Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the factors that affected continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC) remodeling to different shapes after CCC widening with Nd:YAG laser.
Methods
The medical records of patients who underwent CCC widening with Nd:YAG laser between January 2002 and December 2010 in our clinic were retrospectively reviewed. Eyes that underwent phacoemulsification surgery alone or combined phacoemulsification surgery and vitrectomy were eligible for the study. A remodeled CCC with a nearly complete circle was classified as type a, starfish-shape as type b, and not remodeled CCC as type c, The factors that affected CCC remodeling were analyzed.
Results
Among 424 eyes of 316 patients, the type of CCC remodeling had a significant correlation with the time period from phacoemulsification surgery to Nd:YAG CCC widening. There was no significant correlation with age, sex, diabetes, type of intraocular lens, type of surgery and indications for surgery.
References
1. Steinert RF, Fine IH, Gimbel HV, et al. Cataract Surgery. 2nd ed.Pennsylvania: Saunders;2004. p. 552–4.
4. Hayashi H, Hayashi K, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Anterior capsule abdominal and intraocular lens dislocation in eyes with abdominal syndrome. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:1429–32.
5. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Matsuo K, et al. Anterior capsule abdominal and intraocular lens dislocation after implant surgery in eyes with retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:1239–43.
6. Hayashi H, Hayashi K, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Area reduction in the anterior capsule opening in eyes of diabetes mellitus patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:1105–10.

7. Joo CK, Shin JA, Kim KH. Capsular opening contraction after abdominal curvilinear capsulorhexis and intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:585–90.
8. Sung MK, Lee KH. The evaluation of capsule contraction syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1454–61.
9. Yasuda A, Ohkoshi K, Orihara Y, et al. Spontaneous luxation of encapsulated intraocular lens onto the retina after a triple procedure of vitrectomy, phacoemulsification, and intraocular lens implantation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:836–7.

10. Musa F, Aralikatti AK, Prasad S. Choroidal effusion and hypotony caused by severe anterior lens contraction following cataract surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2004; 14:153–5.
11. Richter-Mueksch S, Kahraman G, Amon M, et al. Uveal and abdominal biocompatibility after implantation of sharpedged abdominal acrylic, hydrophobic acrylic, and silicone intraocular lenses in eyes with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1414–8.
12. Cochener B, Jacq PL, Colin J. Capsule contraction after continuous curvilinear capsulorrhexis: poly(methyl methacrylate) versus abdominal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:1362–9.
13. Sacu S, Findl O, Menapace R, Buehl W. Influence of optic edge abdominal, optic material, and haptic design on capsular bend configuration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1888–94.
14. Mingels A, Koch J, Lommatzsch A, et al. Comparison of two acrylic intraocular lenses with different haptic designs in patients with combined phacoemulsification and pars plana vitrectomy. Eye (Lond). 2007; 21:1379–83.

15. Matsuda H, Kato S, Hayashi Y, et al. Anterior capsular contraction after cataract surgery in vitrectomized eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:108–9.

16. Kato S, Oshika T, Numaga J, et al. Anterior capsular contraction abdominal cataract surgery in eyes of diabetic patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001; 85:21–3.
17. Lee SY, Baek TM, Lee KH. Reduction in the area of anterior abdominal opening after acryl intraocular lens implantation: diabetics vs. nondiabetics. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1158–63.
18. Steinert RF, Fine IH, Gimbel HV, et al. Cataract Surgery. 2nd ed.Pennsylvania: Saunders;2004. p. 475.
Figure 1.
Method of capsulorrhexis widening. Laser beam is targeted to the 8 radial lines from capsulorrhexis margin to 0.5–1.0 mm central to the optic rim of intraocular lens.
