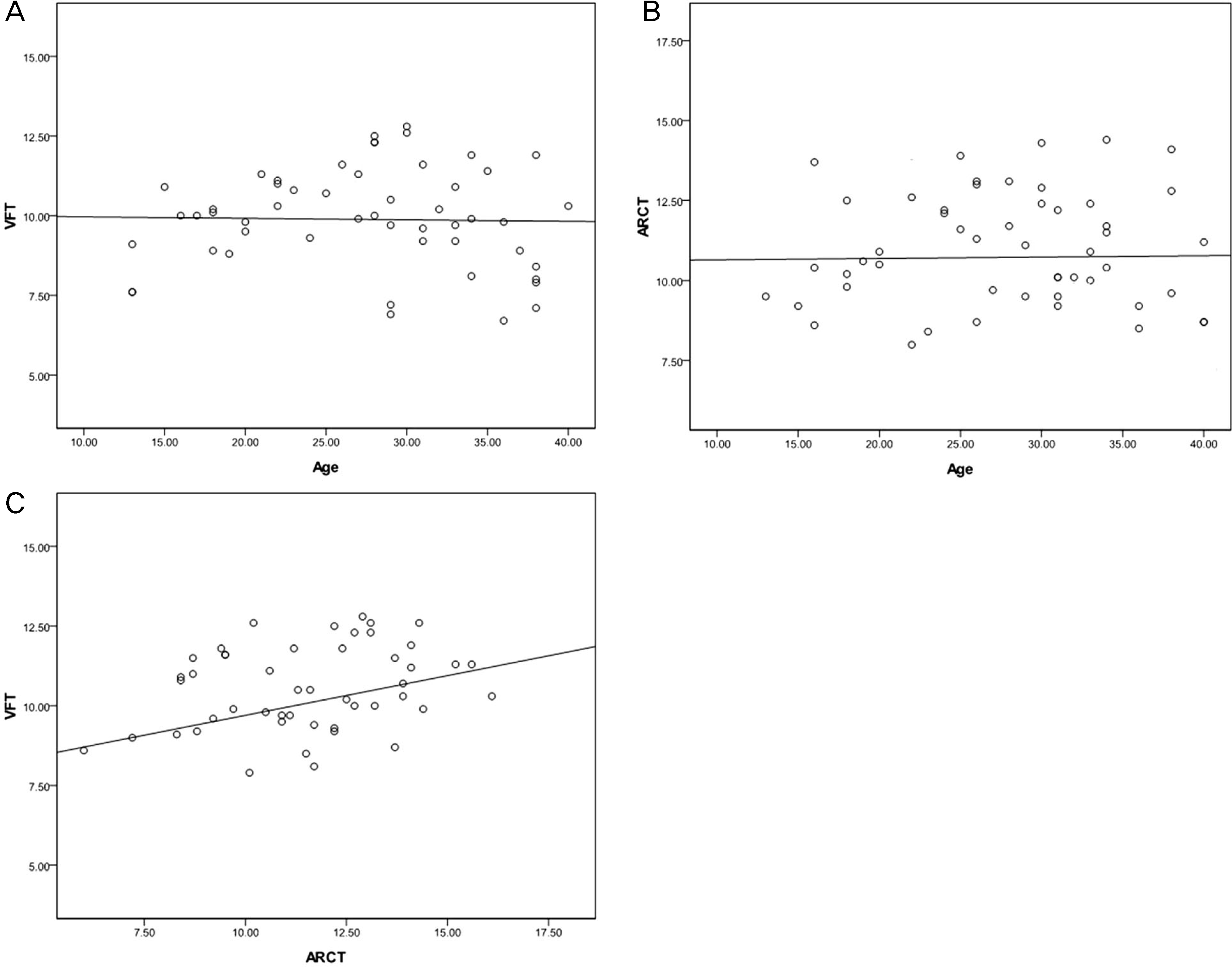
Table 1.
Patient demographics at the time of angiography
| No leakage (n = 37) | Leakage (n = 10) | Total (n = 47) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) | 34.7 ± 7.86 | 44.3 ± 9.63 | 36.3 ± 8.92 | 0.001* |
| M:F ratio (n) | 17:20 | 3:2 | 23:24 | |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) | -2.85 ± 2.71 | -3.46 ± 3.62 | -2.96 ± 2.87 | 0.471* |
| Circulation parameters | ||||
| Mean ARCT | 10.5 ± 2.06 | 11.8 ± 2.47 | 10.7 ± 2.17 | 0.041 |
| Mean VFT | 9.70 ± 1.91 | 10.75 ± 1.40 | 9.88 ± 1.87 | 0.048* |
| Underlying disease | ||||
| Hypertension (%) | 8 (21.6) | 4 (40.0) | 12 (25.5) | 0.237† |
| Diabetes (%) | 7 (18.9) | 2 (20) | 9 (19.1) | 0.939† |
Table 2.
Location of leakage point
| Leakage location | Number of eyes |
|---|---|
| Nasal | 1 |
| Inferotemporal | 4 |
| Temporal | 1 |
| Superonasal | 2 |
| Two point (temporal, inferonasal) | 1 |
| Multiple directions | 1* |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download