Abstract
Purpose
To assess the influence of body position on intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients who underwent vitrectomy and intraocular gas tamponade.
Methods
Patients who did not undergo any surgery were defined as Group 1. The remaining patients were divided into 3 groups according to the surgery performed (Group 2; cataract surgery, Group 3; vitrectomy and cataract surgery, Group 4; vitrectomy with intraocular gas tamponade and cataract surgery). IOP was measured by a noncontact tonometer, Goldmann applanation tonometer, and Tono-Pen in the sitting, supine, and prone positions.
Results
The difference of IOP measured in the sitting position among the 4 groups was not significant. IOP was significantly elevated by 2.04 mm Hg on average when the posture was changed from sitting to supine or prone in all 4 groups. The IOP discrepancy between supine and sitting positions was significantly greater in group 4 by 3.61 mm Hg than the other groups (p = 0.003, ANOVA test). The IOP difference between the prone and sitting position was also significantly higher in group 4 by 3.82 mm Hg than the other groups (p = 0.001, ANOVA test).
Go to : 
References
1. Rosengren B. Cases of retinal detachment treated with diathermy and injection of air into the vitreous body. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh). 1938; 16:573–9.
2. Norton EW. Intraocular gas in the management of selected retinal detachments. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1973; 77:OP85–98.
3. McLean EB, Norton EW. Use of intraocular air and sulfur abdominal gas in the repair of selected retinal detachments. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1974; 12:428–35.
4. Kobayashi H, Kishi S. Vitreous surgery for highly myopic eyes with foveal detachment and retinoschisis. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1702–7.
5. Bainbridge J, Herbert E, Gregor Z. Macular holes: vitreoretinal abdominalships and surgical approaches. Eye (Lond). 2008; 22:1301–9.
7. Kreiglstein GK, Brethfeld V, von Collani E. [Comparative abdominal pressure measurements with position independent hand-ap-planatation tonometers (author's transl)]. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1976; 199:101–13.
8. Blondeau P, Tétrault JP, Papamarkakis C. Diurnal variation of abdominal venous pressure in healthy patients: a pilot study. J Glaucoma. 2001; 10:18–24.
9. Anderson DR, Grant WM. The influence of position on intraocular pressure. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973; 12:204–12.
10. Jain MR, Marmion VJ. Rapid pneumatic and Mackey-Marg abdominal tonometry to evaluate the postural effect on intraocular pressure. Br J Ophthalmol. 1976; 60:687–93.
11. Parsley J, Powell RG, Keightley SJ, Elkington AR. Postural abdominal of intraocular pressure in chronic open-angle glaucoma abdominal trabeculectomy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1987; 71:494–6.
12. Weinreb RN, Cook J, Friberg TR. Effect of inverted body position on intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98:784–7.

13. Leonard TJ, Kerr Muir MG, Kirkby GR, Hitchings RA. Ocular hypertension and posture. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983; 67:362–6.

14. Prata TS, De Moraes CG, Kanadani FN, et al. Posture-induced abdominal pressure changes: considerations regarding body position in glaucoma patients. Surv Ophthalmol. 2010; 55:445–53.
15. Williams BI, Peart WS, Letley E. Abnormal intraocular pressure control in systemic hypertension and diabetic mellitus. Br J Ophthalmol. 1980; 64:845–51.

