Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the influence of preoperative endothelial cell loss on the outcome of keratoplasty for keratoconus in imported donor corneas.
Methods
Eighteen imported corneas used in keratoplasty for keratoconus patients were evaluated. Corneal endothelial cell density at the moment of preservation was obtained from the medical records and was measured immediately before the keratoplasty. Correlation of the endothelial cell loss count before and after keratoplasty was analyzed and post-operative endothelial cell loss count according to the range of preoperative endothelial cell loss was evaluated.
Results
Mean endothelial cell loss before and after keratoplasty was 258.94 ± 128.58 cells/mm2 and 355.44 ± 371.83 cells/mm2, respectively. There was a positive correlation between preoperative and postoperative endothelial cell loss count (r = 0.431, p = 0.074). The results showed statistically significant higher endothelial cell loss count after keratoplasty in the range above 250 cells/mm2 rather than below 250 cells/mm2 of preoperative endothelial cell loss count (p = 0.033).
Go to : 
References
1. Kim TK, Byun YS, Kim MS. Analysis of factors affecting corneal endothelial cell loss after penetrating keratoplasty. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 52:807–15.

2. Cho EY, Kim MS. Penetrating keratoplasty before and after estab-lishment of Korean network for organ sharing. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2006; 47:525–30.
3. Park SH, Kim JH, Joo CK. The clinical evaluations of the penetrating keratoplasty with imported donor corneas. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 46:28–34.
4. Kong SJ, Cho K, Kim MS. Analysis of factors affecting the endo-thelial cell density in imported donor corneas. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2012; 53:20–6.
5. Williams KA, Roder D, Esterman A. . Factors predictive of corneal graft survival. Report from the Australian Corneal Graft Registry. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:403–14.

6. Kim MK, Lee JH. Long-term outcome of graft rejection after pene-trating keratoplasty. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:1553–60.
7. Ha DW, Kim CK, Lee SE. . Penetrating keratoplasty results in 275 cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:20–9.
8. Boruchoffe SA, Jensen AD, Dohlman CH. Comparison of suturing technique in keratoplasty for keratoconus. Ann Ophthalmol. 1975; 7:433–6.
9. Buxton JN, Apisson JG, Hoefle FB. Corticosteroids in 100 keratoplasties. Am J Ophthalmol. 1969; 67:46–51.

10. Lee HS, Kim MS. Influential factors on the survival of endothelial cells after penetrating keratoplasty. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2009; 19:930–5.

11. Langenbucher A, Seitz B, Nguyen NX, Naumann GO. Corneal en-dothelial cell loss after nonmechanical penetrating keratoplasty de-pends on diagnosis: a regression analysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2002; 240:387–92.

12. Kim SH, Ahn BC, Chung YT. Endothelial cell changes after pene-trating keratoplasty. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1124–31.
13. Means TL, Geroski DH, Hernault N. . The corneal epi-thelium after optisol-GS storage. Cornea. 1996; 15:599–605.

14. Means TL, Geroski DH, Hardley A. . Viability of human cor-neal endothelium following optisol-GS storage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995; 113:805–9.

15. Wang IJ, Hu FR. Effect of shaking of corneal endothelial preservation. Curr Eye Res. 1997; 16:1111–8.
16. Na YS, Woo SW, Kang JH, Joo MJ. Microbiologic study of im-ported donor corneas and preserved solutions. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 46:1974–7.
17. Hu FR, Tsai AC, Wang IJ, Chang SW. Outcomes of penetrating keratoplasty with imported donor corneas. Cornea. 1999; 18:182–7.

18. Culberston WW, Abbott RL, Forster RK. Endothelial cell loss in penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmol. 1982; 89:600–4.
19. Bourne WM, O'Fallon WM. Endothelial cell loss during penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978; 85:760–6.

20. Obata H, Ishida K, Murao M. . Corneal endothelial cell damage in penetrating keratoplasty. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1991; 35:411–6.
21. Bourne WM. Penetrating keratoplasty with fresh and cryopreserved corneas. Donor endothelial cell survival in primates. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978; 96:1073–4.

22. Musch DC, Meyer RF, Sugar A. Predictive factors for endothelial cell loss after penetrating keratoplasty. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:80–3.

