Abstract
Purpose
To present the results of patients undergoing surgical treatment and determine clinical guidelines for the face turn, and up and down shoot in Duane retraction syndrome (DRS).
Methods
Thirty-four patients with DRS were treated with single horizontal rectus muscle recession, lateral rectus (LR) recession with Y-splitting, or LR recession with Y-splitting combined with medial rectus (MR) recession. The different treatment approaches were based on the angle of deviation in the primary position, versions, and ductions. In all patients, ocular alignment, face turn and up and down shoot were assessed preoperatively and postoperatively.
Results
The average standard deviation reduced from 18.5 ± 6.5 prism diopters (PD) to 4.6 ± 5.8 PD in horizontal rectus muscle recession and 14.4 ± 5.5 PD to 1.6 ± 2.8 PD in LR recession with Y-splitting. LR recession with Y-splitting com-bined with MR recession was effective in reducing globe retraction. Postoperative 4-mm LR recession with Y-splitting did not change ocular alignment; 7-mm LR recession with Y-splitting showed an average correction of 12.8 PD. Postoperatively, all patients presented a reduction in face turn; however, there was no statistically significant difference between the 2 pro-cedures (Mann-Whitney U test, p = 0.620).
Conclusions
Decisions regarding surgical approaches in DRS should be based on the amount of deviation in primary eye position, the expression of up and down shoot, and the degree of face turn. Surgeons planning Y-splitting of LR with MR re-cession must consider modifying the MR recession amount due to the smaller LR recession effect of Y-splitting compared with conventional LR recession.
References
1. Scott AB, Wong GY. Duane's syndrome. An electromyographic study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1972; 87:140–7.

4. Huber A, Esslen E. [Duane's syndrome; observations on the patho-genesis and etiology of different forms of the Stilling-Duane-Turk retraction syndrome]. Doc Ophthalmol. 1969; 26:619–28.
5. Ozkurt H, Basak M, Oral Y, Ozkurt Y. Magnetic resonance imaging in Duane's retraction syndrome. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2003; 40:19–22.

6. Kim JH, Hwang JM. Presence of the abducens nerve according to the type of Duane's retraction syndrome. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:109–13.

7. Denis D, Dauletbekov D, Alessi G. . Duane retraction syndrome: MRI features in two cases. J Neuroradiol. 2007; 34:137–40.
8. Denis D, Dauletbekov D, Girard N. Duane retraction syndrome: Type II with severe abducens nerve hypoplasia on magnetic reso-nance imaging. J AAPOS. 2008; 12:91–3.

9. Kim JH, Hwang JM. Abducens nerve is present in patients with type 2 Duane's retraction syndrome. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:403–6.

10. Mims JL 3rd. Describing Duane's (Retraction Syndrome). Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 2002; 17:86–8.
11. Chung M, Stout JT, Borchert MS. Clinical diversity of hereditary Duane's retraction syndrome. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:500–3.
13. Kraft SP. A surgical approach for Duane syndrome. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1988; 25:119–30.

14. Feretis D, Papastratigakis B, Tsamparlakis J. Planning surgery in Duane's syndrome. Ophthalmologica. 1981; 183:148–53.

16. Rogers GL, Bremer DL. Surgical treatment of the upshoot and downshoot in Duanes' retraction syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:1380–3.

17. Park WH, Son DH, Yoon SW. . The clinical features of Korean patients with Duane’s retraction syndrome. Korean J Ophthalmology. 2005; 19:132–5.

18. Sterk CC, van Hulst-Ginjaar SP, Swart-van den Berg M. Improvement of horizontal excursion and abduction by vertical muscle transposition in patients with Duane's retraction syndrome type I. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2004; 41:204–8; quiz 230-1.

