Abstract
Purpose
In the present study we compared the intraocular pressure (IOP) after cataract surgery according to incisional techniques.
Methods
Patients who underwent phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation were divided into 2 groups: clear corneal incision group (CC group), and scleral tunnel incision group (ST group). All complicated cases were excluded. IOP was measured preoperatively and at 1 week, 1, 3, 6, 12, 18 and 24 months after surgery.
Results
Seventy-seven patients (100 eyes) were enrolled in the present study; CC group (28 patients, 33 eyes), ST group (49 patients 67 eyes). Preoperative IOPs in both groups were not significantly different (p = 0.908, student’s t-test). IOP in the CC group at 1 week after surgery significantly decreased 2.22 ± 2.57 mm Hg compared to preoperative IOP (p < 0.001, repeated-measures ANOVA with post hoc analysis), and the IOP of the ST group decreased 2.11 ± 2.50 mm Hg (p < 0.001, repeated-measures ANOVA with post hoc analysis). The lowered IOP was maintained for 24 months postoperatively. There was no significant difference in IOP change after surgery depending on incisional techniques (p = 0.848, repeated measures ANOVA).
Go to : 
References
1. Mitchell P, Cumming RG, Attebo K, Panchapakesan J. Prevalence of cataract in Australia: the Blue Mountains eye study. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:581–8.
2. Leske MC, Connell AM, Wu SY. . Prevalence of lens opacities in the Barbados Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997; 115:105–11.

3. Klein BE, Klein R, Linton KL. Prevalence of age-related lens opac-ities in a population. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:546–52.
4. Thylefors B, Négrel AD, Pararajasegaram R, Dadzie KY. Global data on blindness. Bull World Health Organ. 1995; 73:115–21.
5. Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine. Cataract. revised edition. Seoul: Ilchokak;2011. chap. 1.
6. Lai JS, Tham CC, Lam DS. The efficacy and safety of combined phacoemulsification, intraocular lens implantation, and limited go-niosynechialysis, followed by diode laser peripheral iridoplasty, in the treatment of cataract and chronic angle-closure glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2001; 10:309–15.

7. Ge J, Guo Y, Liu Y. Preliminary clinical study on the management of angle closure glaucoma by phacoemulsification with foldable posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation. ZhonghuaYan Ke Za Zhi. 2001; 37:355–8.
8. Euswas A, Warrasak S. Intraocular pressure control following pha-coemulsification in patients with chronic angle closure glaucoma. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005; 88(Suppl 9):S121–5.
9. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Changes in anterior chamber angle width and depth after intraocular lens implantation in eyes with glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:698–703.

10. Lai JS, Tham CC, Chan JC. The clinical outcomes of cataract ex-traction by phacoemulsification in eyes with primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG) and co-existing cataract: a prospective case series. J Glaucoma. 2006; 15:47–52.

11. Mathalone N, Hyams M, Neiman S. . Long-term intraocular pressure control after clear corneal phacoemulsification in glauco-ma patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:479–83.

12. Shingleton BJ, Gamell LS, O'Donoghue MW. . Long-term-changes in intraocular pressure after clear corneal phacoemulsifi-cation: normal patients versus glaucoma suspect and glaucoma patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:885–90.
13. Shingleton BJ, Pasternack JJ, Hung JW, O'Donoghue MW. Three and five year changes in intraocular pressures after clear corneal phacoemulsification in open angle glaucoma patients, glaucoma suspects, and normal patients. J Glaucoma. 2006; 15:494–8.

14. Poley BJ, Lindstrom RL, Samuelson TW. Long-term effects of phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation in normo-tensive and ocular hypertensive eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:735–42.

15. Tham CC, Kwong YY, Leung DY. . Phacoemulsification ver-sus combined phacotrabeculectomy in medically controlled chron-ic angle closure glaucoma with cataract. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:2167–73.

16. Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine. Cataract. revised edition. Seoul: Ilchokak;2011. chap. 15.
17. Seo BJ, Joo CK. Long-term course of induced astigmatism after temporal clear corneal incision in cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3038–43.
18. Poley BJ, Lindstrom RL, Samuelson TW, Schulze R Jr.traocular pressure reduction after phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation in glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous eyes: evalua-tion of a causal relationship between the natural lens and open-angle glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1946–55.
19. Mansberger SL, Gordon MO, Jampel H. . Reduction in intra-ocular pressure after cataract extraction: the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1826–31.

20. Bigger JF, Becker B. Cataracts and primary open-angle glaucoma: the effect of uncomplicated cataract extraction on glaucoma control. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1971; 75:260–72.
21. Shrivastava A, Singh K. The effect of cataract extraction on intra-ocular pressure. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2010; 21:118–22.

22. Van Buskirk EM. Changes in the facility of aqueous outflow in-duced by lens depression and intraocular pressure in excised hu-man eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976; 82:736–40.

23. Kee C, Moon SH. Effect of cataract extraction and posterior cham-ber lens implantation on outflow facility and its response to pilocarpine in Korean subjects. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:987–9.

24. Kook KH, Lim SJ, Kim HB. Intraocular pressure following cata-ract surgery using sutureless clear corneal incision. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1395–400.
25. Kim TI, Tchah H. Short- and long-term effect of midlimbal in-cision on intraocular pressure: compare to normal eye. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:42–6.
26. Parrish RK II, Minckler DS, Lam D. . Guidelines of design and reporting of glaucoma surgical trials. World Glaucoma Association. Shaarawy TM, Sherwood MB, Grehn F, editors. Guidelines on Design and Reporting of Glaucoma Surgical Trials. The Hague, Netherlands: Kugler;2008. p. 8–9.
