Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of bilateral occlusive retinal vasculitis presumed to be associated with intravenous ceftriaxone injection.
Case summary
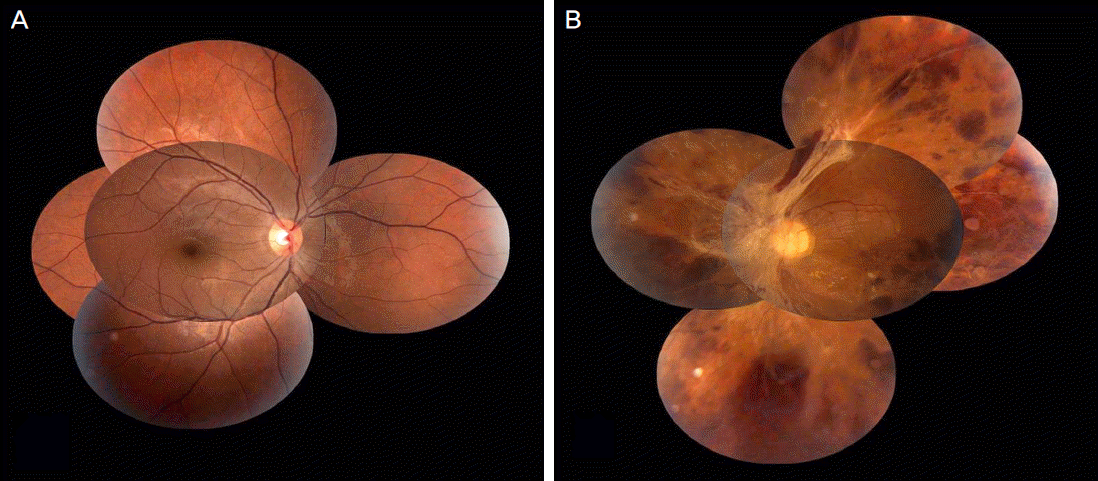
A 26-year-old woman presented with a sudden visual impairment which developed 2 days earlier in her left eye combined with an anaphylactoid reaction. The patient was administered intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g / day) 9 times for 14 days due to aggravation of chronic osteomyelitis on her left ankle. There were no adverse events until the 7th intravenous ceftriaxone administration. However, anaphylactoid reactions occurred shortly after the 8th and 9th administration. On the 1st visit, her best corrected visual acuity in the right eye was 1.0, and in the left eye 0.1. On fundus examination, retinal hemorrhages and perivascular sheathing were observed in the superonasal area in the right eye and in the entire retina in the left eye. Anterior chamber cell reactions were not noted on slit lamp examination, and vitritis was absent in both eyes. Laboratory data showed no conclusive evidence of autoimmune or origin of infection. On the last visit, 25 months after the initial visit, the patient's best corrected visual acuity was 0.02 in the left eye and visual acuity and fundus appearance were normal in the right eye.
Go to : 
References
1. Abu El-Asrar AM, Herbort CP, Tabbara KF. Differential diagnosis of retinal vasculitis. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2009; 16:202–18.
2. Ryan SJ. Drug toxicity of the posterior segment. In : Mitta RA, Mieler WF, editors. Retina. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier;2006. v. 2. chap. 108.
3. Häusermann P, Bircher AJ. Immediate and delayed hyper-sensitivity to ceftriaxone, and anaphylaxis due to intradermal testing with other beta-lactam antibiotics, in a previously amoxicillin-sensitized patient. Contact Dermatitis. 2002; 47:311–2.
4. Demoly P, Messaad D, Sahla H, et al. Immediate hypersensitivity to ceftriaxone. Allergy. 2000; 55:418–9.

5. Torres MJ, Blanca M. The complex clinical picture of beta-lactam hypersensitivity: penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems, and clavams. Med Clin North Am. 2010; 94:805–20.
6. Perez-Inestrosa E, Suau R, Montañez MI, et al. Cephalosporin chemical reactivity and its immunological implications. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5:323–30.

7. Schiavino D, Nucera E, Lombardo C, et al. Cross-reactivity and tolerability of imipenem in patients with delayed-type, cell-mediated hypersensitivity to beta-lactams. Allergy. 2009; 64:1644–8.
8. Cantini F, Niccoli L, Nannini C, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in refractory Behçet's disease-associated and idiopathic posterior segment uveitis: a prospective, follow-up study of 50 patients. Biologics. 2012; 6:5–12.
9. Romano A, Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Viola M, et al. Diagnosing immediate reactions to cephalosporins. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:1234–42.