19. Wright KW, Siegel PH. Pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus. New Yor: Springer;2003..
Figure 1.
Postoperative change in face turn. LR = lateral rec-tus; MR = medial rectus; rec = recession. Graph shows a re-duction in face turn between two procedures. There is no stat-istically significant difference within the two procedures (Mann-Whitney U test, p = 0.620).
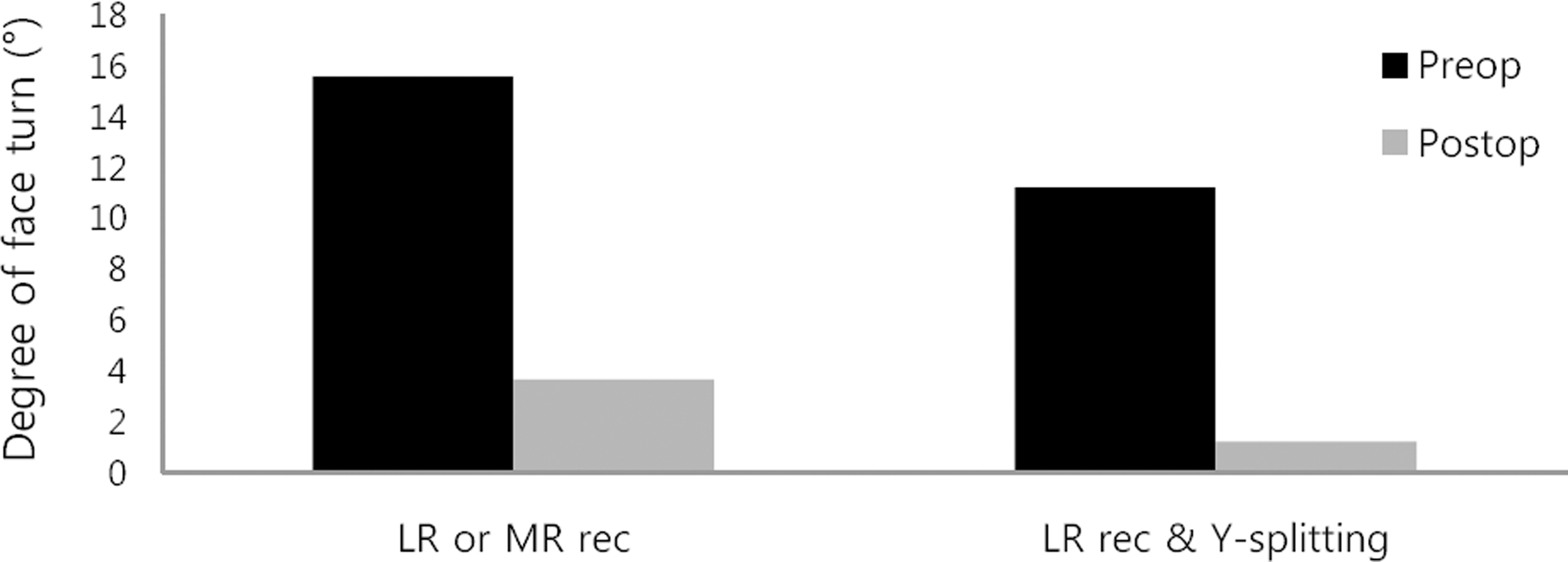
Table 1.
Patient characteristics of Duane’s retraction syndrom
| Baseline characteristics | No |
|---|---|
| Patients | 34 |
| Sex (male : female) | 21 : 13 |
| Laterality (OD*: OS†) | 9 : 25 |
| Age at diagnosis (year) | 7.0 ± 9.0 (0-41 |
| Age at operation (year) | 9.0 ± 8.6 (3-41 |
| Type Ⅰ: Ⅱ: Ⅲ‡ | 26 : 4 : 4 |
| Esotropia : Exotropia : Orthotropia | 17 : 14 : 3 |
| Horizontal rectus muscle rec : LR rec & | 15 : 16 : 3 |
| Y-splitting : LR rec & Y-splitting with MR rec | |
Table 2.
Ocular deviation for each type of Duane’s retraction syndrome
| Type | Esotropia | Exotropia | Orthotropia | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 16 (61.5%) | 8 (30.8%) | 2 (7.7%) | 26 |
| Ⅱ | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 3 |
| Ⅲ | 1 (20.0%) | 3 (60.0%) | 1 (20.0%) | 5 |
| Total | 17 | 14 | 3 | 34 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download