Abstract
Case summary
A 44-year-old woman was referred to the ophthalmology department due to decreased vision which began 10 days prior to presentation. The patient history indicated that she had undergone chemotherapy for ovarian cancer and she had been dependent on total parenteral nutrition for 3 weeks due to nausea and vomiting. Her best corrected vision of the right and the left eyes were 0.15 and 0.2, respectively. Color vision was severely impaired in both eyes without retrobulbar pain. There was marginal blurring on the temporal side of the optic discs of both eyes. The optic nerves were unremarkable on orbital and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). There was high signal intensities in both the mammillary body and periaqueductal gray matter on T2-weighted imaging. In addition, the patient exhibited ataxia along with short-term memory loss. She was diagnosed with Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Thiamine was administrated based on the diagnosis, and after 2 days of administration, the patient’s vision and neurologic symptoms began to improve. Two weeks later, the patient recovered her vision.
Go to : 
References
2. Lee JR, Kim YD, Choi JY, Choi JW. Optic neuropathy from vitamin B12 deficiency associated with alcoholism and malnutrition. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:963–7.

3. Yoon CK, Chang MH, Lee DC. Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome as-sociated with hyperemesis gravidarum. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:239–42.

4. Zuccoli G, Pipitone N. Neuroimaging findings in acute Wernicke's encephalopathy: review of the literature. Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:501–8.

5. Spinazzi M, Angelini C, Patrini C. Subacute sensory ataxia and op-tic neuropathy with thiamine deficiency. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010; 6:288–93.

6. Sechi GP, Serra A. Wernicke's encephalopathy: new clinical settings and recent advances in diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:442–55.

7. Victor M, Adams RD, Collins GH. The Wernicke-Korsakoff syn-drome (WKS) and related neurologic disorders due to alcoholism and malnutrition. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: FA Davis;1989. p. 61–110.
8. Antunez E, Estruch R, Cardenal C. . Usefulness of CT and MR imaging in the diagnosis of acute Wernicke's encephalopathy. Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 171:1131–7.

9. van Noort BA, Bos PJ, Klopping C. . Optic neuropathy from thiamine deficiency in a patient with ulcerative colitis. Doc Ophthalmol. 1987; 67:45–51.