16. Costarides AP, Alabata P, Bergstrom C. Elevated intraocular abdominal following vitreoretinal surgery. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2004; 17:507–12.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Posture of intraocular pressure measurement. NCT = noncontact tonometer; Goldmann = goldmann applanation tonometer. |
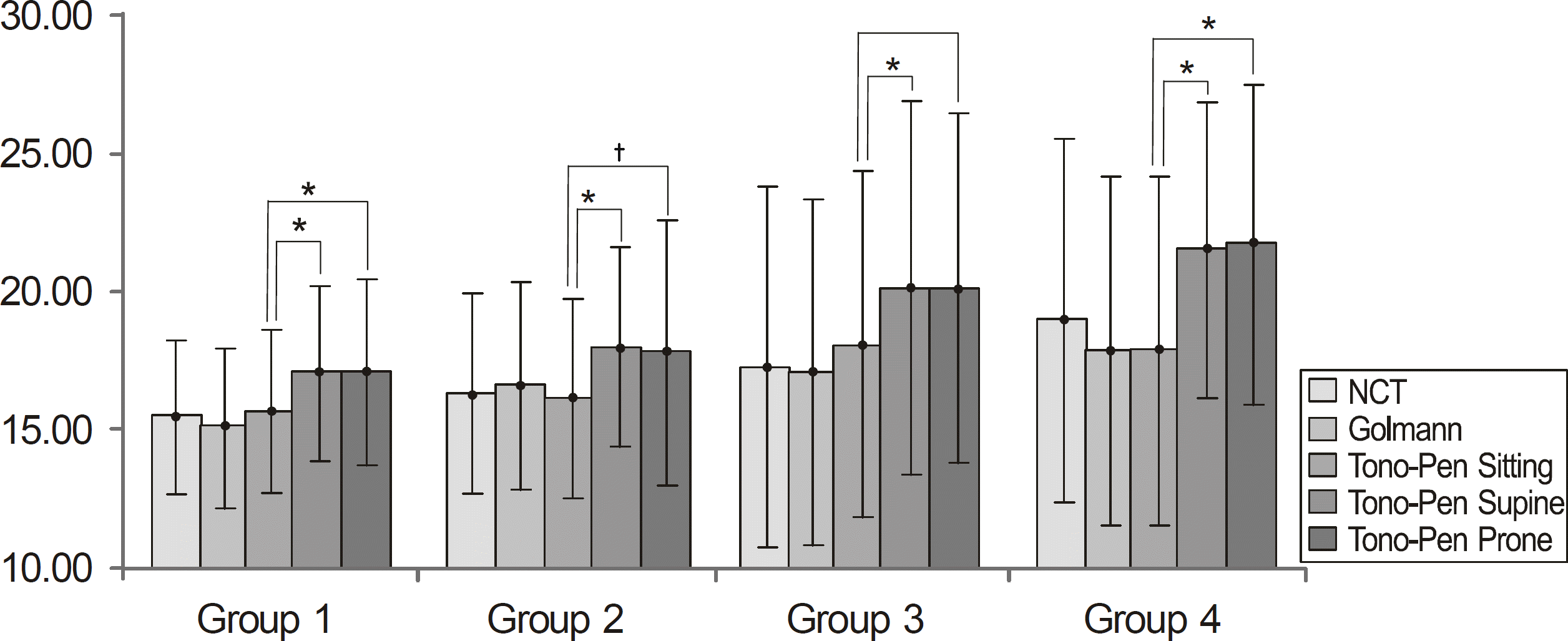 | Figure 2.Comparison of intraocular pressure according to the posture and methods of the measurement. * p<0.001 † p<0.05, tested by paired-sample t-test. |
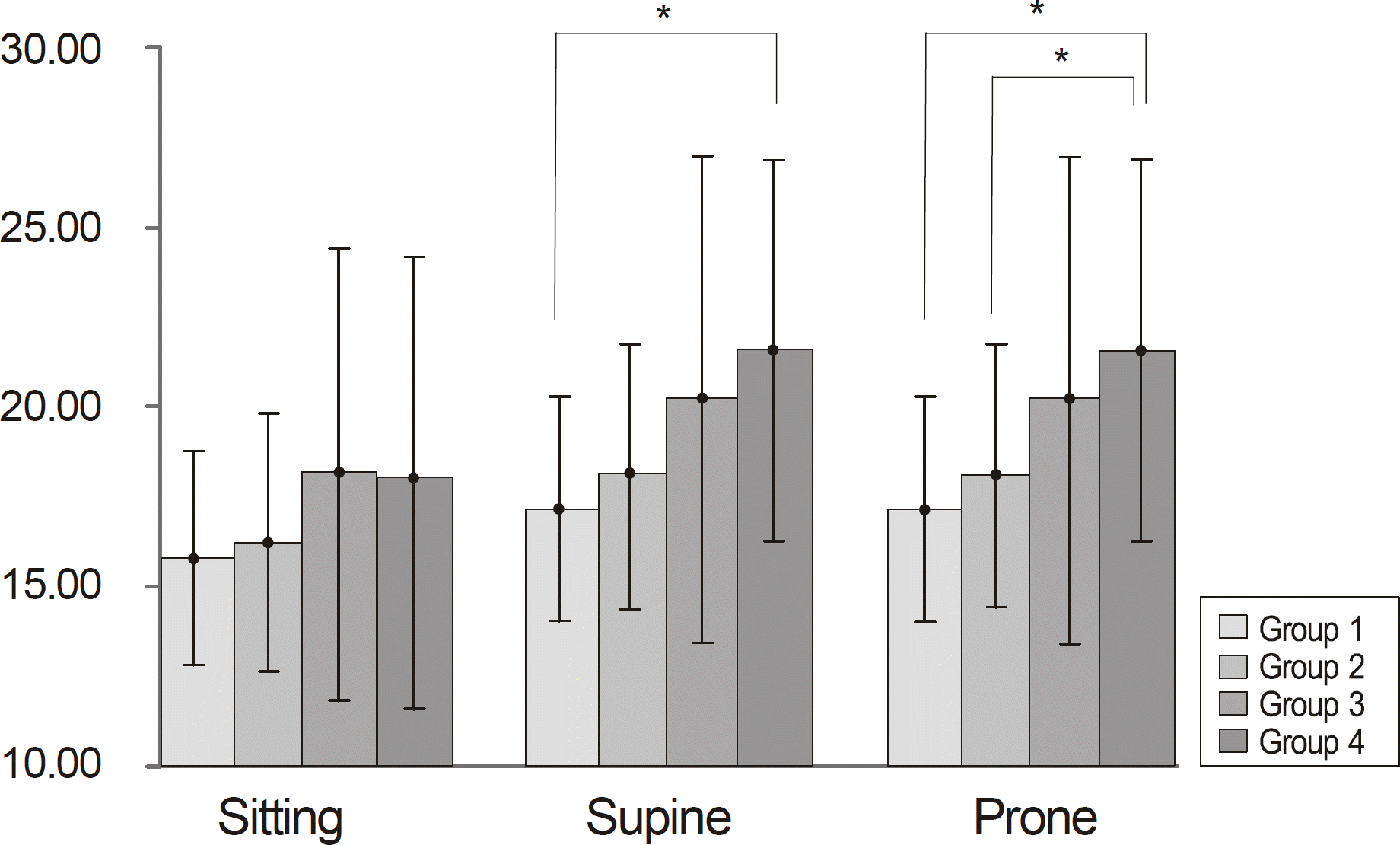 | Figure 3.Comparison of intraocular pressure measured by * p<0.05, tested by paired-Tono-Pen in different postures. sample t-test. |