23. Böhringer D, Reinhard T, Spelsberg H, Sundmacher R. Influencing factors on chronic endothelial cell loss characterised in a homoge-neous group of patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:35–8.
Go to : 
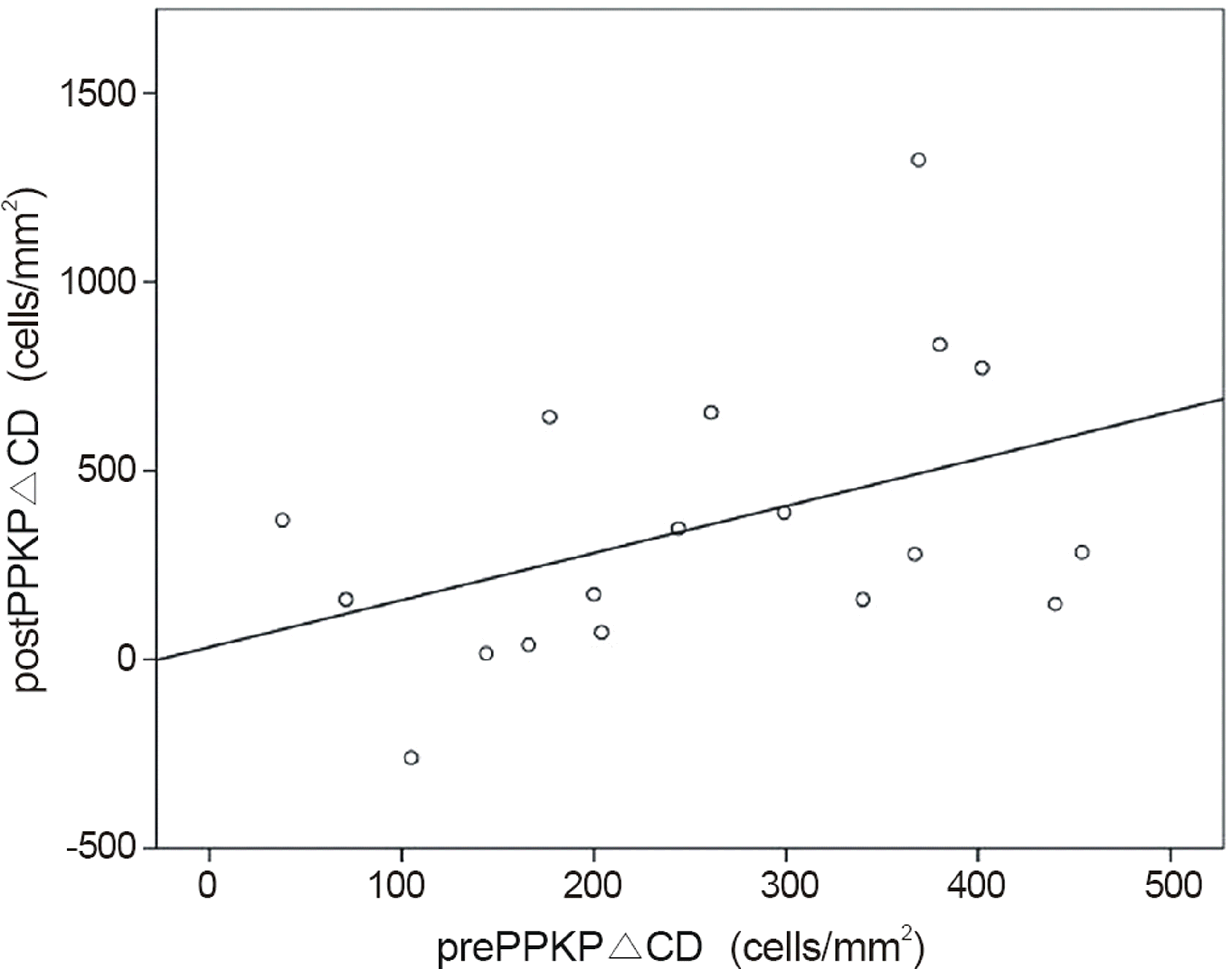 | Figure 2.Correlation between prePPKP△ CD and postPPKP△ CD (r = 0.431, p = 0.074). prePPKP△ CD = decrease in endo-thelial density before penetrating keratoplasty; postPPKP△ CD = decrease in endothelial density after penetrating keratoplasty. |
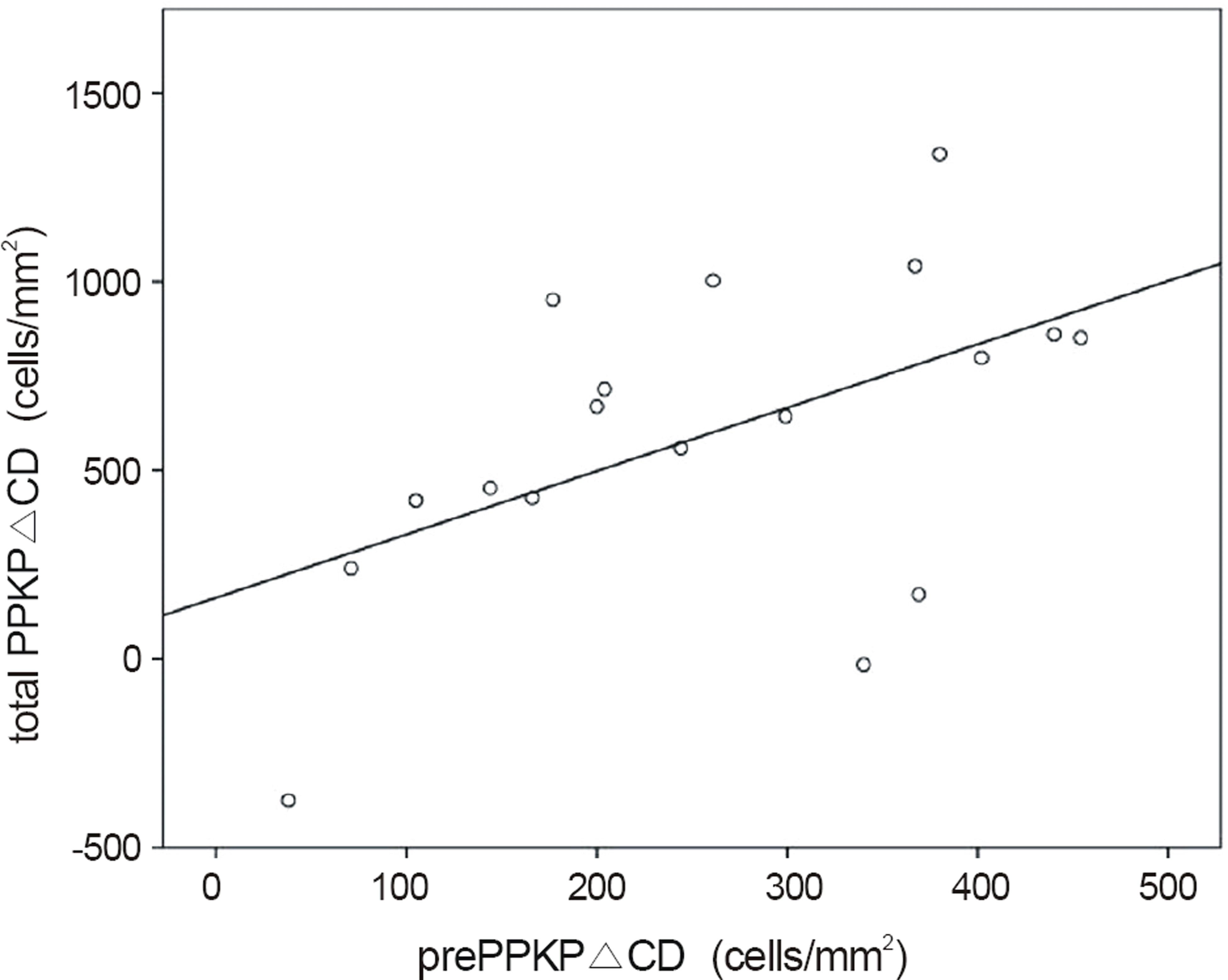 | Figure 3.Correlation between prePPKP△ CD and total PPKP △CD (r = 0.519, p = 0.027). prePPKP△CD = decrease in endothelial density before penetrating keratoplasty; total PPKP △CD = decrease in endothelial density since preservation. |
Table 1.
Endothelial cell density change before and after pene-trating keratoplasty
Table 2.
Comparison of endothelial cell density-related factors according to preoperative cell loss count
| Group 1* | Group 2† | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor age (years) | 58.00 ± 13.32 | 51.22 ± 19.37 | 0.400 |