10. Suzuki S, Kumanomido T, Nagata E. . Optic neuropathy from thiamine deficiency. Intern Med. 1997; 36:532.

Go to : 
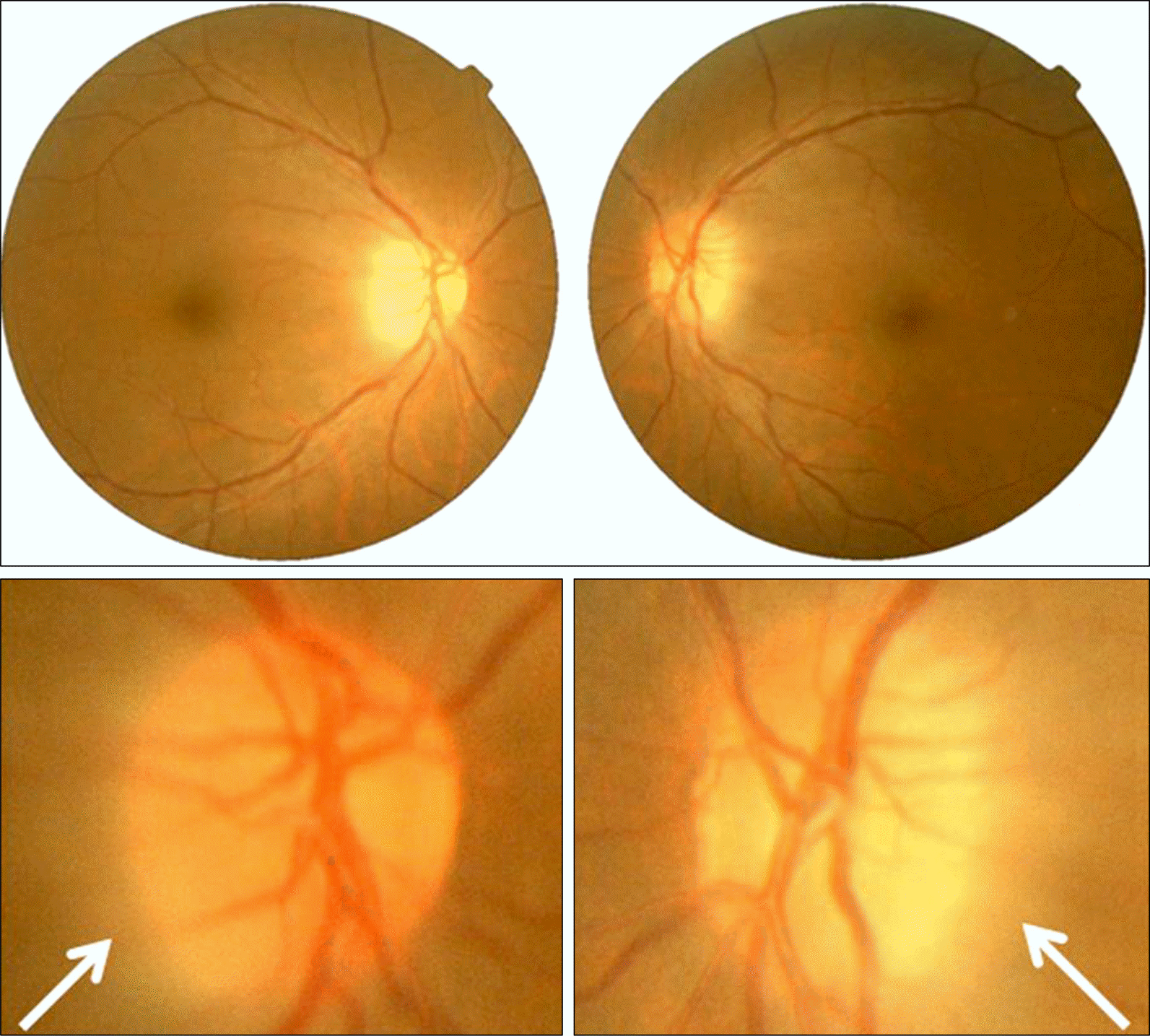 | Figure 1.Fundus and disc photographs. Both eye show disc swellings in the temporal areas (arrow). |
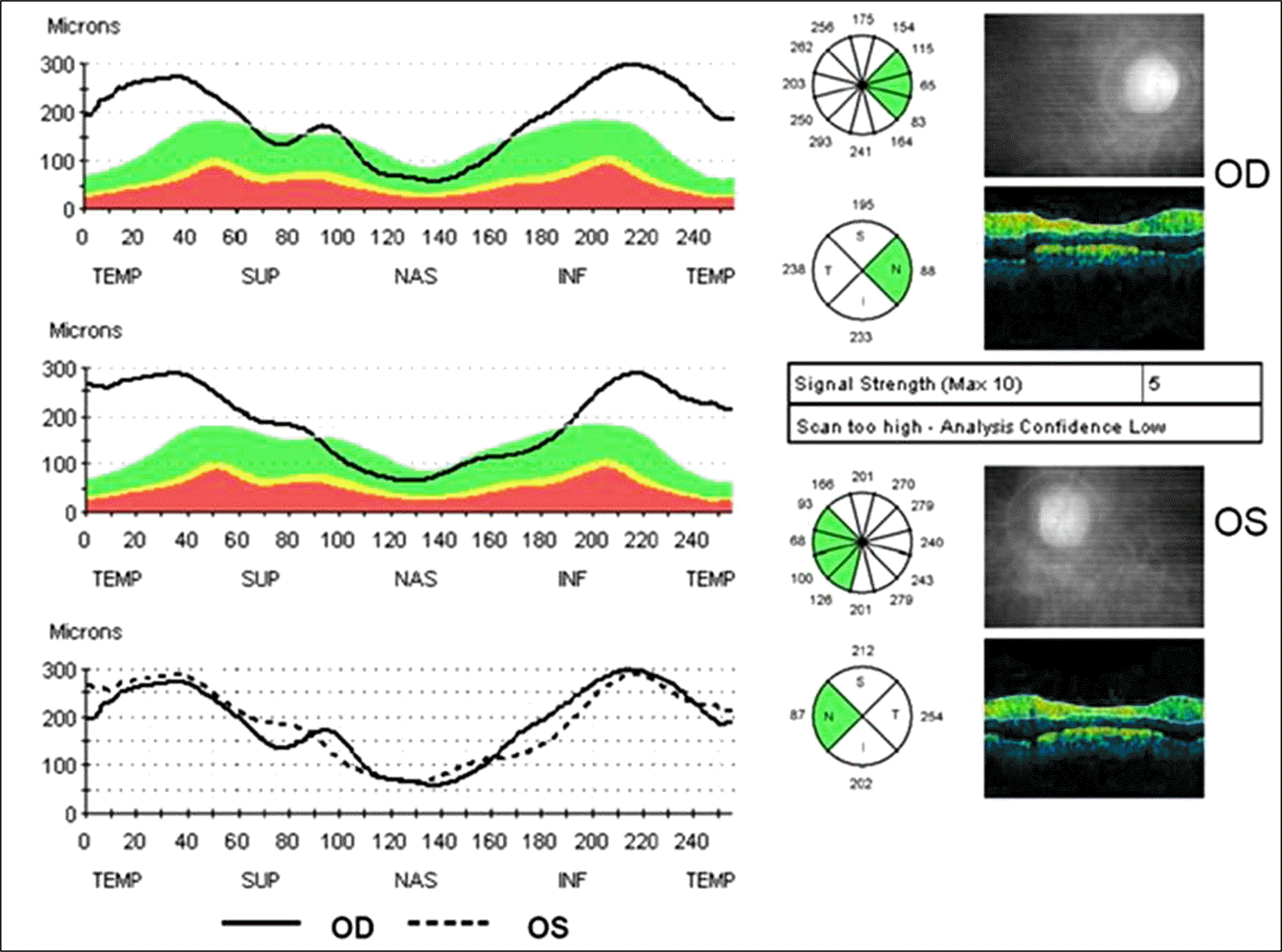 | Figure 2.Retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness in optical coherence tomography. RNFL thickness is increased in the temporal areas. |
 | Figure 3.Orbital magnetic resonance image (MRI) with enhance (A) and brain T2 weighted MRI (B, C). The optic nerves, optic chiasm and optic tracts are unremarkable (A). There are high signal intensities in both periaqueductal area (B) and mammillary body (C) which are characteristic features of Wernicke’s encephalopathy (arrow). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download