Go to : 
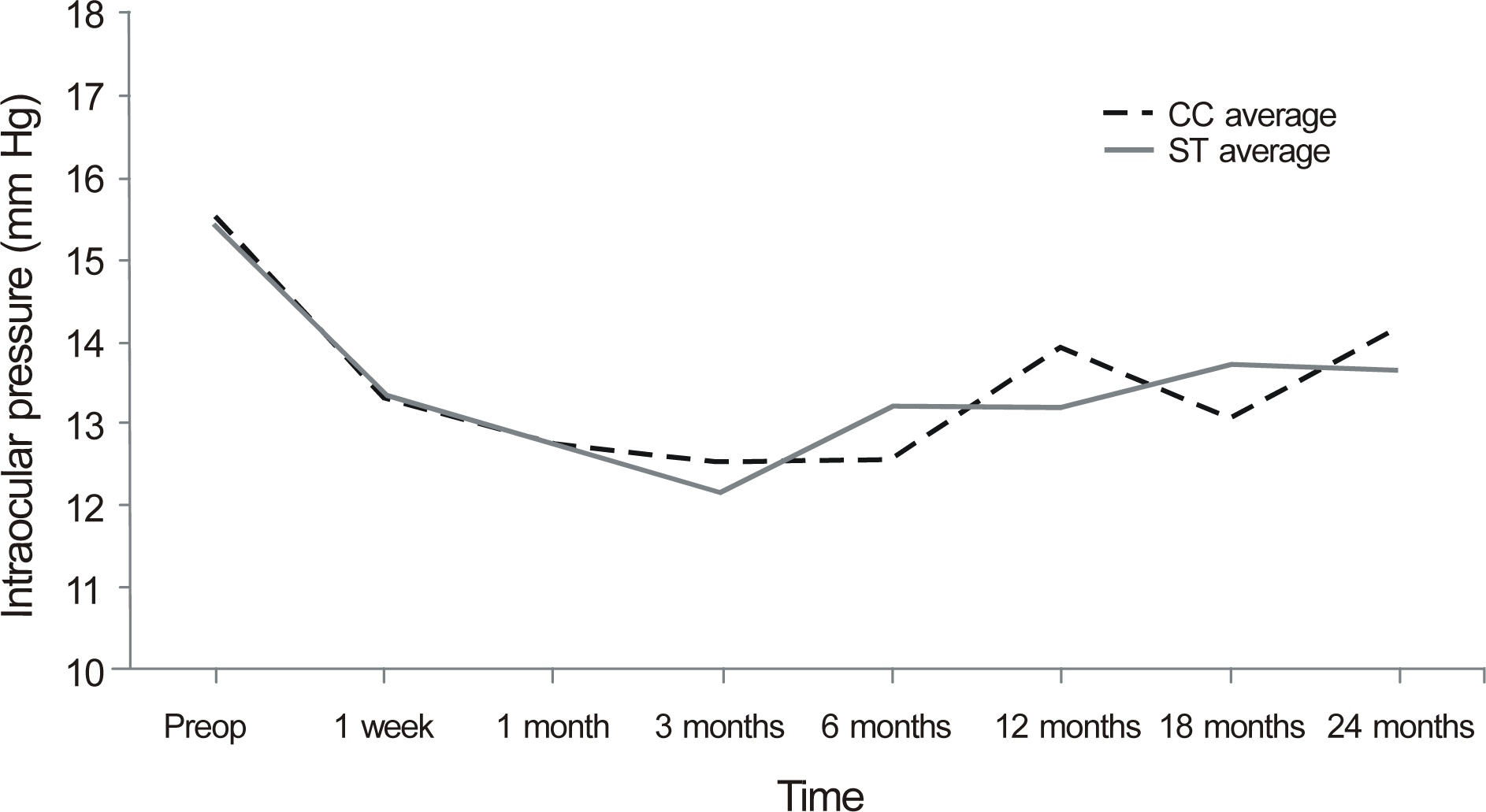 | Figure 1.Intraocular pressure change after surgery showed no significant difference between clear corneal incision group (CC group) and sclera tunnel incision group (ST group). |
Table 1.
Demographic data of patients
| Clear corneal incision group (n = 33) | Scleral tunnel incision group (n = 67) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Female | 18 | 47 | 0.180* |
| Male | 15 | 20 | |
| Mean age ± SD (years) | 65.27 ± 9.95 | 67.07 ± 9.27 | 0.375† |
| Right : Left | 16:17 | 30:37 | 0.509* |
| Corneal astigmatism (diopter) | -0.39 ± 1.05 | -0.17 ± 1.24 | 0.414† |
Table 2.
Intraocular pressure of patients
| Clear corneal incision group (mm Hg) | p-value* | Scleral tunnel incision group (mm Hg) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | 15.48 ± 3.54 | 15.40 ± 2.74 | ||
| Postop 1 week | 13.31 ± 3.43 | <0.001 | 13.34 ± 2.96 | <0.001 |
| Postop 1 month | 12.73 ± 3.38 | <0.001 | 12.76 ± 2.95 | <0.001 |
| Postop 3 months | 12.52 ± 2.87 | <0.001 | 12.13 ± 2.65 | <0.001 |
| Postop 6 months | 12.57 ± 2.39 | 0.001 | 13.23 ± 2.92 | <0.001 |
| Postop 12 months | 13.95 ± 3.96 | 0.006 | 13.20 ± 3.15 | <0.001 |
| Postop 18 months | 13.04 ± 3.68 | 0.003 | 13.76 ± 2.69 | <0.001 |
| Postop 24 months | 14.19 ± 3.22 | 0.016 | 13.65 ± 3.02 | <0.001 |
Table 3.
Corneal astigmatism of patients
| Clear corneal incision group (D) | p-value* | Scleral tunnel incision group (D) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | -0.39 ± 1.05 | -0.17 ± 1.24 | ||
| Postop 1 week | -0.41 ± 1.13 | 0.884 | -0.17 ± 1.31 | 0.622 |
| Postop 1 month | -0.22 ± 1.23 | 0.493 | -0.16 ± 1.33 | 0.456 |
| Postop 3 months | -0.28 ± 1.36 | 0.233 | 0.36 ± 1.39 | 0.526 |
| Postop 6 months | -0.50 ± 1.23 | 0.788 | 0.04 ± 1.35 | 0.431 |
| Postop 12 months | -0.06 ± 1.22 | 0.258 | -0.43 ± 1.59 | 0.082 |
| Postop 18 months | -0.08 ± 1.28 | 0.289 | 0.48 ± 1.29 | 0.297 |
| Postop 24 months | 0.03 ± 0.78 | 0.580 | -0.39 ± 1.28 | 0.864 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download