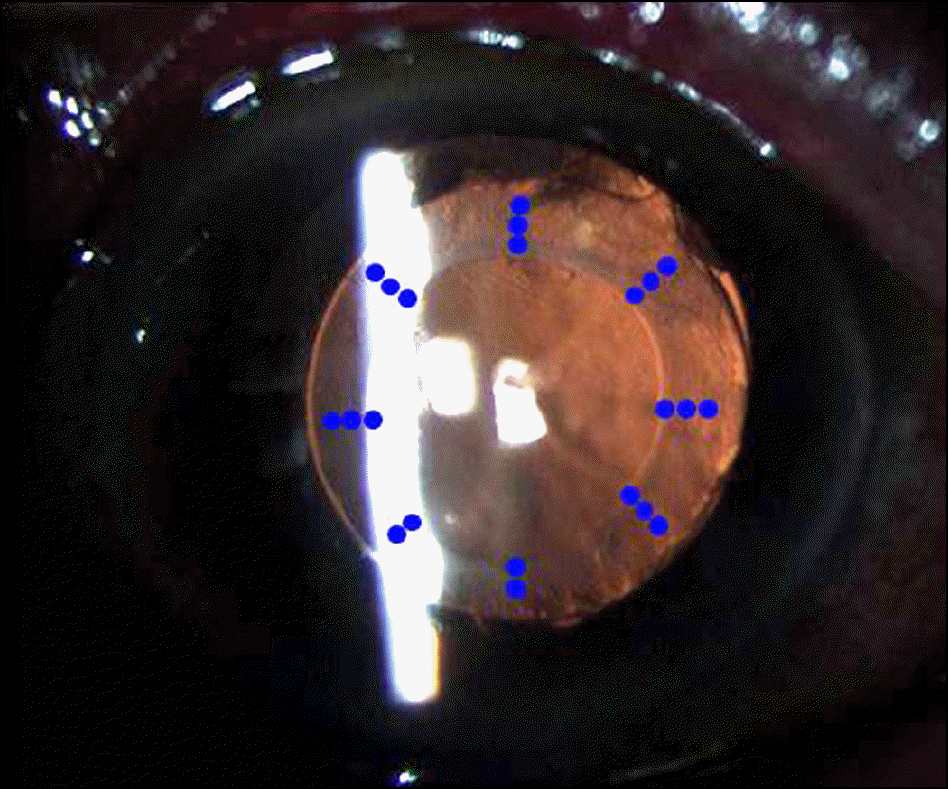
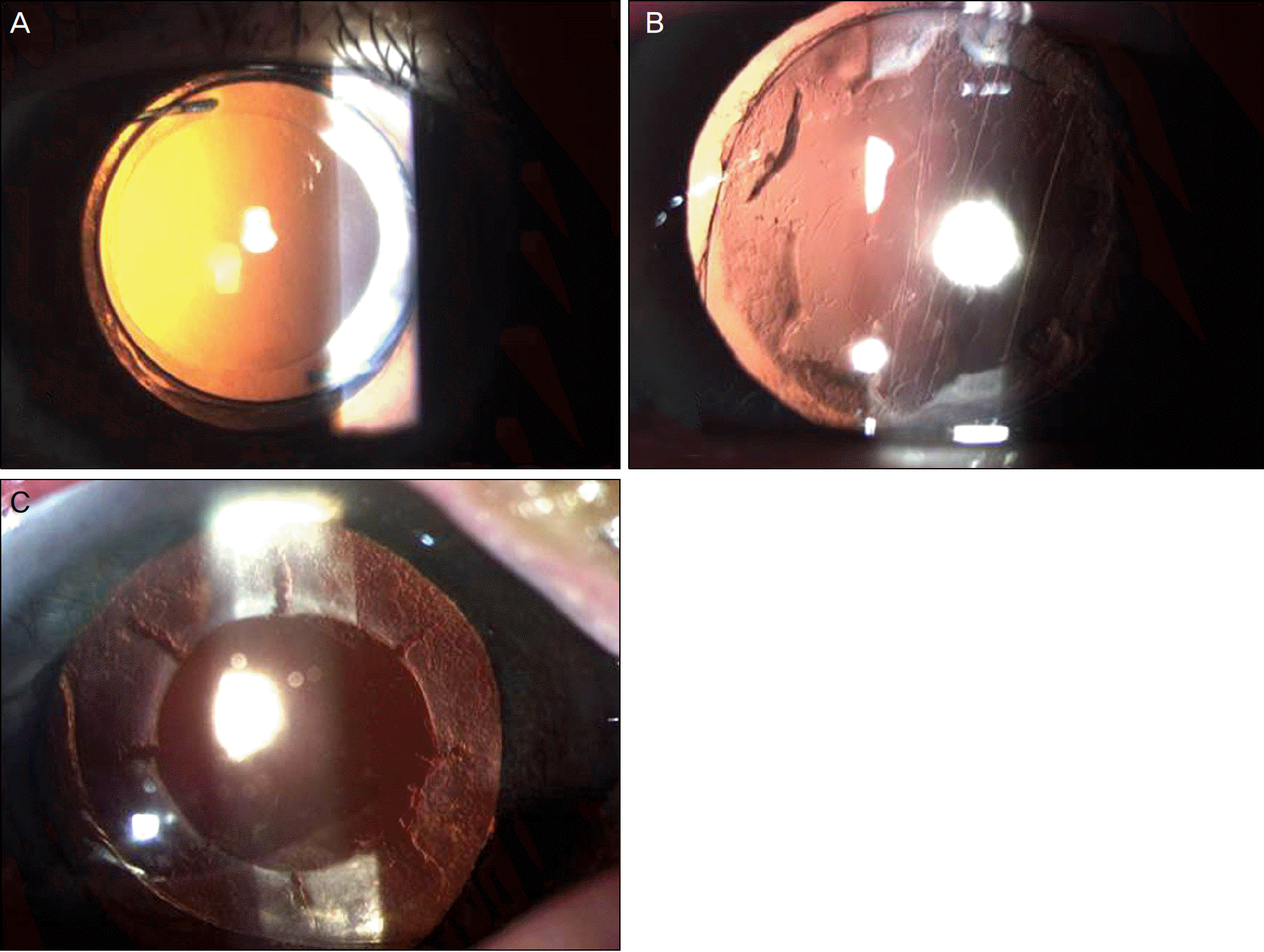
Figure 3.