10. Inamura H, Igarashi Y, Kashiwase Y, et al. Mast cells in cutaneous allergic vasculitis: a case report. Allergol Int. 2006; 55:343–5.

11. Johnston B, Burns AR, Kubes P. A role for mast cells in the development of adjuvant-induced vasculitis and arthritis. Am J Pathol. 1998; 152:555–63.
Go to : 
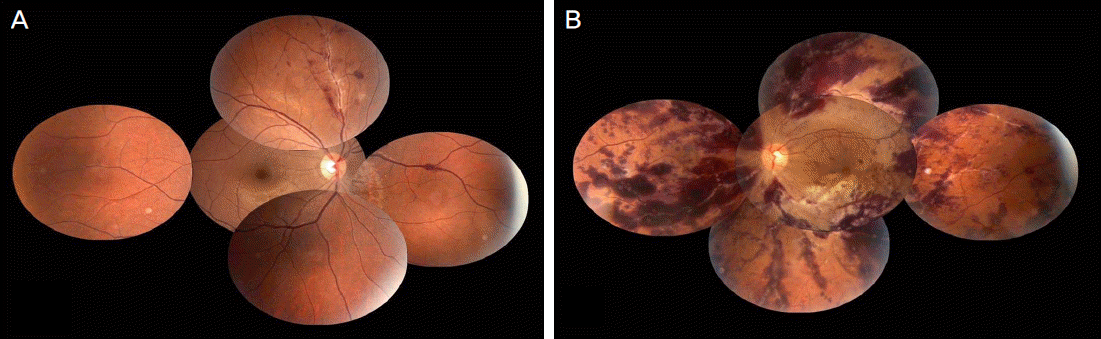 | Figure 1.Fundus photographys at initial visit. (A) Fundus photograph of right eye shows perivascular sheathing with intraretinal hemorrhages in superonasal area. (B) Fundus photograph of left eye shows perivascular sheathing with intraretinal hemorrhages in entire retina. |
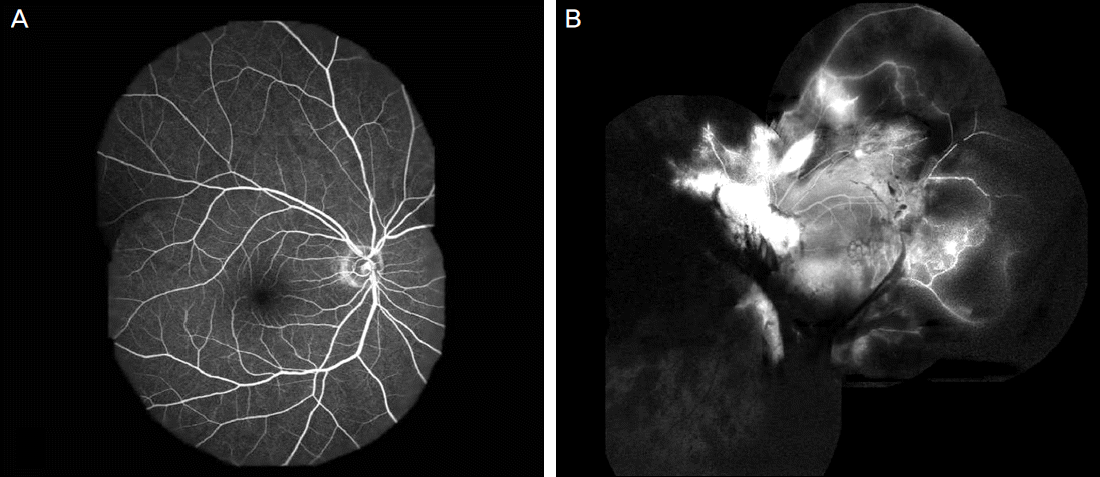 | Figure 2.Fluorescein angiographys (FA) of both eyes 2 months after onset. (A) Late-phase FA in the right eye shows normal fundus. (B) Late-phase FA in the left eye shows hyperfluorescence due to vascular leakage in the peripapillary area and cystoid macular edema, extensive non-perfusion areas around the midperiphery of the entire fundus, and blocked fluorescence due to preretinal hemorrhages. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download