| Donor cell count (cells/mm2) | 2769.44 ± 184.19 | 2886.56 ± 315.53 | 0.351 |
| Death to preserve time (hours) | 11.21 ± 8.34 | 9.03 ± 7.02 | 0.559 |
| Preservation time (hours) | 178.13 ± 41.50 | 182.97 ± 42.94 | 0.811 |
| Death to graft time (hours) | 189.33 ± 42.33 | 192.00 ± 43.27 | 0.897 |
| Postoperative cell loss (cells/mm2) | 173.00 ± 257.18 | 537.89 ± 390.89 | 0.033‡ |
Table 3.
Comparison of endothelial cell density-related factors according to range of preoperative cell loss count
| Group I* | Group II† | Group III‡ | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor age (years) | 49.50 ± 15.93 | 57.25 ± 18.45 | 54.50 ± 16.28 | 0.768 |
| Donor cell count (cells/mm2) | 2889.00 ± 228.78 | 2765.88 ± 221.74 | 2870.17 ± 338.21 | 0.681 |
| Death to preserve time (hours) | 11.81 ± 10.94 | 7.43 ± 7.01 | 12.58 ± 5.73 | 0.423 |
| Preservation time (hours) | 204.19 ± 33.90 | 172.57 ± 43.51 | 175.43 ± 42.51 | 0.449 |
| Death to graft time (hours) | 216.00 ± 39.19 | 180.00 ± 40.57 | 188.00 ± 44.04 | 0.384 |
| Postoperative cell loss (cells/mm2) | 71.00 ± 264.03 | 309.38 ± 241.37 | 606.50 ± 450.54 | 0.065 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download