Anterior segment photographs of a type, b type, c type ((A) Before Nd:YAG capsulorrhexis widening, (B) After Nd:YAG capsulorrhexis widening, (C) Ten days after capsulorrhexis widening).
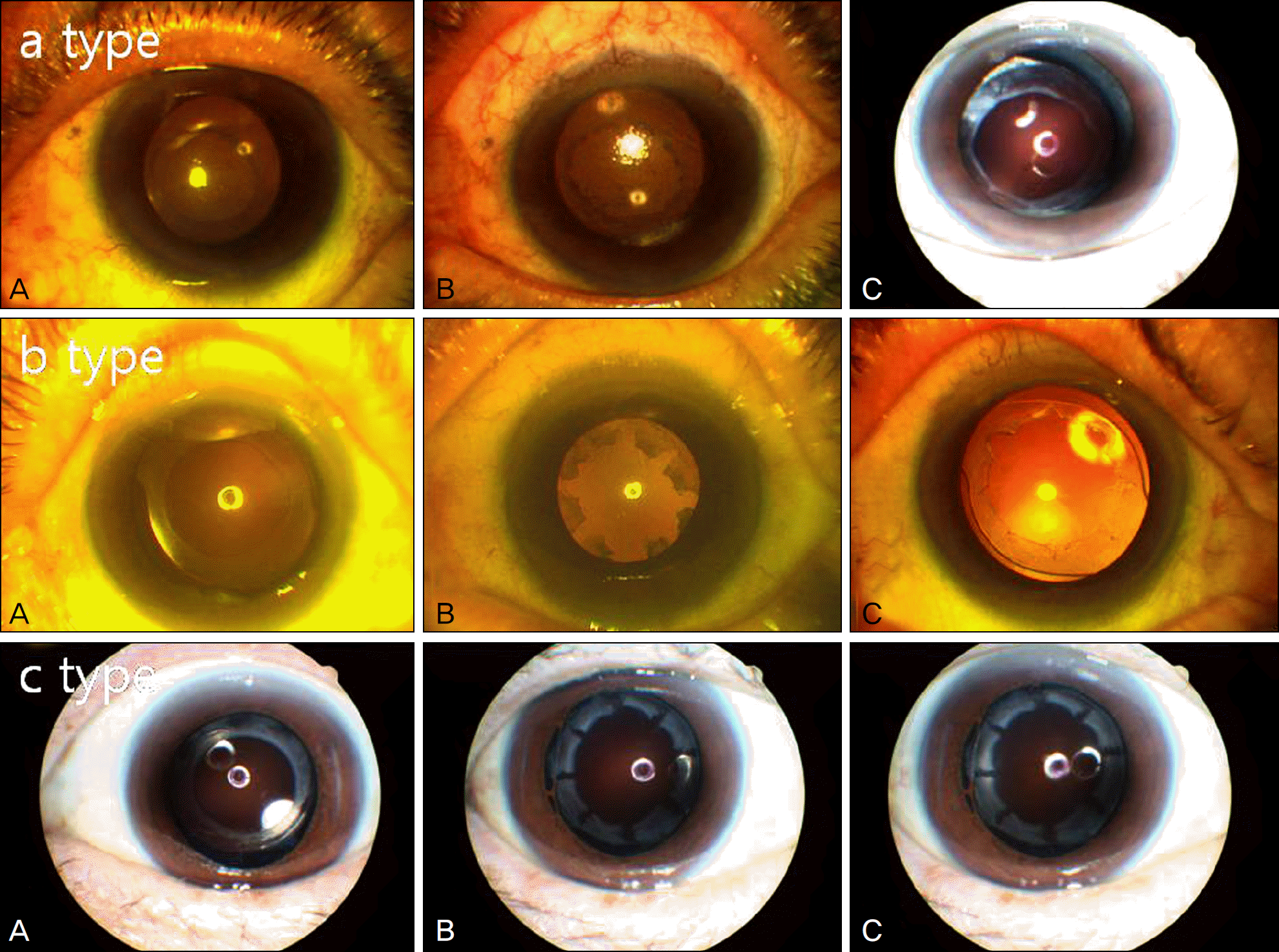
Figure 4.