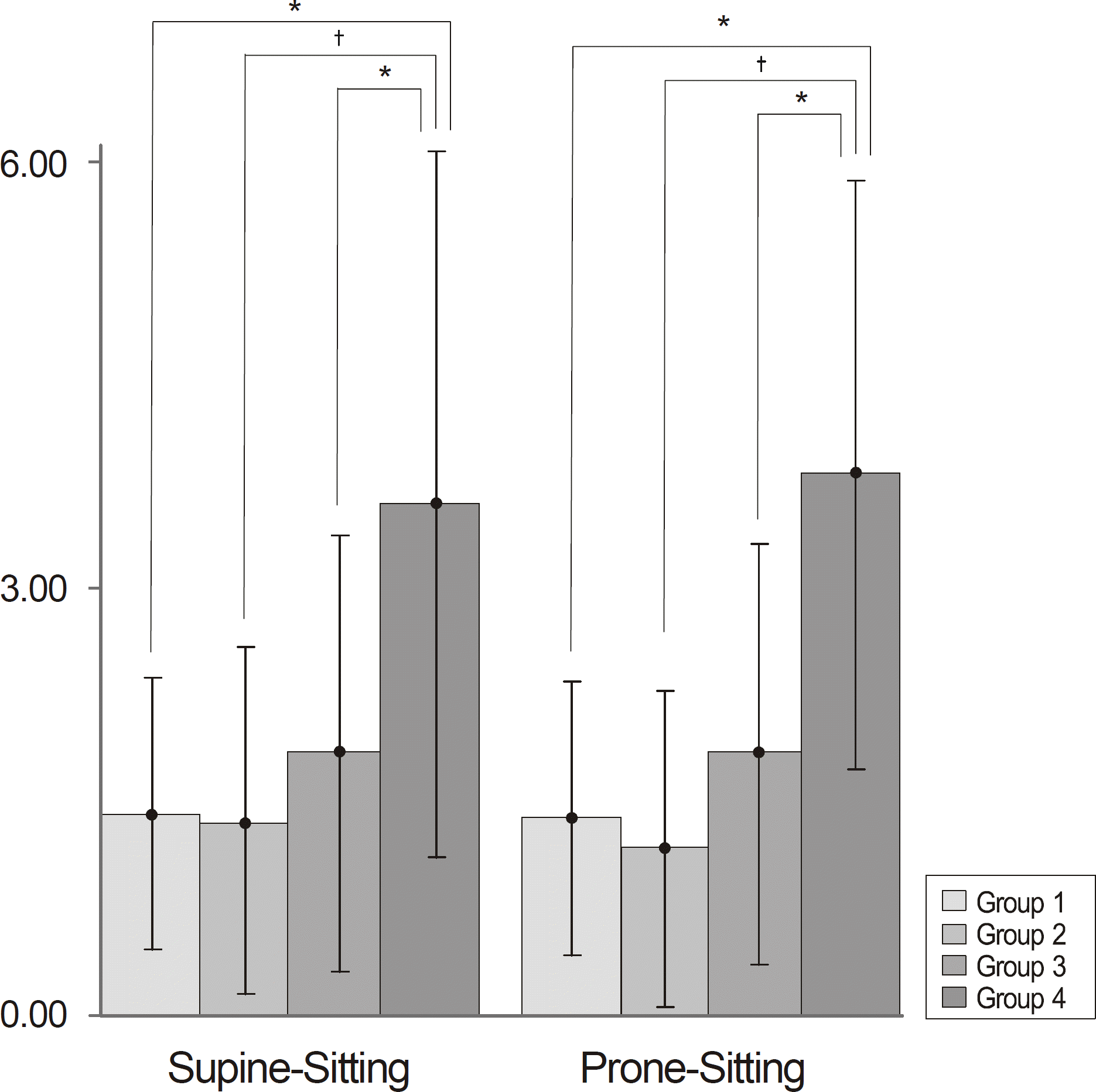 | Figure 4.Comparison of intraocular pressure difference between supine and sitting position and between prone and sitting position. * p<0.05; † p<0.01, post-hoc analysis by Tukey. |
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of enrolled patients
| Group 1* | Group 2† | Group 3‡ | Group 4§ | p-vlaue∏ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 40 | 56 | 42 | 38 | |
| Age (yr) | 50.24 | 64.07 | 52.04 | 61.31 | 0.366 |
| Sex ratio (M/F) | 1 | 0.27 | 0.61 | 0.35 | 0.066 |
| Diabetes | 10 (25.0) | 15 (26.7) | 12 (28.5) | 16 (42.1) | 0.380 |
| Hypertension | 10 (25.0) | 18 (32.1) | 14 (33.1) | 21 (55.2) | 0.058 |
Table 2.
Measurement of intraocular pressure and discrepancy between transverse position and sitting position
|
IOP (mm Hg) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1* | Group 2† | Group 3‡ | Group 4§ | p-value∏ | |
| NCT | |||||
| Pre-op | 15.60 | 16.21 | 16.03 | 16.42 | 0.232 |
| Post-op | 16.39 | 17.38 | 19.05 | 0.131 | |
| Goldmann | 15.15 | 16.73 | 17.18 | 17.95 | 0.348 |
| Tono-Pen | |||||
| Sitting | 15.80 | 16.28 | 18.17 | 17.99 | 0.281 |
| Supine | 17.17 | 18.09 | 20.22 | 21.58 | 0.019 |
| Prone | 17.20 | 17.91 | 20.21 | 21.79 | 0.017 |
| Supine – Sitting | 1.43 | 1.37 | 1.85 | 3.61 | 0.003 |
| Prone – Sitting | 1.40 | 1.18 | 1.85 | 3.82 | 0.001 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download