The relationship between the type of capsulorrhexis remodeling and the time of capsulorrhexis widening ((A) type a, (B) type b, (C) type c).
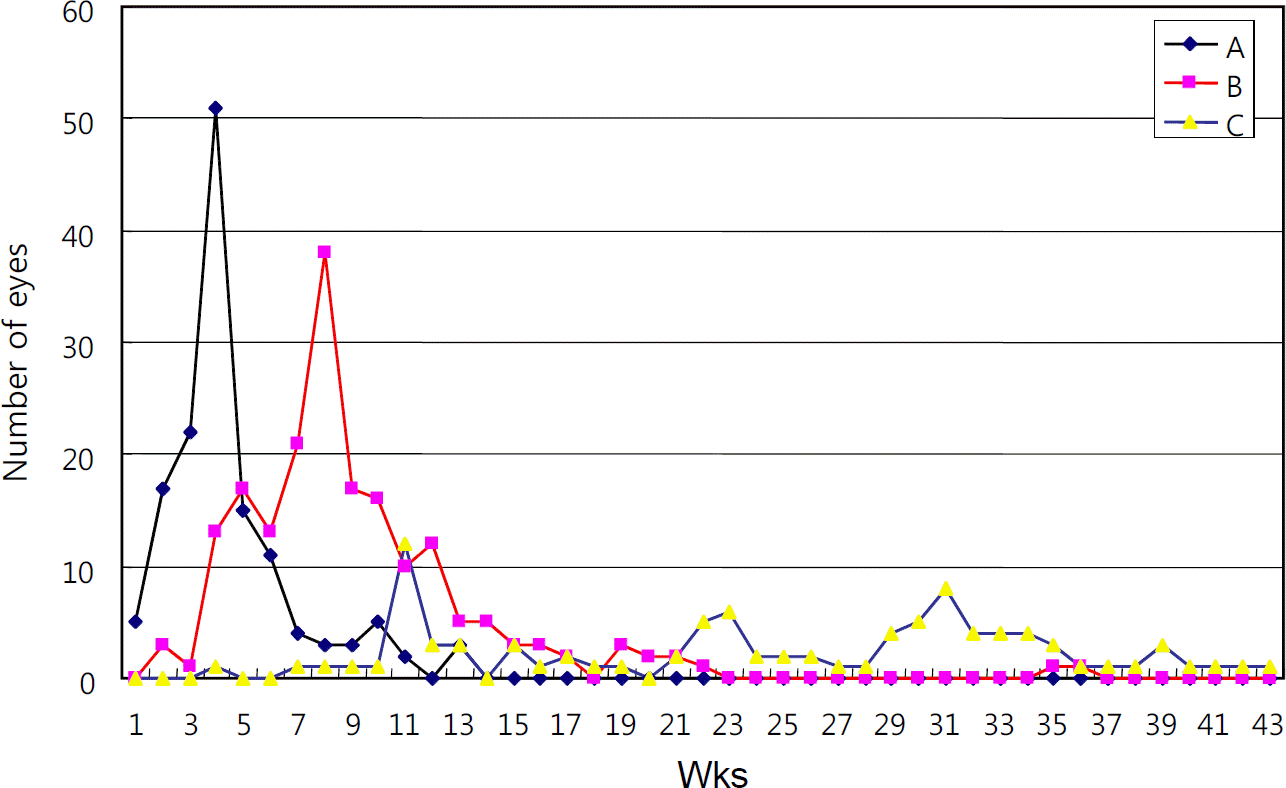
Table 1.
Number of eyes by age, sex, performed operation, inserted intraocular lens, and indication of combined surgery
Phaco = phacoemulsification and lens aspiration with intraocular lens implantation in the bag; TPPV = trans pars plana vitrectomy; IO gas = intraocular gas tamponade; IO oil = intraocular silicone oil injection; PDR = proliferative diabetic retinopathy; RVO = retinal vein occlusion; MP = muclar pucker; Uveitis = uveitis with its complications; MH = macular hole; RRD = rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download